Managing retained placenta in first-parity doe and administering vitamin A, D, and E as supportive treatment
Downloads
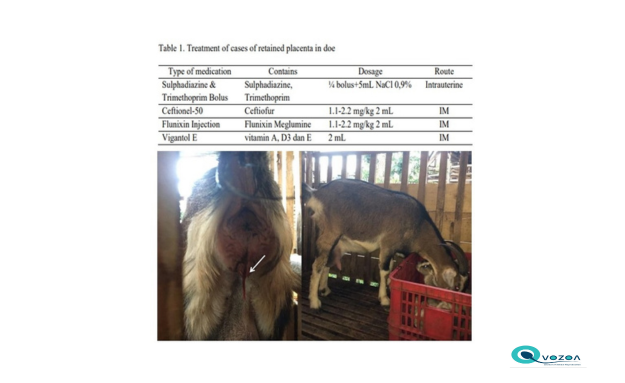
This study aims to report the treatment of retained placenta in a doe by administration of intrauterine antibiotics, accompanied by intramuscular injection of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, and injection of vitamins A, D, and E as supportive treatment. The Saanen doe was brown, approximately two years old with a BCS of 3/5 and kidding for the first time on January 11, 2023. The following day, it was reported that the doe's placenta had not been expelled until 24 hours after kidding. Physically the doe was weak, unable to stand, and reddish-brown discharge was seen came out of the vulva. Based on these conditions the doe was diagnosed as having retained placenta with a fausta prognosis. The doe was treated with a bolus of antibiotics contained 250 mg sulphadiazine and 50 mg trimethoprim which was diluted with 5 mL of 0.9% NaCl for uterine lavage. Systemic treatment consisted of intramuscular injection of ceftiofur at 1.1 mg/kg bw, flunixin meglumine at 1.1 mg/kg bw, as well as a combination of 300,000 IU of vitamin A palmitate, 100,000 IU of vitamin D3, and 50 mg of vitamin E acetate as supportive treatment. The treatment was successful, the doe was able to stand and eat when examined the next day after treatment. The doe returned to estrus 42 days after treatment. It could be concluded that treatment of retained placenta in a doe with intrauterine broad-spectrum antibiotics, beta-lactamase antibiotics and intramuscular anti-inflammatory, with vitamins A, D and E as supportive therapy was effective and the doe returned to estrus 42 days after treatment.
Akar Y, Gazioglu A. 2006. Relationship between vitamin A and beta-carotene levels during the postpartum period and fertility parameters in cows with and without retained placenta. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 50: 93-6.
Al-Yamani H, ALkarmah M, Koşum N. 2021. Some reproductive problems in Friesian cows raised in Yemen (2- retained placenta). Biomed J Sci Tech Res 40: 32548-54.
Arrebola FA, Torres-Martell R, González-Casquet O, Meza-Herrera CA, Pérez-Marín CC. 2022. Periovulatory hormonal profiles after estrus induction and conception rate by fixed-time AI in Payoya goats during the anestrous season. Animals 12: 2853.
Beagley JC, Whitman KJ, Baptiste KE, Scherzer J. 2010. Physiology and treatment of retained fetal membranes in cattle. J Vet Intern Med. 24: 261-8.
Bozhkov AI, Novikova AV, Klimova EM, Ionov IA, Akzhyhitov RA, Kurhuzova NI, Bilovetska SG, Moskalov VB, Haiovyi SS. 2023. Vitamin A reduces the mortality of animals with induced liver fibrosis by providing a multi-level body defense system. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 13: 48-63.
Brahmanand B, Kaurav PS, Sharm CS. 2022. Retained placenta in zebu cattle-report of two cases. Pharm Innov J. SP-11: 1896-8.
Dai T, Ma Z, Guo X, Wei S, Ding B, Ma Y, Dan X. 2023. Study on the pattern of postpartum uterine involution in dairy cows. Animals 13: 3693.
Dervishi E, Zhang G, Hailemariam D, Dunn SM, Ametaj BN. 2016. Occurrence of retained placenta is preceded by an inflammatory state and alterations of energy metabolism in transition dairy cows. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 7: 26.
Dhara S, Thakur S, Anwar SMS, Maiti A, Ghosh T, Houzha R. 2022. Selenium and vitamin E on reproductive health of dairy cattle: An overview. Int J Curr Microbiol Apl Sci. 11: 95-107.
Eder K, Grundmann SM. 2022. Vitamin D in dairy cows: metabolism, status and functions in the immune system. Arch Anim Nutr. 76: 1-33.
Faradillah AN, Agustina GC. 2023. Handling of endometritis in dairy cow after infection with foot and mouth disease and abortion. Ovozoa : J Anim Reprod. 12: 101-10.
Haga S, Ishizaki H, Roh S. 2021. The physiological roles of vitamin E and hypovitaminosis E in the transition period of high-yielding dairy cows. Animals 11: 1088.
Harrison JH, Hancock DD, Conrad HR. 1984. Vitamin E and Selenium for reproduction of the diary cow. J Dairy Sci. 67: 123-32.
Harwood D, Mueller K. 2018. Goat medicine and surgery. 1st Ed. CRC Press. Boca Raton, US.
Heppelmann M, Volland J, Pfarrer C, Kietzmann M, Bäumer W, Merbach S, Schoon HA, Wellnitz O, Schmicke M, Hoedemaker M, Bollwein H. 2018. Effects of oxytocin and PGF2α on uterine contractility in cows with and without metritis-An in-vitro study. Anim Reprod Sci. 188: 144-54.
Hossein-Zadeh NG, Ardalan M. 2011. Cow-specific risk factors for retained placenta, metritis and clinical mastitis in Holstein cows. Vet Res Commun. 35: 345-54.
Inaba R, Kawahara-Miki R, Shinozawa A, Yasuhara T, Fujii T, Koyama K, Murata-Okubo M, Souma K, Hirayama H. 2021. Impaired placentomal interferon signaling as the possible cause of retained fetal membrane in parturition-induced cows. J Reprod Dev. 68: 30-7.
Königsson K, Gustafsson H, Gunnarsson A, Kindahl H. 2001. Clinical and bacteriological aspects on the use of oxytetracycline and flunixin in primiparous cows with induced retained placenta and post-partal endometritis. Reprod Domest Anim. 36: 247-56.
Leonardo P. Mesquita LP, Costa RC, Nogueira CI, Abreu CC, Orlando DR, Junior IA, Peconick AP, Varaschin MS. 2018. Placental lesions associated with abortion and stillbirth in goats naturally infected by Neospora caninum. Pesq Vet Bras. 38: 444-9.
Li Y, Wen H, Yang Y, Zhao Z, Gao H, Li H, Huang M. 2022. Potential prognostic markers of retained placenta in dairy cows identified by plasma metabolomics coupled with clinical laboratory indicators. Vet Quart. 42: 199-212.
Majeed AF, Mansour AR, Mohammed TR. 2003. Treatment of retained placenta in goat. Al-Anbar J Agric Sci. 1: 1-5.
Mogiye SL, Nafiu LO, Pagala MA. 2020. Reproductive characteristics of peranakan Etawa and kacang goats in different maintenance systems in the Toari district, Kolaka regency. Int J Sci Res Sci Eng Technol. 7: 442-46.
Niki E. 2014. Role of vitamin E as a lipid-soluble peroxyl radical scavenger: in vitro and in vivo evidence. Free Radic Biol Med. 66: 3-12.
Noakes DE. 2001. The puerperium and the care of the newborn. In: Noakes DE, Parkinson TJ, England GCW (Eds). Arthur's veterinary reproduction and obstetrics. 8th Ed. W.B. Saunders. UK. 189-202.
Paiano RB, Becker Birgel D, Birgel EH. 2019. Uterine involution and reproductive performance in dairy cows with metabolic diseases. Animals 9: 93.
Papich MG. 2021. Papich handbook of veterinary drugs 5th Ed. Elsevier.
Poindexter MB, Zimpel R, Vieira-Neto A, Husnain A, Silva ACM, Faccenda A, Sanches de Avila A, Celi P, Cortinhas C, Santos JEP, Nelson CD. 2022. Effect of prepartum source and amount of vitamin D supplementation on lactation performance of dairy cows. J Dairy Sci. 106: 974-89.
Pontes GCS, Monteiro PLJ, Prata AB, Guardieiro MM, Pinto DAM, Fernandes GO, Wiltbank MC, Santos JEP, Sartori R. 2015. Effect of injectable vitamin E on incidence of retained fetal membranes and reproductive performance of dairy cows. J Dairy Sci. 98: 2437-49.
Pugh DG, Baird AN, Edmondson M, Passler T. 2021. Sheep, goat, and cervid medicine. 3rd Ed. Elsevier.
Rahim NI, Hendrawan VF, Tuska HSA, Agustina GC. 2023. Use of vitamin E and selenium injections as supportive treatment of retained placenta in dairy cattle. Ovozoa : J Anim Reprod. 12: 158-63.
Rizzo A, Gazza C, Silvestre A, Maresca L, Sciorsci RL. 2018. Scopolamine for uterine involution of dairy cows. Theriogenology 122: 35-40.
Rohmah SD, Ratnani H, Warsito SH, Rimayanti R, Madyawati SP, Mulyati S, Hasib A. 2023. Retained placenta in dairy cows living in an all-day cowshed rearing system. Ovozoa : J Anim Reprod. 12: 71-80.
Sheldon IM, Williams EJ, Miller AN, Nash DM, Herath S. 2008. Uterine diseases in cattle after parturition. Vet J. 176: 115-21.
Strickland JM, Wisnieski L, Mavangira V, Sordillo LM. 2021. Serum vitamin D is associated with antioxidant potential in peri-parturient cows. Antioxidants 10: 1420.
Tanner AR, Kennedy VC, Lynch CS, Hord TK, Winger QA, Rozance PJ, Anthony RV. 2022. In vivo investigation of ruminant placenta function and physiology-a review. J Anim Sci. 100: skac045.
Tuscho T. 2017. Review on retention of placenta in dairy cows and it is economic and reproductive impacts. J Nat Sci Res. 7: 28-37.
Weir RR, Strain JJ, Johnston M, Lowis C, Fearon AM, Stewart S, Pourshahidi LK. 2017. Environmental and genetic factors influence the vitamin D content of cows' milk. Proc Nutr Soc. 76: 76-82.
Xiao J, Khan MZ, Ma Y, Alugongo GM, Ma J, Chen T, Khan A, Cao Z. 2021. The antioxidant properties of selenium and vitamin E; Their role in periparturient dairy cattle health regulation. Antioxidants 10: 1555.
Copyright (c) 2024 Dhea Salsabila, Viski Fitri Hendrawan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Ovozoa by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
4. The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.