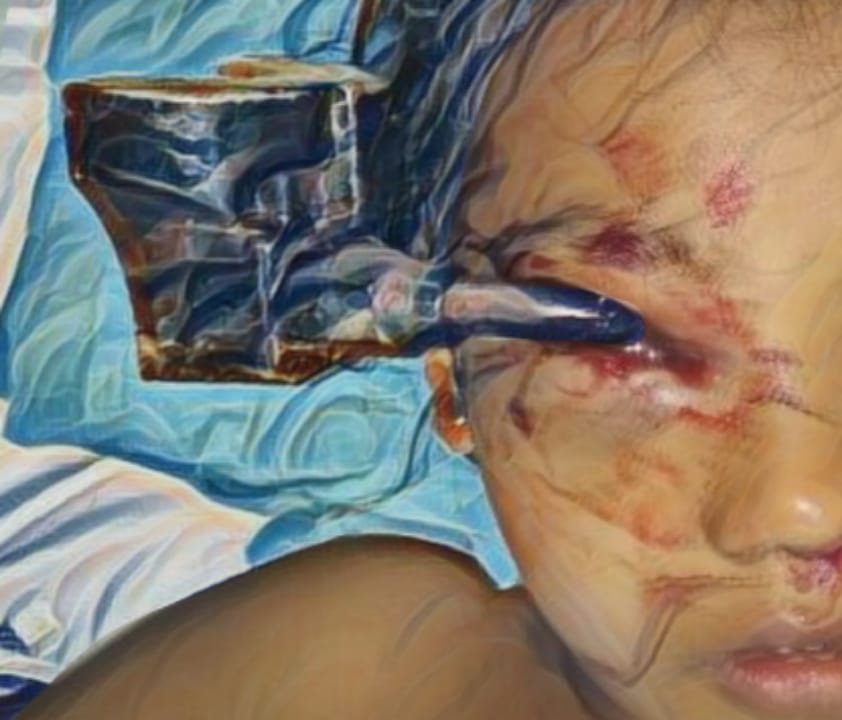
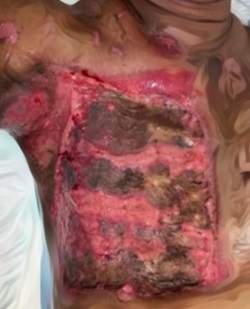
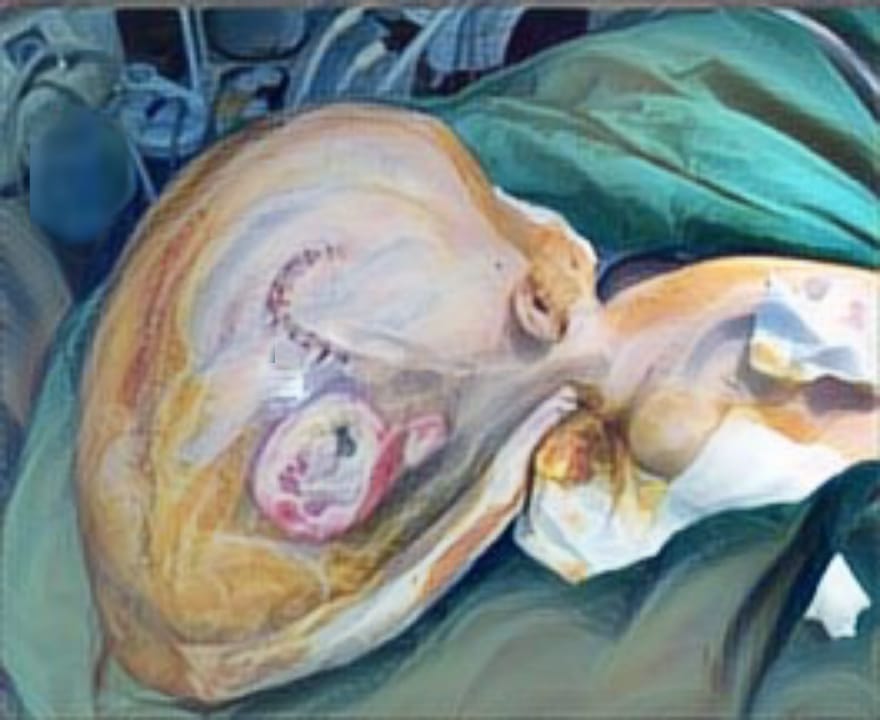
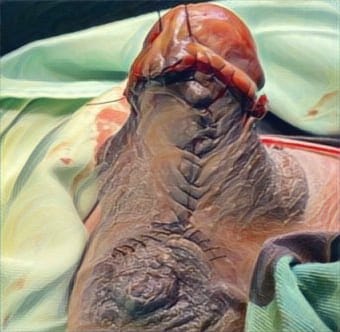
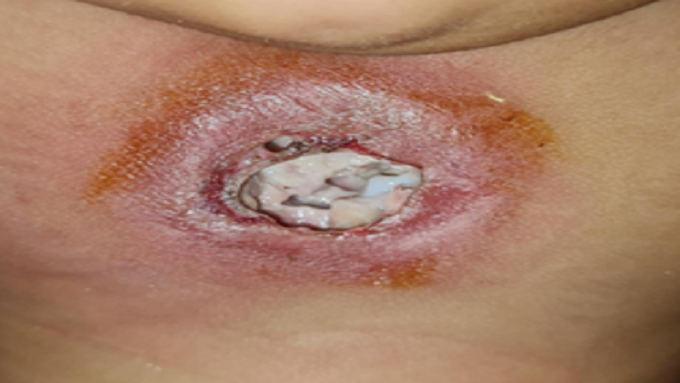
MANAGEMENT OF A RARE CASE OF PEDIATRIC DEEP STERNAL WOUND INFECTION WITH VACUUM-ASSISTED CLOSURE (VAC)
Downloads
HIGHLIGHTS:
1.This case series demonstrates that the combination of micro and nano fat shows promising results for overcoming facial contour deformity.
2. Growth factors and stem cells in nano fat complemented the micro fat properties, thus increasing the survivability rate.
ABSTRACT:
Background: Patients with craniofacial clefts who have had reconstructive surgery often develop problems,such as contour deformity that will cause psychological issues. Micro and nano fat grafting are various methods utilized to overcome these issues. Case and Operation Technique: This case series describes two patients with facial contour deformities due to Tessier 3 and 4 craniofacial clefts, respectively. Each patient underwent secondary reconstruction correction surgery followed by a combination of micro and nano fat grafting. Discussion: Results on day 7 after surgery were promising. Growth factors and stem cells in nano fat complemented the micro fat properties, thus increasing the survivability rate. Conclusion: This case series demonstrates that the combination of micro and nano fat shows promising results for overcoming facial contour deformity.
Hever P, et al The management of deep sternal wound infection?:Literature review and reconstructive algorithm.JPRAS Open 2021;28:77–89.
Rupprecht L, Schmid C. Deep Sternal Wound Complications: An Overview of Old and new Therapeutic Options. Open J Cardiovasc Surg 2013;6.
Paradiso FV, et al. Vacuum-assisted closure for the treatment of complex wounds and enterocutaneous fistulas in full-term and premature neonates?: a case report. Ital J Pediatr 2016:10–3.
Singh K, Anderson E, Harper JG. Overview and Management of Sternal Wound Infection 2011;1:25–33.
Santosa KB, et al. ScienceDirect egative Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy in Infants and Children?: A Population-Based Study. J Surg Res 2018;235:560–8.
Kubota H et al. Deep sternal wound infection after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Surg 2013; 8: 132.
Sherman G, et al. Vacuum-Assisted Closure for the Treatment of Deep Sternal Wound Infection After Pediatric Cardiac Surgery 2019:1–6.
De Caridi G, et al. VAC therapy for the treatment of complex wounds after cardiothoracic surgery. Int Wound J 2016;13:759–62.
Cho KE, Kim JH, Lee MJ, Kim M, Yoon C. Spontaneous Mediastinitis in a Ten- year-old Girl?: 2011:87–90.
Ramnarine IR, Mclean A, Pollock JCS. Vacuum-assisted closure in the paediatric patient with post- cardiotomy mediastinitis. Eur J Cardio- Thoracic Surg 2012;22:1029–31.
Mendonca D, Papini R. Negative- pressure wound therapy?: a snapshot of the evidence The management of deep sternal wound infections using vacuum-assisted closure TM ( V . A . C . í’ ) therapy Die Behandlung tief reichender sternaler Wundinfektionen under Einsatz einer. Int Wound J 2006;3:261–71.
Bovill E, Banwell PE, Teot L, Eriksson E, Song C, Mahoney J, et al. Topical negative pressure wound therapy: A review of its role and guidelines for its use in the management of acute wounds. Int Wound J 2008;5:511–29.
Robicsek F, Daugherty H, Cook J. The prevention and treatment of sternum separation following open heart surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1977;73:267.
Fuke Y, Ushijima T, Matsuyama S, Kimura S, Sonoda H, Osawa S. A new combination technique of the modified Robicsek wire fixation and plate fixation achieves effective repair of transverse sternal fracture?: a report of two cases. Surg Case Reports 2021:3–7.
Lafci G, Yasar E, Cicek OF. A novel modified Robicsek technique for sternal closure:"Double-check”Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 2015;22:758–60.
Ikonomidis J. A Preliminary Argument for the Selective Use of the Robiscek Weave. J Card Surg 2021;2:1–3.
Kaul P. Sternal reconstruction after post- sternotomy mediastinitis. J Cardiothorac Surg 2017;12:1–10.
Kaul P. Sternal reconstruction after post- sternotomy mediastinitis. J Cardiothorac Surg 2017;12:1–10.
Choukairi F, Ring J, Thekkudan J, Enoch S. Management of sternal wound dehiscence. Wounds Uk 2011;7:99– 105.
Lee AB Jr, Schimert G, Shaktin S, Seigel JH. Total excision of the sternum and thoracic pedicle transposition of the greater omentum; useful strategems in managing severe mediastinal infection following open heart surgery. Surg. 1976;80(4):433-6
Jurkiewicz MJ, Arnold PG. The omentum: an account of its use in the reconstruction of the chest wall. Ann Surg. 1977;185(5): 548-54
Copyright (c) 2022 Rianto Noviady Ramli, Ayu Prima Kusumaputri, Arif Yudho Prabowo, Yunanto Kurnia, Almas Nur Prawoto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)