DISCREPANCY INR VALUE (INTERNATIONAL NORMALIZED RATIO) IN OPTICAL AND ELECTROMECHANICAL METHOD

Downloads
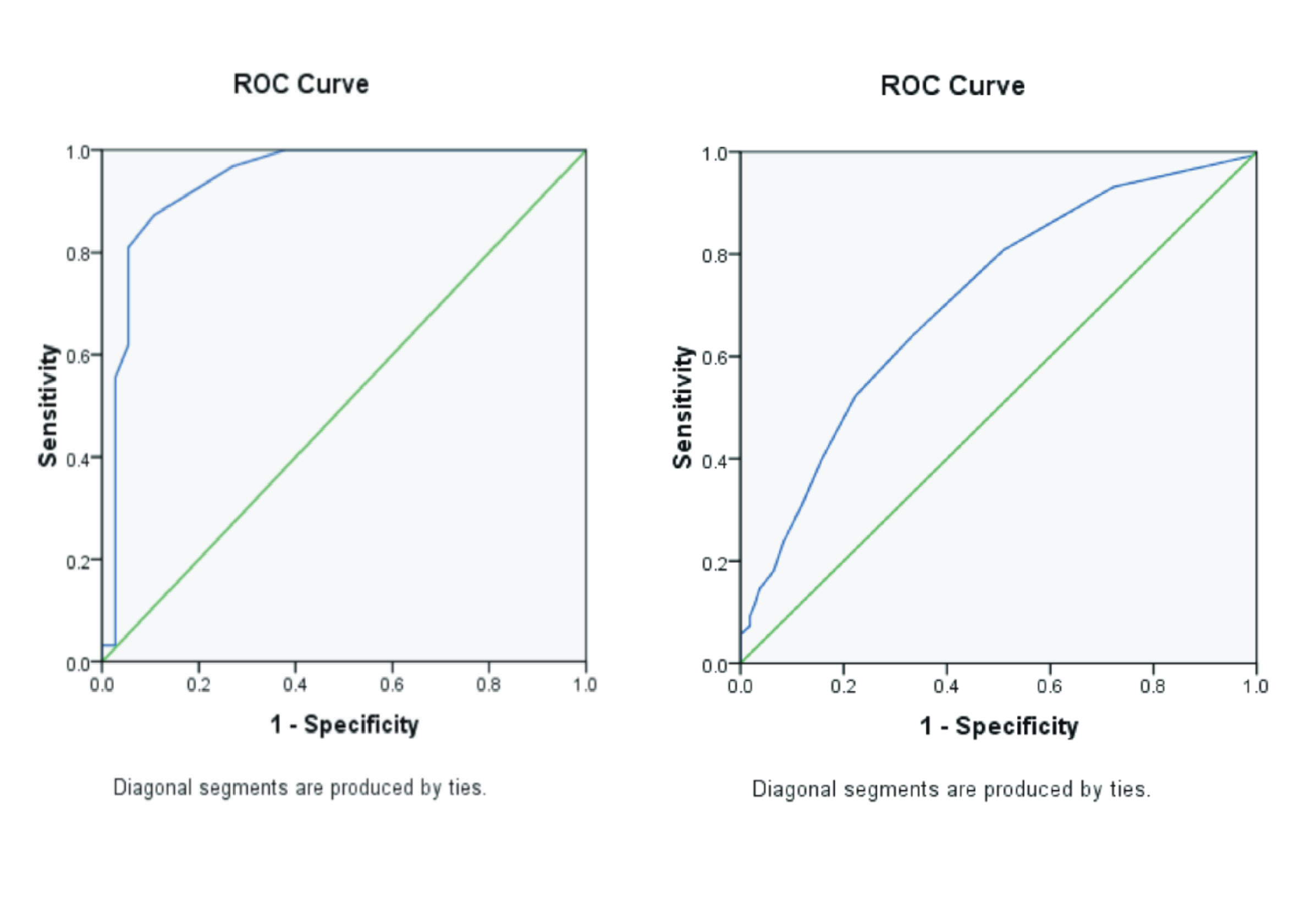
Background: INR examination services at laboratories in hospitals and clinics use different methods and tools therefore, results of the INR examination are different. Purpose: To determine whether there are differences in the INR value between using the photo optic method and electromechanical method. Method: This study used a citrate blood sample with a ratio of blood and anticoagulant 9: 1 and used the Sysmex CA-600 device for the photo optic method and used the Thrombostat device for the electromechanical method. The sample consisted of 32 samples, namely 10 treatment samples to be analyzed and 22 normal samples. Using SPSS 25.0 to test data that was tested for normality test and in a different test. Result: The result of INR with the electromechanical method was significantly longer than INR with the photo optic method. In the hemolytic sample, the result was significantly higher than the INR result with normal samples. Conclusion: There are significant differences between results of the INR value using photo optic and electromechanical due to the difference in the detection principle between the two methods.
Bai, B., Christie, D.J., Gorman, R.T., Wu, J.R., 2008. Comprison of Optical and Mechanical Clot Detection for Routine Coagulation Testing in A Large Volume Clinical Laboratory. Blood Coagulation & Fibrinolysis 19, 569–576.
Dorn-Beineke, A., Dempfle, C.-E., Bertsch, T., Wisser, H., 2005. Evaluation of The Automated Coagulation Analyzer Sysmex CA-7000. Trombos. Res. 116, 171–179.
Howanitz, P.J., Lehman, C.M., Jones, B.A., Meier, F.A., Horowitz, G.L., 2015. Clinical Laboratory Quality Practices When Hemolysis Occurs. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 139, 901–906.
Laga, A.C., Cheves, T.A., Sweeney, J.D., 2006. The Effect of Sample Hemolysis on Coagulation Test Results. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 126, 748–755.
Lefkowitz, J.B., DeBoom, T., Weller, A., Clarke, S., Lavrinets, D., 2020. Fibrinogen Longmont: A Dysfibrinogenemia that Causes Prolonged Clot"based Test Results Only When Using An Optical Detection Method. Am. J. Hematol. 63, 149–155.
Marchesi, V.T., Furthmayr, H., Tomita, M., 1976. The Red Cell Membrane. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 45, 667–698.
McPherson, R., Pincus, M., 2011. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods, 22nd ed. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Sukorini, U., Nugroho, D.K., Rizki, M., Hendriawan, P.J.B., 2010. Pemantapan Mutu Internal Laboratorium Klinik. Kanal Medika dan Alfamedia Citra, Laboratorium Yogyakarta.
Toh, C.H., Ticknor, L.O., Downey, C., Giles, A.R., Paton, R.C., Wenstone, R., 2003. Early Identification OfSepsis And Mortality Risks Through Simple, RapidClotwafeform Analysis. Implications Of Lipoprotein-Complexed C Reactive Protein Formation. IntensiveCare Med. 29, 55–61.
Woolley, A., Golmard, J.-L., Kitchen, S., 2016. Effect Of Haemolysis, Icterus And Lipaemia on Coagulation Test as Performed on Stago STA-Cmpact Max Analyser. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 38, 375–388
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of Vocational Health Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The authors agree to transfer the transfer copyright of the article to the Journal of Vocational Health Studies (JVHS) effective if and when the paper is accepted for publication.
- Legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), implies that publication can be used for non-commercial purposes in its original form.
- Every publications (printed/electronic) are open access for educational purposes, research, and library. Other that the aims mentioned above, editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.
Journal of Vocational Health Studies is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License