QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENT OF BILATERAL CHEILORRHAPHY: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY
Downloads
Highlights:
- There were no significant differences in anthropometric measurements across various groups indicating consistent results in these facial parameters.
- Bilateral cheilorrhaphy using the Djohansjah technique at the Surabaya CLP Center achieved satisfactory symmetry of the lips, nose, and philtrum, with consistent anthropometric measurements in preoperative cleft conditions.
Abstract:
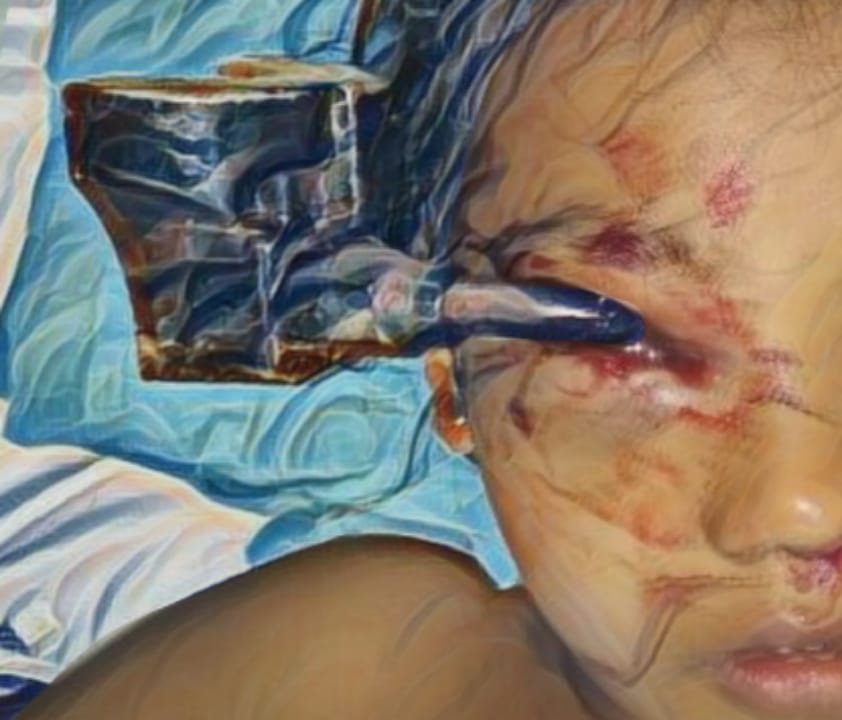
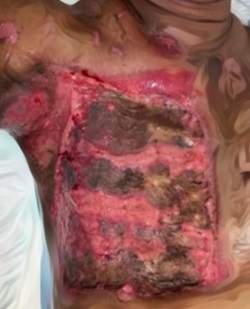
Introduction: Bilateral cheilorraphy has higher complexity compared to unilateral cheilorraphy. Anthropometric measurements provide nasolabial identification of the surgery result objectively. This study aims to assess the outcome of bilateral cheilorrhaphy with the Djohansjah technique at Surabaya CLP Center.
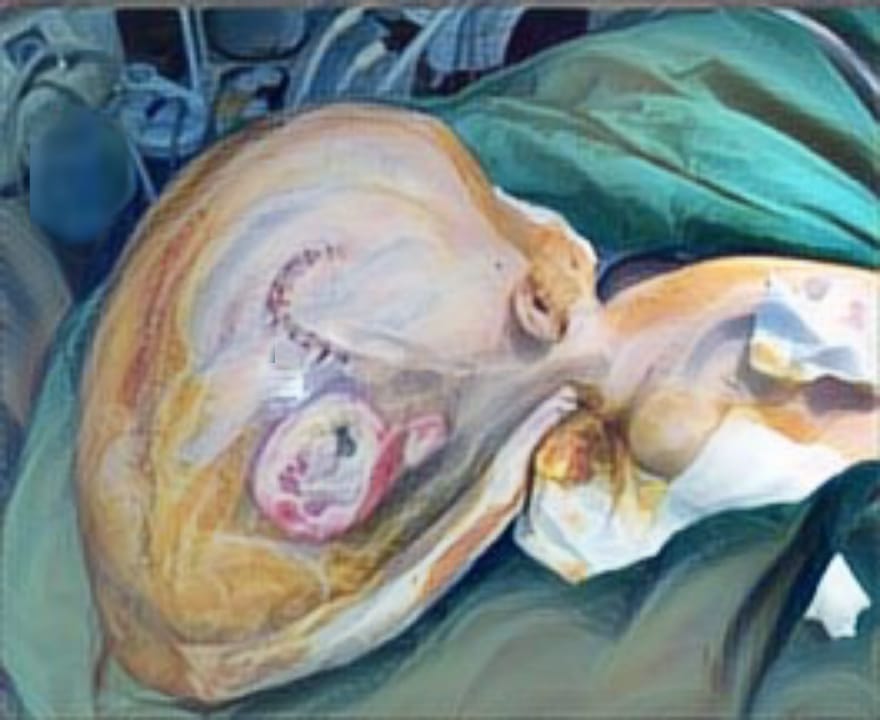
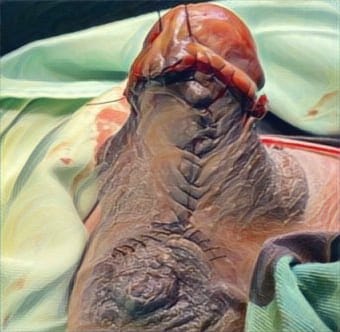
Methods: 26 patients underwent bilateral cheilorrhaphy from January 1 to December 31, 2018, at the Surabaya CLP Center. Anthropometric measurements were performed on control photos one-year post-surgery with the GIMP application (GNU Image Manipulation Software) version 2.10.12 to measure the cupid's bow width ratio, hemilabial length ratio, nasal width ratio, and philtrum ridge length ratio. A statistical analysis was performed using Independent Sample t-Tes and Mann-Whitney Test.
Results: An anthropometric size difference test based on preoperative condition was performed. No significant difference of the cupid's bow width ratio, hemilabial length ratio, nasal width ratio, and philtrum ridge length ratio between the group of identical cleft lip and unidentical cleft lip with p > 0.05 was found. Likewise, there was no difference between the identical cleft alveolar and unidentical cleft alveolar, as well as the group with or without cleft palate.
Conclusions: Symmetry of lips, nose, and philtrum was achieved with bilateral cheilorrhaphy with the Djohansjah technique at the Surabaya CLP Center and there was no significant difference in cupid's bow width ratio, hemilabial length ratio, nasal width ratio, and philtrum ridge length ratio on preoperative cleft condition.
Hopper, R. A., Cleft Lip and Palate: Embryology, Principles, and Treatment. In Thorne, C. H. et al. (eds) Grabb and Smith's Plastic Surgery 7th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2014. 173– 199.
Singh, A. K. et al. Bilateral Cleft Lip Nasal Deformity. Indian J. Plastic Surgery, 2009.42(2): 235-241. 3.
Pigott R.,Organisation of Cleft Lip and Palate Services. Br J Plast Surgery Journal; 1992. 45(5): 385-387.
Millard, D. R., 1977. Cleft Craft: the Evolution of its Surgery, Vol 2: Bilateral and Rare Deformities. Boston: Little, Brown & Co.
Marzoeki, D., Jailani, M. & Perdanakusuma, D. S., 2002. Tehnik Pembedahan Celah Bibir dan Langit- langit. Jakarta: Sagung Seto.
Sitzman TJ, et al. Current Surgical Practices in Cleft Care: Unilateral Cleft Lip Repair. Plast Reconstr Surg.;2008.121(5):261e-270e
Mulliken, JB, et al. Repair of Bilateral Cleft Lip: Review, Revisions, and Reflections. The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 200. 14(5):609-620.
Adetayo AM, et al. Unilateral cleft lip repair: a comparison of treatment outcome with two surgical techniques using quantitative (anthropometry) assessment. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.;2018.44(1):3– 11.
Richardson, S.et al. Evaluation of esthetic outcome following bilateral cleft lip repair using the Mulliken technique: An assessment of 284 cases. Journal of Cleft Lip Palate and Craniofacial Anomalies, 2017.4(3): 94.
Matsumoto, K., et al. ostoperative Lip and Nose Forms Following Primary Bilateral Cleft Lip Repair Selecting One/ Two Stage Surgery in Comparison to Those of Healthy Children. Oral Science International. Japanese Stomatological Society,2013. 10(2):77–86.
Thomas, M. D., et al. Normal Nasolabial Anatomy in Infants Younger Than 1 Year of Age. Pediatric Dentistry and Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.2012.
Farkas, L. G., et al. 1992. Growth Patterns of the Nasolabial Region: Morphometric Study. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal,1992.29(4): 318-324.
Anastassov, Y. 2003. Analysis of nasal and labial deformities in cleft lip, alveolus and palate patients by a new rating scale: preliminary report. Journal of Cranio- Maxillofacial Surgery,2003. 31: 299-303.
Bermudez, L., et al. Surgical Outcomes Auditing Systems in Humanitarian Organizations. World Journal Surgery, 2010. 34: 403-410.
Lun Jou Lo, et al. Assessment of Bilateral Cleft Lip Nose Deformity: A Comparison of Result as Judged by Cleft Surgeons and Laypersons. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Chang Gung Memorial Hospital: 2002. 733-738.
Copyright (c) 2020 Lobredia Zarasade, Pratidina Wulandari, Indri Lakhsmi Putri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)