SITUATION ANALYSIS AND SPATIAL MAPPING STUDY OF STUNTING INCIDENTS IN TUBAN REGENCY, INDONESIA
Downloads
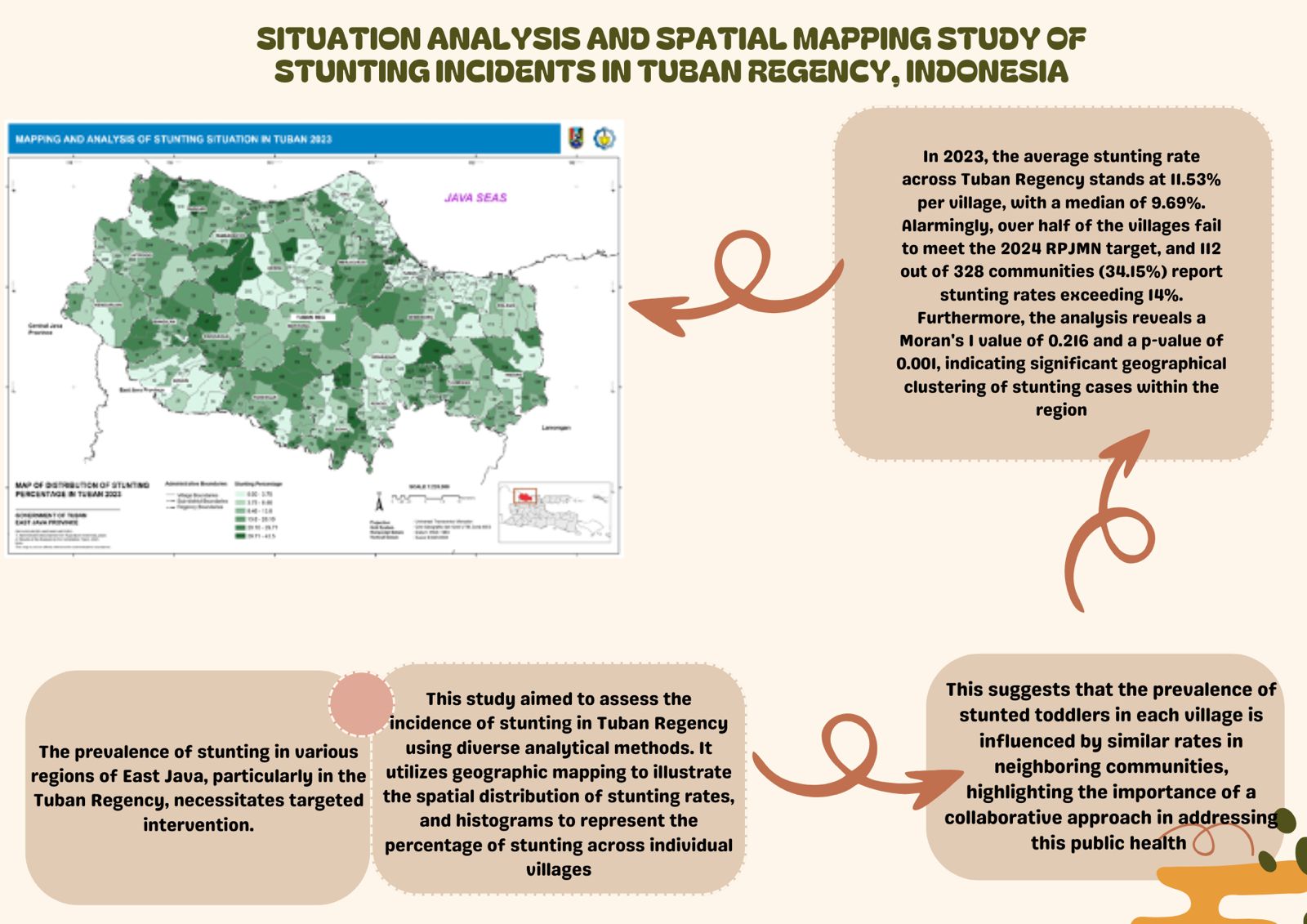
The prevalence of stunting in various regions of East Java, particularly in the Tuban Regency, necessitates targeted intervention. This study aimed to assess the incidence of stunting in Tuban Regency using diverse analytical methods. It utilizes geographic mapping to illustrate the spatial distribution of stunting rates, and histograms to represent the percentage of stunting across individual villages. Notably, Mander Village in Tambakboyo District exhibits the highest prevalence, with 43.59% of toddlers affected by stunting. In 2023, the average stunting rate across the Tuban Regency was 11.53% per village, with a median of 9.69%. Alarmingly, over half of the villages failed to meet the 2024 RPJMN target, and 112 of 328 communities (34.15%) reported stunting rates exceeding 14%. Furthermore, the analysis revealed a Moran's I value of 0.216 and a p-value of 0.001, indicating significant geographical clustering of stunting cases within the region. This suggests that the prevalence of stunted toddlers in each village is influenced by similar rates in neighboring communities, highlighting the importance of a collaborative approach in addressing this public health challenge.
Abdeeq, Barkhad, Ahmed Mohamed, Abdiwahab Abdi, Jama Mohamed, Dessalegn Tamiru, and Kalkidan Abate. 2024. “Prevalence of Stunting and Its Associated Factors Among Children Residing in Internally Displaced Persons (IDP) Camps in Hargeisa, Somaliland: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study.” Pediatric Health, Medicine and Therapeutics Volume 15. doi: 10.2147/phmt.s439586.
Atamou, Lasarus, Dwi Cahya Rahmadiyah, Hamidah Hassan, and Agus Setiawan. 2023. “Analysis of the Determinants of Stunting among Children Aged below Five Years in Stunting Locus Villages in Indonesia.” Healthcare (Switzerland) 11(6). doi: 10.3390/healthcare11060810.
Bitew, Fikrewold H., Corey S. Sparks, Samuel H. Nyarko, and Lauren Apgar. 2023. “Spatiotemporal Variations and Determinants of Under-Five Stunting in Ethiopia.” Food and Nutrition Bulletin 44(1). doi: 10.1177/03795721231158503.
Chowdhury, Mashfiqul Huq, Mst Farjana Aktar, Md Akhtarul Islam, and Noor Muhammad Khan. 2023. “Factors Associated with Stunting Status among Under-5 Years Children in Bangladesh: Quantile Regression Modelling Approach.” Children and Youth Services Review 155. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2023.107199.
Dewey, Kathryn G., Christine P. Stewart, K. Ryan Wessells, Elizabeth L. Prado, and Charles D. Arnold. 2021. “Small-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements for the Prevention of Child Malnutrition and Promotion of Healthy Development: Overview of Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis and Programmatic Implications.” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 114.
Fajrianti, Dita, Esti Yunitasari, and Retnayu Pradanie. 2020. “The Correlation Between Personal Reference: Health Workers and Health Facilities with Parenting in Stunting Prevention.” Pediomaternal Nursing Journal 6(2). doi: 10.20473/pmnj.v6i2.20966.
Fidyah Aminin, Melly Damayanti, Nurul Aini Suria Saputri, and Darwitri Darwitri. 2022. “DETERMINANTS OF STUNTING: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW.” International Journal of Social Science 1(6). doi: 10.53625/ijss.v1i6.2425.
Hasanah, Uswatun, Ida Leida Maria, Nurhaedar Jafar, Andi Hardianti, Anwar Mallongi, and Aminuddin Syam. 2020. “Water, Sanitation Dan Hygiene Analysis, and Individual Factors for Stunting among Children under Two Years in Ambon.” Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences 8(T2):22–26. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2020.5177.
Hendraswari, Chatrine Aprilia, Yuliasti Eka Purnamaningrum, Tri Maryani, Yani Widyastuti, and Sakinah Harith. 2021. “The Determinants of Stunting for Children Aged 24-59 Months in Kulon Progo District 2019.” Kesmas 16(2). doi: 10.21109/KESMAS.V16I2.3305.
Huriah, Titih, and Nurjannah Nurjannah. 2020. “Risk Factors of Stunting in Developing Countries: A Scoping Review.” Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences 8(F). doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2020.4466.
Krisnana, Ilya, Ika Nur Pratiwi, and Adam Cahyadi. 2020. “The Relationship between Socio-Economic Factors and Parenting Styles with the Incidence of Stunting in Children.” Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy 11(5). doi: 10.31838/srp.2020.5.106.
Kwami, Corina Shika, Samuel Godfrey, Hippolyte Gavilan, Monica Lakhanpaul, and Priti Parikh. 2019. “Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: Linkages with Stunting in Rural Ethiopia.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16(20). doi: 10.3390/ijerph16203793.
Marume, Anesu, Moherndran Archary, and Saajida Mahomed. 2023. “Predictors of Stunting among Children Aged 6-59 Months, Zimbabwe.” Public Health Nutrition 26(4). doi: 10.1017/S1368980023000046.
Nisar, Yasir Bin, Victor M. Aguayo, Sk Masum Billah, and Michael J. Dibley. 2020. “Antenatal Iron-Folic Acid Supplementation Is Associated with Improved Linear Growth and Reduced Risk of Stunting or Severe Stunting in South Asian Children Less than Two Years of Age: A Pooled Analysis from Seven Countries.” Nutrients 12(9). doi: 10.3390/nu12092632.
Nita, Flaviani Angela, Evy Ernawati, Fatimah Sari, Juda Julia Kristiarini, and Indah Purnamasari. 2023. “The Influence of Parenting on the Incidence of Stunting in Toddlers Aged 1-3 Year.” Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan Sandi Husada 12(2). doi: 10.35816/jiskh.v12i2.1107.
Nugroho, Efa, Puput Arisma Wanti, Cahyani Wulan Suci, Bambang Budi Raharjo, and Najib. 2023. “Social Determinants of Stunting in Indonesia.” Kemas 18(4). doi: 10.15294/kemas.v18i4.40875.
Nurhayati, Risa, Rahayu Budi Utami, and Ana Amelia Irawan. 2020. “Health Education about Stunting Nutrition in Mothers to Weight Stunting Children Aged 2-5 Years.” Journal for Quality in Public Health 4(1). doi: 10.30994/jqph.v4i1.148.
Pertiwi, Melinda Restu, Pudji Lestari, and Elida Ulfiana. 2019a. “Relationship Between Parenting Style and Perceived Information Sources With Stunting Among Children.” International Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS) 2(4).
Pertiwi, Melinda Restu, Pudji Lestari, and Elida Ulfiana. 2019b. “Relationship Between Parenting Style and Perceived Information Sources With Stunting Among Children.” International Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS) 2(4).
Rizal, Muhammad Fikru, and Eddy van Doorslaer. 2019. “Explaining the Fall of Socioeconomic Inequality in Childhood Stunting in Indonesia.” SSM - Population Health 9. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2019.100469.
Sadida, Zayyana Jasmine, Ratna Indriyanti, and Arlette Suzy Setiawan. 2022. “Does Growth Stunting Correlate with Oral Health in Children?: A Systematic Review.” European Journal of Dentistry 16(1).
Santosa, Agus, Essa Novanda Arif, and Dinal Abdul Ghoni. 2022. “Effect of Maternal and Child Factors on Stunting: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling.” Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics 65(2). doi: 10.3345/cep.2021.00094.
Soekatri, Moesijanti Y. E., Sandjaja Sandjaja, and Ahmad Syauqy. 2020. “Stunting Was Associated with Reported Morbidity, Parental Education and Socioeconomic Status in 0.5–12-Year-Old Indonesian Children.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17(17). doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176204.
Sufri, Sofyan, Nurhasanah, Misbahul Jannah, Teungku Puspa Dewi, Fathima Sirasa, and Saiful Bakri. 2023. “Child Stunting Reduction in Aceh Province: Challenges and a Way Ahead.” Maternal and Child Health Journal 27(5). doi: 10.1007/s10995-023-03601-y.
Syam, Rizky Chaeraty, Muhammad Syafar, M. Alimin Maidin, Muhammad Rachmat, Uyuun Wiji Ismita, Iva Hardi Yanti, and Erniwati Ibrahim. 2020. “Reinforcers and Inhibitors of Family-Based Stunting Children Parenting (Case Studies in Slums Area of Makassar City).” Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences 8(T2). doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2020.5209.
Wibowo, Diki Prayuga, Irmawati, Deby Tristiyanti, Normila, and Agung Sutriyawan. 2023. “Pola Asuh Ibu Dan Pola Pemberian Makanan Berhubungan Dengan Kejadian Stunting.” JI-KES: Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan 6(2).
Widiyanto, Aris, Joko Tri Atmojo, and Aquartuti Tri Darmayanti. 2019. “Pengaruh Faktor Kerawanan Pangan Dan Lingkungan Terhadap Stunting.” Interest : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan 8(1). doi: 10.37341/interest.v8i1.118.
Widyaningsih, Vitri, Tri Mulyaningsih, Fitria Nur Rahmawati, and Dhian Adhitya. 2022. “Determinants of Socioeconomic and Rural-Urban Disparities in Stunting: Evidence from Indonesia.” Rural and Remote Health 22(1). doi: 10.22605/RRH7082.
WILLYA ACHMAD et al. 2023. “MALNUTRITION, PARENTING, POVERTY: CONSTRUCTION AND STUNTING PHENOMENA IN INDONESIA.” Russian Law Journal 11(2s). doi: 10.52783/rlj.v11i2s.565.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- MEDIA GIZI INDONESIA Journal is the copyright owner of all materials published on this website.
- The formal legal provisions for access to digital articles of this electronic journal are subject to the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0), which means that MEDIA GIZI INDONESIA Journal and readers reserve the right to save, transmit media / format, manage in database, maintain, and publish articles as long as it continues to include the name of the Author.
- Printed and published print and electronic manuscripts are open access for educational, research and library purposes. In addition to these objectives, the editorial board shall not be liable for violations of copyright law.


2.png)





















