PROFILE OF KELOID PATIENTS IN SURGICAL WOUNDS: A STUDY AT DEPARTMENT OF PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY, DR. SOETOMO GENERAL ACADEMIC HOSPITAL, SURABAYA, INDONESIA (2019-2022)
Downloads
Highlights:
- Previous keloid surgery mostly caused keloid recurrence.
- The most common symptom that accompanies keloids in surgical wounds was itching.
- Surgery and combination therapy were the most used therapy.
Abstract:
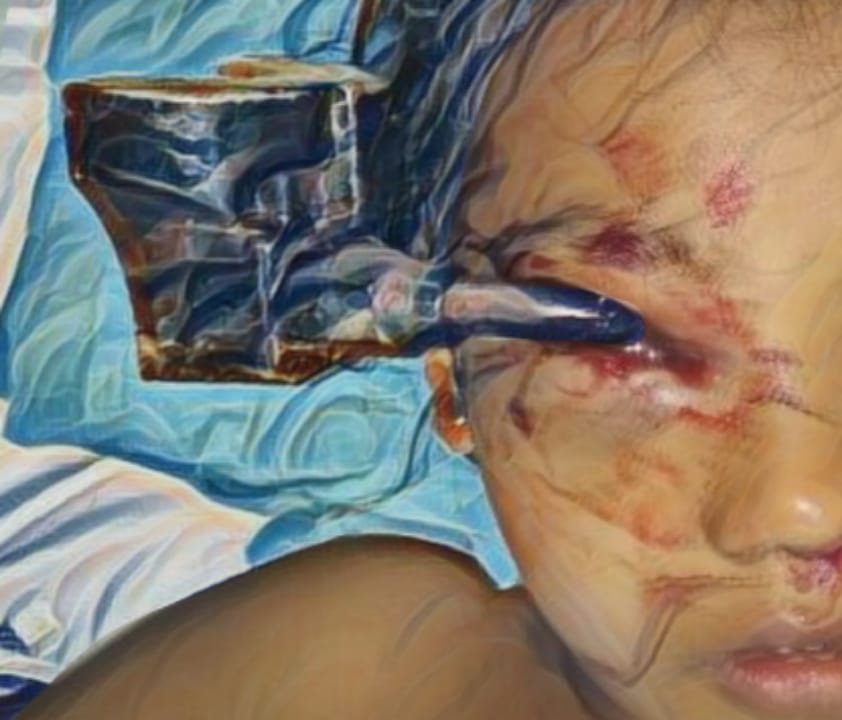
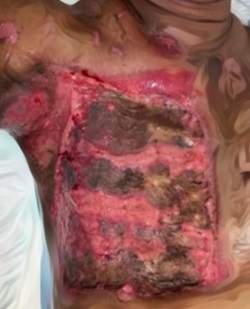
Introduction: Keloid is an abnormal scar resulting from disruptions in the wound healing process. Clinically, keloids extend beyond the original wound margins and progressively enlarge into dense, firm nodules. They can develop following various forms of trauma, including surgical procedures. Several factors contribute to keloid formation in surgical wounds, such as age, gender, genetics, skin color, hormones, incision location, wound tension, and delayed healing.
Methods: This retrospective descriptive study analyzes medical records of patients diagnosed with keloids due to surgical wounds at the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Dr. Soetomo General Academic Hospital, Surabaya, between 2019 and 2022.
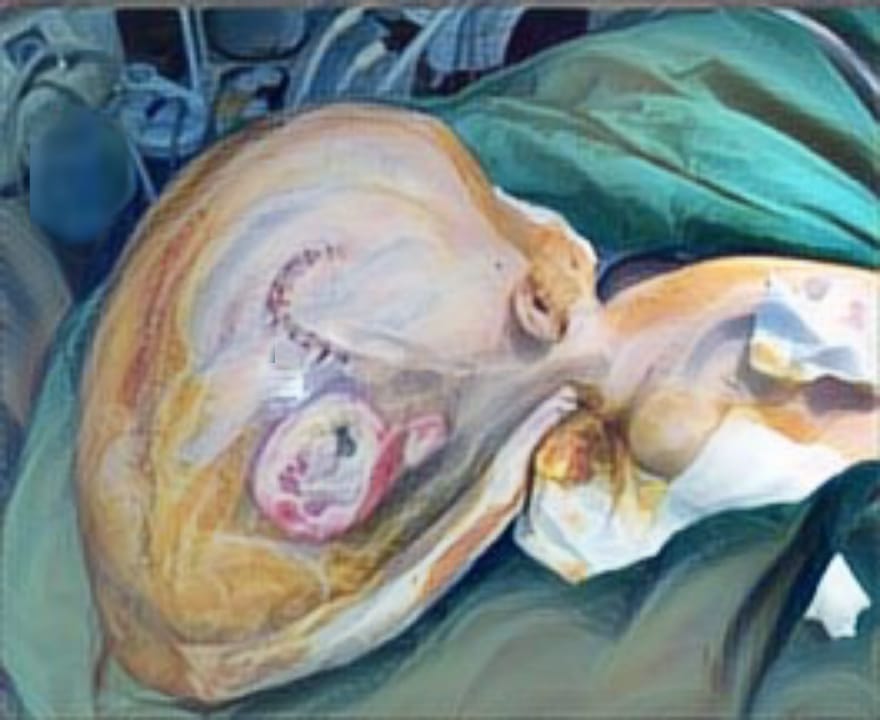
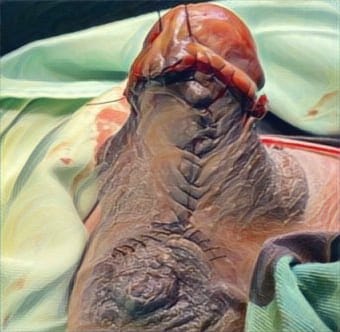
Results: Among 58 keloid patients, 23 developed keloids following surgery. The most common risk factor was a history of previous keloid surgery. The majority of patients were female, aged 17–25 years, students, and had no family history of keloids. The most frequent keloid location was the chest, with an onset of ≥1 year, a size of <20 cm², and associated itching. Surgical excision and combination therapy were the most commonly used treatment approaches.
Conclusion: Previous keloid surgery is the primary risk factor for developing keloids in surgical wounds. Surgery and combination therapy remain the most frequently employed treatment strategies.
Nangole FW & Agak GW. Keloid Pathophysiology: Fibroblast or Inflammatory Disorders? Pathophysiology of Keloids. JPRAS Open. 2019;22:44–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra. 20 19.09.004
Rodrigues M, Kosaric N, Bonham CA & Gurtner GC. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol Rev. 2019; 99(1): 665–706. DOI:10.1152/physrev. 00067. 2017
Kim SW. Management of Keloid Scars: Noninvasive and Invasive Treatments. Arch Plast Surg. 2021; 48(2):149-157. DOI: 10.5999/aps.2020.01914
Choirunanda A, Praharsini I. Profil Gangguan Kualitas Hidup Akibat Keloid pada Mahasiswa Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Udayana Angkatan 2012–2014. Medika Udayan. 2019;8.
Mishra B & Arora C. Epidemiology of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital of Northern India. Int J Sci Res. 2020.
Téot L, Mustoe TA, Middelkoop E & Gauglitz GG. State of the Art Management and Emerging Technologies. Switzerland: Textbook on Scar Management; 2020.
Liu R, Xiao H, Wang R, Li W, Deng K, Cen Y, et al. Risk Factors Associated with the Progression from Keloids to Severe Keloids. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022; 135(07): 828-836. DOI:10.1097/CM9.0 00000000 0002093
Asri E. Pengaruh Pemberian (+)-Catechin Gambir (Uncaria Gambir Roxburgh) Terhadap Proliferasi, Tgf-β1, Smad3, dan Kolagen Tipe I Sel Fibroblas Keloid Manusia Secara In Vitro. Doctoral Thesis, Universitas Andalas. 2024
Fania AWN. Profil Pasien Keloid Dan Skar Hipertrofik Usia Produktif Di Departemen/SMF Bedah Plastik Rekonstruksi & Estetik RSUD Dr. Soetomo Surabaya Periode 2014-2017. 2018. PhD Thesis. Universitas Airlangga.
Birawati S & Asri E. Keloids profile in the Dermatovenerology Clinic of RSUP Dr. M. Djamil Padang Indonesia from January 2014 to December 2018. International Journal of Pharm Tech Research. 2020; 13(04): 383-387. DOI: 10.20902/IJPTR.2019.130410
Limandjaja GC, Niessen FB, Scheper RJ & Gibbs S. The Keloid Disorder: Heterogeneity, Histopathology, Mechanisms and Models. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020; 8. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020. 00360
Son D & Harijan A. Overview of Surgical Scar Prevention and Management. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29(6): 751. DOI: 10.3346/ jkms.2014.29.6.751
Pooja SY, Kevin MK, Jordan G, Andres M, Carisa MC & Damon SC. Keloids: A Retrospective Review and Treatment Algorithm. Ann Plast Reconstr Sur. 2023.7(2):1108.
Azzahra AM, Perdanakusuma DS, Indramaya DM & Saputro ID. Keloid and Hypertrophic Scar Post-Excision Recurrence: A Retrospective Study. Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi 2023; 9(2): 58–63. DOI: 10.14228/jprjournal.v9i2. 343
Ogawa R. The Most Current Algorithms for the Treatment and Prevention of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: A 2020 Update of the Algorithms Published 10 Years Ago. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022; 149(1): 79e-94e. DOI:10.10 97/ PRS.0000000000008667
Cecarani O. Profil Keloid pada Pasien RSUP Dr. M. Djamil Padang Tahun 2016-2020. 2021. PhD Thesis. Universitas Andalas.
Kluger N, Misery L, Seité S & Taieb C. Body Piercing: A National Survey in France. Dermatology. 2018; 235(1): 71-78. DOI:10.1159/000494350
Nainpuriya DRY & Mewara DRBC. Trends in Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars. Int J Surg Sci. 2021;5(2): 261-265. DOI:10.33545/surgery.2021.v5.i2e.704
Shaheen AA. Risk Factors of Keloids: A Mini Review. Austin J Dermatol . 2017; 4(2):1074.DOI:10.26420/austinjdermatolog.2017.1074
Huang C & Ogawa R. Keloidal Pathophysiology: Current Notions. Scars Burn Heal. 2021;7. DOI:10.1177/ 2059513120980320
Andisi RDS, Suling PL & Kapantow MG. Profil Keloid di Poliklinik Kulit dan Kelamin RSUP Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado Periode Januari 2011-Desember 2015. Jurnal E-Clinic (ECL). 2016;4(2). DOI: 10.35790/ecl.v4i2.14667
Rani TU, Shanker VK, Vengareddy S, Thotli M KR, Sushrutha A & Makarand M. Comparative Study of Various Topical and Surgical Treatment Modalities in Keloid. Int J Acad Med Pharm. 2022; 4(4): 449-457. DOI:10.47009/jamp.2022.4.4. 89
Reilly DM & Lozano J. Skin Collagen Through the Lifestages: Importance for Skin Health and Beauty. Plast Aesthet Res. 2021; 8. DOI: 10.20517/23479264. 2020.153
Limandjaja GC, Niessen FB, Scheper RJ & Gibbs S. Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: Overview of the Evidence and Practical Guide for Differentiating Between These Abnormal Scars. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30(1):146-161. DOI:10. 1111/exd.14121
McGinty S, Waqas J & Siddiqui. Keloid. StatPearls Publishing. 2021.
Basak AK, Joya Debnath, Hossain MM & Hasanat MA. Effectiveness of Combination Use of Intralesional Steroid with 5-Fluorouracil in the Treatment of Keloid Patients. Mediscope. 2024; 11(1): 41–47. DOI:10. 3329/mediscope.v11i1.71642
Liu AH, Sun XL, Liu DZ, Xu F, Feng SJ, Zhang SY, et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Features of Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid in Chinese College Students: A University-Based Cross-Sectional Survey. Heliyon. 2023; 9(4): e15345. DOI:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15345
Hawash AA, Ingrasci G, Nouri K & Yosipovitch G. Pruritus in Keloid Scars: Mechanisms and Treatments. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021; 101(10): 578. DOI:10.2340/00015555-3923
Rachel E & Bell PhD, Tanya J. Keloid Tissue Analysis Discredits a Role for Myofibroblasts in Disease Pathogenesis. Wound Repair and Regeneration.2021; 29(4): 637-641. DOI:10.1111/wrr.1292 3
Ogawa R. Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/keloids-and-hypertrophic-scars/print.
Thornton NJ, Garcia BA, Hoyer P & Wilkerson MG. Keloid Scars: An Updated Review of Combination Therapies. Cureus. 2021; 13(1):e12999 DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12999
Ojeh N, Bharatha A, Gaur U & Forde AL. Keloids: Current and Emerging Therapies. Scars Burn Heal. 2020; 6. DOI:10.1177/2059513120940499
Copyright (c) 2025 Diandra Yasmin Nurfaiza, Iswinarno Doso Saputro, Diah Mira Indramaya, Aruja Dhar, Saleh Ashafi, Milan Muhammed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
JURNAL REKONSTRUKSI DAN ESTETIK by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- The journal allows the author to hold copyright of the article without restriction
- The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions.
- The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessbility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA)