ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY COMBINED WITH ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT IN A PATIENT WITH BILATERAL CLEFT LIP, PALATE AND ALVEOLUS, WITHOUT ALVEOLAR BONE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT
Downloads
Highlights:
- The orthognathic surgery combined with orthodontic intervention, leads to positive functional and aesthetic outcomes in individuals diagnosed with bilateral cleft lip and palate.
- It emphasizes the continued importance of adhering to the standard protocol, including alveolar bone grafting before permanent canine eruption, to achieve optimal outcomes.
Abstract:
Introduction: The incidence of cleft lip and palate is 8 in every 10,000 live births. A patient with this condition experiences a deficiency in maxillary growth. Maxillary hypoplasia leads to malocclusion and skeletal disharmony. Orthognathic surgery at skeletal maturity is the standard procedure at the end of the protocol to correct maxillary hypoplasia resulting in malocclusion not correctable with orthodontics alone.
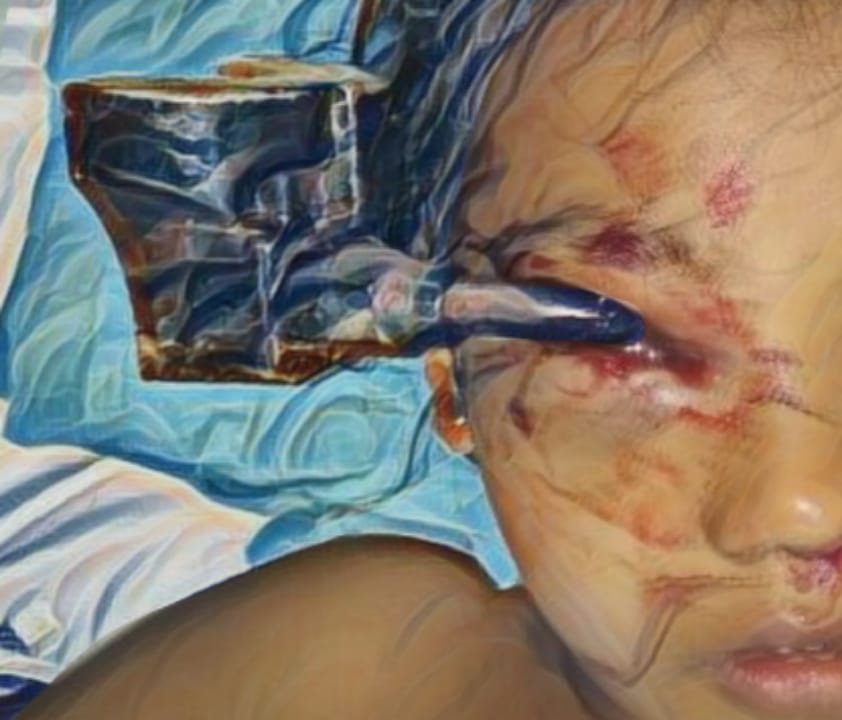
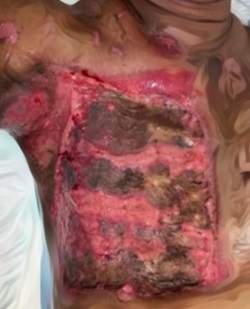
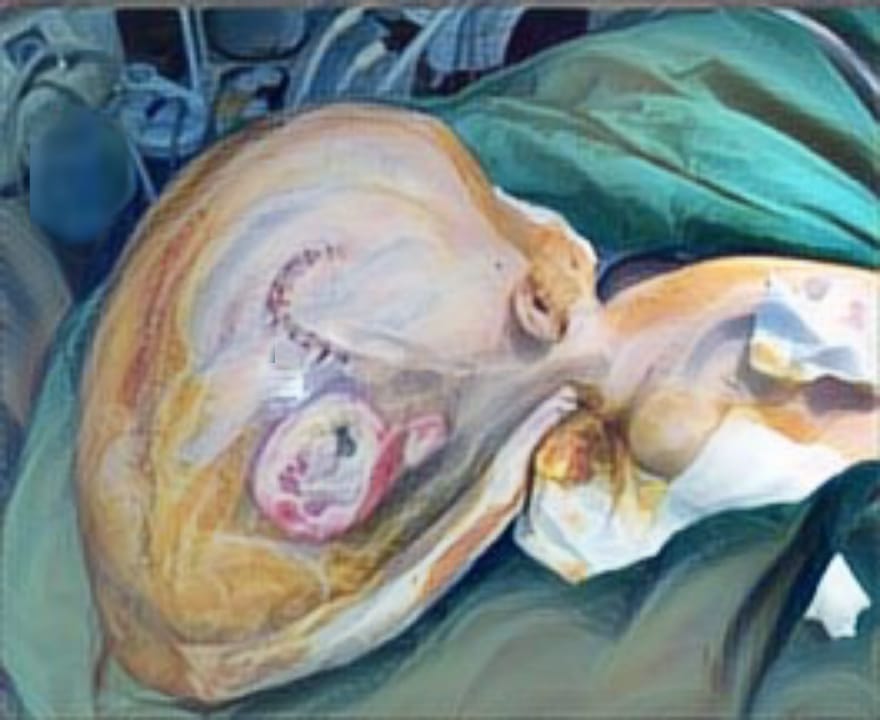
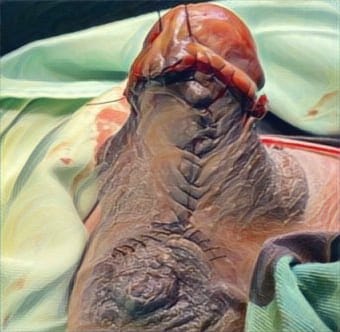
Case Illustration: We report the result of orthognathic surgery performed on a 23 year old male with complete bilateral cleft lip, palate, and alveolus. We proceeded with bimaxillary surgery despite the alveolar cleft. We also recorded a neglected alveolar cleft in which he should have had undergone alveolar bone graft prior to the current procedure. The pre-maxillary segment was stabilized with miniplate followed by Le Fort 1 advancement and mandibular setback guided by an occlusal wafer. Malar augmentation was done by onlay bone grafts. Mandibulo-maxillary fixation was maintained. Postoperatively, a good occlusion and better facial harmony were achieved. He was planned to undergo a septorhinoplasty in the near future.
Discussion: Despite adequate treatments following the protocol recommended by many centres, some patients developed some degree of maxillary hypoplasia. A quarter of this population need osteotomies and Le Fort I maxillary osteotomy is the most common procedure to correct retrognathic maxilla.
Conclusion: Orthognathic surgery combined with orthodontic treatment in a patient with bilateral cleft lip and palate provided good functional and aesthetic result. However, this procedure cannot replace the standard protocol of having an alveolar.
Ross RB. Treatment variables affecting facial growth in complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Part 1: treatment affecting growth. Cleft Palate J. 1987A; 24:5–23.
Mars M, et al. The Goslon Yardstick: a new system of assessing dental arch relationships in children with unilateral clefts of the lip and palate. Br J Plast Surg. 1987.24:314–322.
Capelozza Filho L, Normando AD, da Silva Filho OG. Isolated influences of lip and palate surgery on facial growth: comparison of operated and unoperated male adults with UCL/P. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1996. 33:51–56.
Phillips JH, et al. Orthognathic Surgery in Cleft Patients. Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012.129:535-548.
Daskalogiannakis J, Mehta M. The Need for Orthognathic Surgery in Patients With Repaired Complete Unilateral and Complete Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. Journal of CLP and Orthognathic Surgery. 2009.46:498-502.
DeLuke, et al. Facial growth and the need for orthognathic surgery after cleft palate repair: literature review and report of 28 cases. Journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 1997.55(1): 694-697.
Rosenstein S.W.D.D.S., et al. A long-term retrospective outcome assessment of facial growth, secondary surgical need, and maxillary lateral incisor status in a surgical-orthodontic protocol for complete clefts. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 2003. 111(1): 1-13.
Cohen, Steven R., et al. Cumulative operative procedures in patients aged 14 years and older with unilateral or bilateral cleft lip and palate. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 1995, 96(2): 267-271.
Levy-Bercowski, Daniel, et al. Orthognathic cleft”surgical/orthodontic treatment. In: Seminars in Orthodontics. WB Saunders, 2011:197-206.
Copyright (c) 2018 Yudi Siswanto, Magda Rosalina Hutagalung, Jusuf Sjamsudin, Indri Lakhsmi Putri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)