PENGARUH ORAL N-ACETYLCYSTEIN TERHADAP POLA FAKTOR PERTUMBUHAN ENDOTEL VASKULAR (VEGF) DAN FAKTOR PERTUMBUHAN FIBROBLAS (FGF) PADA MODEL KERETA LISTRIK TIKUS
Downloads
Highlights:
- Kadar rata-rata VEGF pada kelompok tikus yang menerima NAC lebih tinggi daripada kelompok kontrol.
- Hasil FGF pada kelompok tikus kontrol lebih tinggi pada hari ke-0 dan hari ke-8 dibandingkan dengan kelompok tikus yang menerima NAC.
- Di dalam kadar FGF dan VEGF tidak ada perbedaan yang signifikan antara kelompok yang menjalani perlakuan dan kelompok kontrol negatif.
Abstrak:
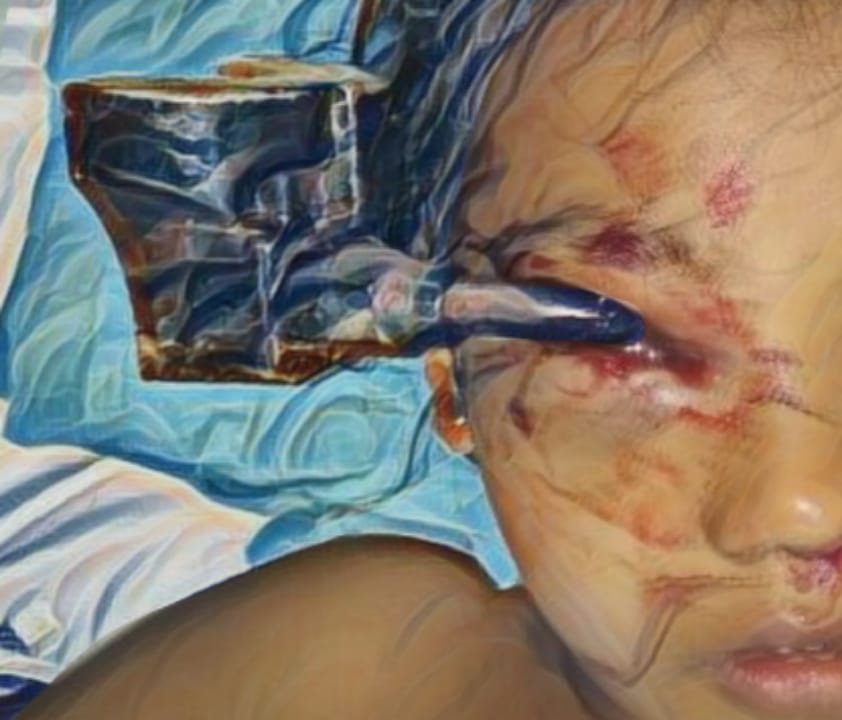
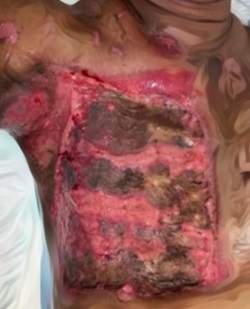
Latar Belakang: Luka bakar listrik menyebabkan cedera serius dengan mortalitas 20-30% dan 74% korban selamat dengan cedera permanen dan sekuel. Tingkat nekrosis pada luka bakar seringkali sulit untuk ditentukan karena sirkulasi mikrovaskuler pada jaringan dalam terlibat. N- acetylcysteine (NAC) dapat mengatasi stres oksidatif dan memiliki efek perlindungan terhadap kerusakan jaringan dari radikal bebas, secara hipotetis dengan sekresi berbagai faktor pertumbuhan yang mempercepat penyembuhan luka. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mempelajari pengaruh NAC terhadap tingkat faktor pertumbuhan endotermal vaskular (VEGF) dan faktor pertumbuhan fibroblast (FGF) dalam model luka bakar listrik tikus.
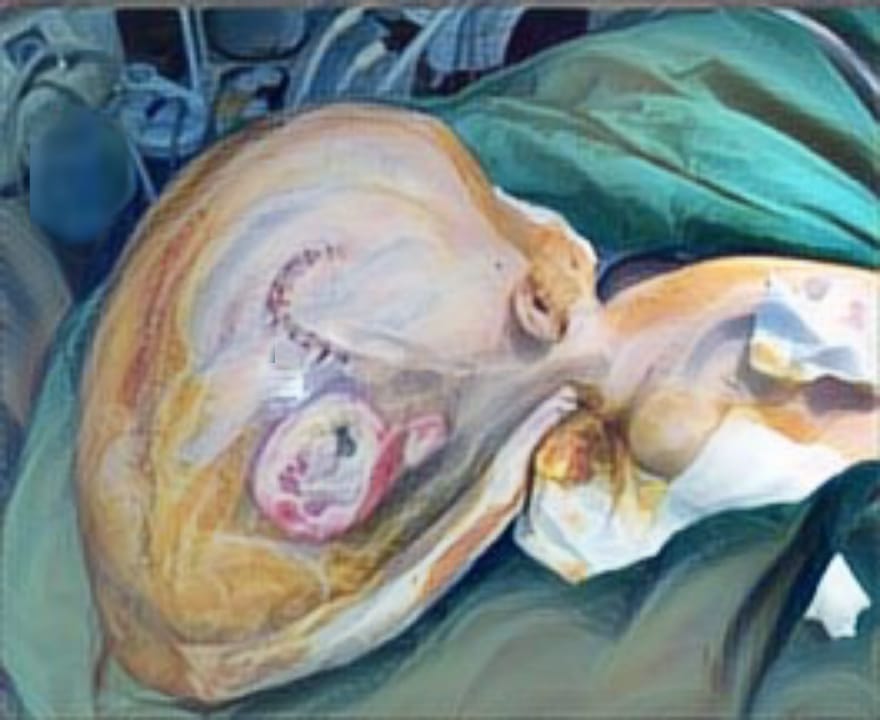
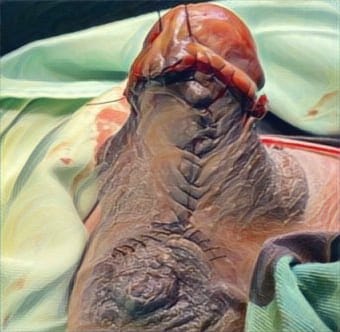
Metode: Penelitian ini menggunakan desain randomized post-test only control group. Dalam penelitian ini, terdapat empat puluh dua tikus jantan galur Wistar yang ditempatkan dalam enam kelompok. Setiap tikus menerima arus bolak listrik sebesar 220 volt dengan intensitas 450-500 mA pada satu ekstremitas. Pengambilan sampel arteri femoralis dilakukan setelah pemberian dosis pertama NAC, setelah dosis pada hari ketiga, dan setelah delapan hari dari masing-masing dosis. Seluruh spesimen arteri femoralis dikenai pewarnaan dengan metode imunohistokimia dan diperiksa di bawah mikroskop dengan pembesaran 300 kali untuk mengevaluasi ekspresi VEGF dan FGF. Data dari seluruh sampel dikumpulkan dan kemudian dianalisis secara statistik.
Hasil: Kadar rata-rata VEGF kelompok tikus yang menerima NAC lebih tinggi daripada kelompok kontrol dari awal pengamatan sampai hari ke 8. Hasil FGF pada tikus kontrol lebih tinggi pada hari ke-0 dan hari ke-8 dibandingkan dengan kelompok tikus yang menerima NAC. Namun, dalam tes yang berbeda tidak ada perbedaan yang signifikan (p>0,05) yang ditemukan pada pengukuran VEGF dan FGF pada hari yang sama antara kelompok kontrol dan kelompok perlakuan.
Kesimpulan: Tidak ada perbedaan yang signifikan pada VEGF dan FGF antara kelompok kontrol negatif dan kelompok yang menjalani perlakuan.
Akın A, et al. Cardiac thrombus developing after an accidental high-voltage electric shock in a child. The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics, 2015. 57 (2): 180- 182.
Aygün D, & Göbüllü H, The Myopathic Effects of Electrical Injury. Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery, 2010. 16(3):225- 228.
Benlier E, et al. Fucoidin, a neutrophil rolling inhibitor, reduces damage in a rat electrical burn injury model. Burns, 2011. 37:1216 – 1221.
Bloomer RJ, The role of nutritional supplements in the prevention and treatment of resistance exerciseinduced skeletal muscle injury. Sports Med, 2007. 37 (6): 519–532.
Budi, AS. 2016. Overview Luka Bakar. Disajikan dalam Symposium dan Workshop Emergency Management of Major Burn. Universitas Airlangga. Surabaya.
Church D, et al. Burn wound infections. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2006. 19 (2):403– 434.
Deniz M, An effective antioxidant drug on prevention of the necrosis of zone of stasis: N-acetylcysteine. Burns. 2013. 39: 320– 325.
Erol Benlier, e. a. Fucoidin, a neutrophil rolling inhibitor, reduces damage in a rat electrical burn injury model. Burns. 2011. 37:1216 –1221.
Gibson KR, Winterburn TJ, Barrett F, Sharma S, et al. Therapeutic potential of Nacetylcysteine as an antiplatelet agent in patients with type-2 diabetes. Cardio-vasc Diabetol, 2011. 10: 43.
Gurtner GC, 2007. Wound healing, norma and abnormal. In: Thorne CH, Beasly RW, Aston SJ, Bartlett SP, Gurtner GC, Spear SL, eds. Grabb and Smith's Plastic Surgery, 6th ed., Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 15-22.
Jeremias A, et al. Effects of N-acetyl-cysteine on endothelial function and inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Heart Int, 2009. 4, e7.
Kon M, et al. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation on exercise-induced muscular injury of rats. Exerc Immunol Rev, 2007.13, 76–88.
Maluegha DPTR, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells lowering effect and compensative mechanism in electrical burn injury models of rat. Biomarkers and Genomic Medicine, 2015. 7:78e82.
Perdanakusuma DS, 2017. Cara Mudah Merawat Luka. Surabaya: Airlangga University Press.
Sadowska AM, et al. Antioxidant and antiinflammatory efficacy of NAC in the treatment of COPD: Discordant in vitro and in vivo dose effects: A review. Pulm Pharmacol Ther, 2007.20 (1), 9-22.
Sahib AS, et al. Effect of antioxidants on the incidence of wound infection in burn patients. Ann Burn Fire Disasters, 2010. 23: 199– 205.
Saleh AAS, 2014. Synergistic effect of Nacetylcysteine and folic acid against aspartame-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int J Adv Res, 2014.2(5):363–373.
Shevchenko RV, et al. A review of tissue-engineered skin bioconstructs available for skin reconstruction. J R Soc Interface, 2010.7 (43): 229–258.
Suha T, et al. Effects of N-acetyl-cysteine and ethyl pyruvate on ischemia-reperfusion injury in experimental electrical burn model. Am J Emerg Med, 2016. 34 (7):1217-1224.
Steinstraesser L, Al-Benna S. 2012. Acute Management of Burn/ Electrical Injuries. In: Song DH ed. Neligan Plastic Surgery, 3rd ed, Lower extremity, trunk and burns volume 4. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier.
Toussaint J & Singer AJ, The evaluation and management of thermal injuries: 2014 update. Clin Exp Emerg Med, 2014.1(1), 8-18.
Whitehead NP, et al. N-Acetylcysteine ameliorates skeletal muscle patho-physiology in mdx mice. J Physiol, 2008. 586 (7), 2003-2014.
Young DM. 2007. Burn and Electrical Injury. In: Mathes Plastic Surgery, General Principles Volume 1. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier.
Copyright (c) 2020 Elisabeth Prajanti Sintaningrum, Iswinarno Doso Saputro, Lobredia Zarasade

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)