Date Log
Copyright (c) 2023 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
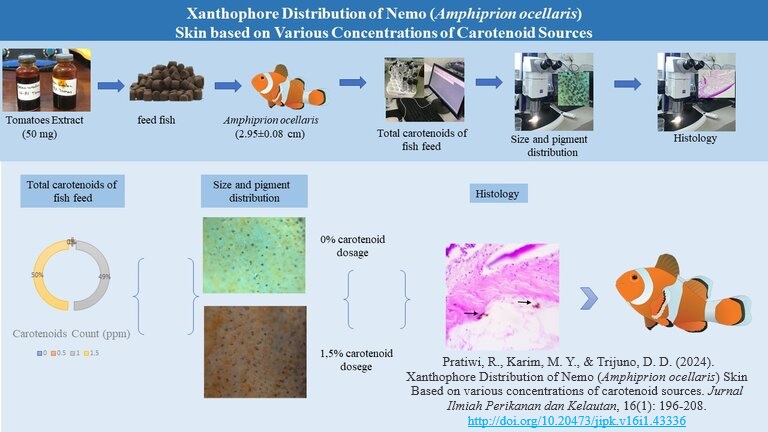
Xanthophore Distribution of Nemo (Amphiprion ocellaris) Skin Based on various Concentrations of Carotenoid Sources
Corresponding Author(s) : Muhammad Yusri Karim
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 16 No. 1 (2024): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract

Abstract
The decreased color intensity of Nemo is related to the amount of carotenoid concentration in the xanthophore of Nemo's skin. Therefore, efforts are needed to maintain stable carotenoid production. Tomato is one of the most abundant carotenoid producers. The utilization of carotenoids can maintain the morphological color of aquatic organisms. This study aimed to analyze the effect of carotenoid compounds on total carotenoid content, the size, and distribution of xanthophores on Nemo skin. A total of 60 Nemo with an average initial weight of 0.84±0.14 g and an average length of 2.95±0.08 cm. The research was conducted using a completely randomized design (CRD), consisting of four carotenoid concentrations in addition to fish pellet, 0%, 0.5%, 1%, and 1.5% with three replications. The results showed that the optimum dose of carotenoid compounds in increasing the total carotenoid content in nemo fish skin is 1.5%. Carotenoids added to the fish feed affected the distribution and maturity of xanthophore. However, it did not affect the size of the xanthophore.
Highlight Research
- Nemo contains three types of pigment cells, namely melanophores, xanthophores, and iridophores.
- Carotenoid supplementation is related to xanthophore in fish skin
- The pigment pattern is determined mainly by the number, size, and distribution of different cell types
- xanthophores were not found in the histology HE (hematoxylin-eosin) staining method in fish skin.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Ahi, E. P., Lecaudey, L. A., Ziegelbecker, A., Steiner, O., Glabonjat, R., Goessler, W., Hois, V., Wagner, C., Lass, A., & Sefc, K. M. (2020). Comparative transcriptomics reveals candidate carotenoid color genes in an East African cichlid fish. BMC Genomics, 21(1):1-15.
- Alfionita, K., Budhiyanti, S. A., & Ekantari, N. (2022). Effect of homogenization process on the production of Arthrospira platensis carotenoid nanocapsules encapsulated with arabic gum and whey protein concentrate. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 14(1):12-24.
- Bajec, S. S., DjurdjeviÄ, I., Linares Andujar, C., & Kreft, M. E. (2022). Genetic and correlative light and electron microscopy evidence for the unique differentiation pathway of erythrophores in brown trout skin. Scientific Reports, 12(1):1015
- Bao, Y., Yu, Y., Xu, H., Guo, C., Li, J., Sun, S., Zhou, Z.-K., Qiu, C.-W., & Wang, X.-H. (2019). Full-colour nano print-hologram synchronous metasurface with arbitrary hue-saturation-brightness control. Light: Science & Applications, 8(95):1–10.
- Bolker, J. A., & Hill, C. R. (2000). Pigmentation development in hatchery-reared flatfishes. Journal of Fish Biology, 56(5):1029–1052.
- Bonanno, J. A., Breen, N. E., Tlusty, M. F., Andrade, L., & Rhyne, A. L. (2021). The determination of thiocyanate in the blood plasma and holding water of Amphiprion clarkii after exposure to cyanide. PeerJ, 9:e12409.
- Cal, L., Suarez-Bregua, P., Moran, P., Cerdá-Reverter, J. M., & Rotllant, J. (2018). Fish pigmentation. A key issue for the sustainable development of fish farming. In M. Yúfera (Ed.), Emerging issues in fish larvae research. (pp. 229–252). Cham: Springer Cham.
- Chambel, J., Severiano, V., Baptista, T., Mendes, S., & Pedrosa, R. (2015). Effect of stocking density and different feeds on the growth of Percula Clownfish, Amphiprion percula (Lacepede, 1802). SpringerPlus, 4(1):1–7
- D'Alba, L., & Shawkey, M. D. (2019). Melanosomes: Biogenesis, properties, and evolution of an ancient organelle. Physiological Reviews, 99(1):1–19.
- Díaz-Jiménez, L., Hernández-Vergara, M. P., Pérez-Rostro, C. I., & Olvera-Novoa, M. Á. (2021). The effect of two carotenoid sources, background colour, and light spectrum on the body pigmentation of the clownfish Amphiprion ocellaris. Aquaculture Research, 52(7):3052–3061.
- DjurdjeviÄ, I., Kreft, M. E., & Bajec, S. S. (2015). Comparison of pigment cell ultrastructure and organization in the dermis of marble trout and brown trout, and the first description of erythrophore ultrastructure in salmonids. Journal of Anatomy, 227(5):583–595.
- Ebeneezar, S., Prabu, D. L., Chandrasekar, S., Tejpal, C. S., Madhu, K., Sayooj, P., & Vijayagopal, P. (2020). Evaluation of feed oleoresins on the enhancement of skin coloration and growth in the marine ornamental clown fish, Amphiprion ocellaris (Cuvier, 1830). Aquaculture, 529:735728.
- Fang, W., Huang, J., Li, S., & Lu, J. (2022). Identification of pigment genes (melanin, carotenoid, and pteridine) associated with skin color variant in red tilapia using transcriptome analysis. Aquaculture, 547:737429.
- Gedi, M. A., Magee, K. J., Darwish, R., Eakpetch, P., Young, I., & Gray, D. A. (2019). Impact of the partial replacement of fish meal with a chloroplast rich fraction on the growth and selected nutrient profile of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Food & Function, 10(2):733–745.
- Ghosh, S., Kumar, T. A., Vinoth, R., Balasubramanian, T., Dabbagh, A. R., & Keshavarz, M. (2011). Effect of short-term enrichment of wild zooplankton on survival of larval maroon Clownfish (Premnas biaculeatus). Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 7(5):674–677.
- Guo, H., Huang, B., Qi, F., & Zhang, S. (2007). Distribution and ultrastructure of pigment cells in the skins of normal and albino adult turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 25(2):199–208.
- Grether, G. F., Kolluru, G. R., & Nersissian, K. (2004). Individual colour patches as multicomponent signals. Biological Reviews, 79(3):583-610.
- Hamre, L. A., Oldham, T., Oppedal, F., Nilsen, F., & Glover, K. A. (2021). The potential for cleaner fish-driven evolution in the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis: Genetic or environmental control of pigmentation? Ecology and Evolution, 11(12):7865–7878.
- Hirata, M., Nakamura, K., Kanemaru, T., Shibata, Y., & Kondo, S. (2003). Pigment cell organization in the hypodermis of zebrafish. Developmental Dynamics, 227(4):497–503.
- Kumar, A., Kumar, V., Gull, A., & Nayik, G. A. (2020). Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicon). In G. A. Nayik and A. Gull (Ed.), Antioxidants in vegetables and nuts-properties and health benefits. (pp. 191–207). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
- Kumar, S., Kumar, R., Diksha, Kumari, A., & Panwar, A. (2022). Astaxanthin: A super antioxidant from microalgae and its therapeutic potential. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 62(9):1064–1082.
- Liang, Y., Meyer, A., & Kratochwil, C. F. (2020). Neural innervation as a potential trigger of morphological color change and sexual dimorphism in cichlid fish. Scientific Reports, 10(12329):1-16.
- Ligon, R. A., & McCartney, K. L. (2016). Biochemical regulation of pigment motility in vertebrate chromatophores: A review of physiological color change mechanisms. Current Zoology, 62(3):237–252.
- Lim, K. C., Yusoff, F. M., Karim, M., & Natrah, F. M. (2023). Carotenoids modulate stress tolerance and immune responses in aquatic animals. Reviews in Aquaculture, 15(2):872–894.
- Liu, C., Liu, H., Zhu, X., Han, D., Jin, J., Yang, Y., & Xie, S. (2022). The effects of dietary Arthrospira platensis on oxidative stress response and pigmentation in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Antioxidants, 11(6):1100.
- Luo, M., Lu, G., Yin, H., Wang, L., Atuganile, M., & Dong, Z. (2021). Fish pigmentation and coloration: Molecular mechanisms and aquaculture perspectives. Reviews in Aquaculture, 13(4):2395–2412.
- Makri, V., Feidantsis, K., Papadopoulos, D., Lattos, A., Georgoulis, I., Michaelidis, B., & Giantsis, I. A. (2021). Natural-like pigmentation in cultured fish stocks, not only a matter of nutrition. A review of Salmonidae and Sparidae families, with a particular focus on the red porgy Pagrus pagrus. Aquaculture Research, 52(7):2942–2953.
- Maoka, T. (2020). Carotenoids as natural functional pigments. Journal of Natural Medicines, 74(1):1–16.
- Marudhupandi, T., Dhayanithi, N. B., Jeyaprakashsabari, S., Deepa, S. D., & Kumar, T. T. A. (2022). Effect of lipid supplementation, using oil extracted from Nannochloropsis salina on growth indices and expression of gene associated lipid metabolism in clownfish, Amphiprion ocellaris. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1–10.
- Micah, A. D., Wen, B., Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Yusuf, A., Thierry, N. N. B., Tokpanou, O. S., Onimisi, M. M., Adeyemi, S. O., & Gao, J.-Z. (2022). Effect of dietary astaxanthin on growth, body color, biochemical parameters and transcriptome profiling of juvenile blood parrotfish (Vieja melanurus ♀ x Amphilophus citrinellus ♂). Aquaculture Reports, 24:101142.
- Meléndez-Martínez, A. J. (2019). An overview of carotenoids, apocarotenoids, and vitamin A in agro-food, nutrition, health, and disease. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 63(15):1801045.
- Merhan, O. (2017). The biochemistry and antioxidant properties of carotenoids. In D. J. Cvetkovic and G. S. Nikolic (Ed.), Carotenoids. (pp. 51). Croatia: InTech.
- Moore, B., Herrera, M., Gairin, E., Li, C., Miura, S., Jolly, J., Mercader, M., Izumiyama, M., Kawai, E., & Ravasi, T. (2023). The chromosome-scale genome assembly of the yellowtail clownfish Amphiprion Clarkii provides insights into the melanic pigmentation of anemonefish. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 13(3)1-12.
- Nakano, T. (2020). Stress in Fish and application of carotenoid for aquafeed as an antistress supplement. Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology, 2999–3019.
- Navarro, R. E., Ramos-Balderas, J. L., Guerrero, I., Pelcastre, V., & Maldonado, E. (2008). Pigment dilution mutants from fish models with connection to lysosome-related organelles and vesicular traffic genes. Zebrafish, 5(4):309–318.
- Nhan, H. T., Minh, T. X., Liew, H. J., Hien, T. T. T., & Jha, R. (2019). Effects of natural feed carotenoids on skin coloration of false Clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris Cuvier, 1830). Aquaculture Nutrition, 25(3):662–668.
- Nüsslein-Volhard, C., & Singh, A. P. (2017). How fish color their skin: A paradigm for development and evolution of adult patterns. BioEssays, 39(3):1600231.
- Pataro, G., Carullo, D., & Ferrari, G. (2019). Effect of PEF pre-treatment and extraction temperature on the recovery of carotenoids from tomato wastes. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 75:139–144.
- Pietoyo, A., Hidayat, K. W., Nurazizah, S., Arifin, I. F. Z., Prabowo, D. G., Widianto, F. T., & Mustakim, I. (2020). The effect of stocking density on the growth of Ocellaris clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris Cuvier, 1830) with recirculation. Journal of Aquaculture and Fish Health, 9(3):189–193.
- Pinela, J., Oliveira, M., & Ferreira, I. (2016). Bioactive compounds of tomatoes as health promoters. In L. R. da Silva and B. M. Silva (Ed.), Natural bioactive compounds from fruits and vegetables as health promotors: Part II. (pp. 48–91). Sharjah, UAE: Bentham Science Publisher.
- Purnomo, T. A. B., Kurniawan, Y. S., Kesuma, R. F., & Yuliati, L. (2020). Selection of maceration solvent for natural pigment extraction from red fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam). Indonesian Journal of Natural Pigments, 2(1):8–12.
- Pratiwi, R., Mulyono, M., Saputra, A., Farkan, M., Samsuharapan, S. B., & Panjaitan, A. S. (2022). Enhancement of color brightness on clown fish (Amphiprion percula) with addition of tomato powder extract. Asian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Research, 20(6):117–124.
- Rebelo, B. A., Farrona, S., Ventura, M. R., & Abranches, R. (2020). Canthaxanthin, a red-hot carotenoid: applications, synthesis, and biosynthetic evolution. Plants, 9(8):1039.
- Renko, G., DjurdjeviÄ, I., & Bajec, S. S. (2022). Isolation of chromatophores from brown trout (Salmo trutta) skin. Fishes, 7(2):72.
- Riaz, M., Zia-Ul-Haq, M., & Dou, D. (2021). Chemistry of carotenoids. In M. Zia-Ul-Haq, S. Dewanjee, and M. Riaz (Ed.), Carotenoids: structure and function in the human body. (pp. 43–76). Cham: Springer Cham.
- Sheng, J., Guan, L., Sheng, B., Geng, S., Wu, D., Hu, B., Li, Z., Le, S., & Hong, Y. (2021). Analysis of pigment cell composition, pigment content, tyrosinase content, and activity of three kinds of loaches Misgurnus anguillicaudatus from Poyang Lake. Journal of Fish Biology, 100(2):366–377.
- Sinha, A. (2022). Pigmentation in fishes. In P. K. Pandey and J. Parhi (Ed.), Advances in fisheries biotechnology. (pp. 245–261). Singapore: Springer.
- Stahl, W., & Sies, H. (2003). Antioxidant activity of carotenoids. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 24(6):345–351.
- Tian, X., Peng, N., Ma, X., Wu, L., Shi, X., Liu, H., Song, H., Wu, Q., Meng, X., & Li, X. (2022). MicroRNA-430b targets scavenger receptor class B member 1 (scarb1) and inhibits coloration and carotenoid synthesis in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquaculture, 546:737334.
- Toomey, M. B., Marques, C. I., Araújo, P. M., Huang, D., Zhong, S., Liu, Y., Schreiner, G. D., Myers, C. A., Pereira, P., & Afonso, S. (2022). A mechanism for red coloration in vertebrates. Current Biology, 32(19):4201–4214.
- Tran, D. V., Dang, T. T., Cao, T. T., Hua, N. T., & Pham, H. Q. (2022). Natural astaxanthin extracted from shrimp waste for pigment improvement in the orange clownfish, Amphiprion percula. Aquaculture Research, 53(11):4190–4198.
- Vissio, P. G., Darias, M. J., Di Yorio, M. P., Sirkin, D. I. P., & Delgadin, T. H. (2021). Fish skin pigmentation in aquaculture: The influence of rearing conditions and its neuroendocrine regulation. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 301:113662.
- Zhang, Y., Wang, T., Zhang, X., Wei, Y., Chen, P., Zhang, S., Guo, Z., Xiong, Y., Jiang, J., & Huang, X. (2022). Observation of body color formation and pigment cells in grey-black and golden Paramisgumus dabryanus. Aquaculture Research, 53(7):2657–2669.
- Zhao, T., Yan, X., Sun, L., Yang, T., Hu, X., He, Z., Liu, F., & Liu, X. (2019). Research progress on extraction, biological activities, and delivery systems of natural astaxanthin. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 91:354–361.
- Zia-Ul-Haq, M. (2021). Historical and introductory aspects of carotenoids. In M. Zia-Ul-Haq, S. Dewanjee, and M. Riaz (Ed.), Carotenoids: Structure and function in the human body. (pp. 1–42). Cham: Springer Cham.
References
Ahi, E. P., Lecaudey, L. A., Ziegelbecker, A., Steiner, O., Glabonjat, R., Goessler, W., Hois, V., Wagner, C., Lass, A., & Sefc, K. M. (2020). Comparative transcriptomics reveals candidate carotenoid color genes in an East African cichlid fish. BMC Genomics, 21(1):1-15.
Alfionita, K., Budhiyanti, S. A., & Ekantari, N. (2022). Effect of homogenization process on the production of Arthrospira platensis carotenoid nanocapsules encapsulated with arabic gum and whey protein concentrate. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 14(1):12-24.
Bajec, S. S., DjurdjeviÄ, I., Linares Andujar, C., & Kreft, M. E. (2022). Genetic and correlative light and electron microscopy evidence for the unique differentiation pathway of erythrophores in brown trout skin. Scientific Reports, 12(1):1015
Bao, Y., Yu, Y., Xu, H., Guo, C., Li, J., Sun, S., Zhou, Z.-K., Qiu, C.-W., & Wang, X.-H. (2019). Full-colour nano print-hologram synchronous metasurface with arbitrary hue-saturation-brightness control. Light: Science & Applications, 8(95):1–10.
Bolker, J. A., & Hill, C. R. (2000). Pigmentation development in hatchery-reared flatfishes. Journal of Fish Biology, 56(5):1029–1052.
Bonanno, J. A., Breen, N. E., Tlusty, M. F., Andrade, L., & Rhyne, A. L. (2021). The determination of thiocyanate in the blood plasma and holding water of Amphiprion clarkii after exposure to cyanide. PeerJ, 9:e12409.
Cal, L., Suarez-Bregua, P., Moran, P., Cerdá-Reverter, J. M., & Rotllant, J. (2018). Fish pigmentation. A key issue for the sustainable development of fish farming. In M. Yúfera (Ed.), Emerging issues in fish larvae research. (pp. 229–252). Cham: Springer Cham.
Chambel, J., Severiano, V., Baptista, T., Mendes, S., & Pedrosa, R. (2015). Effect of stocking density and different feeds on the growth of Percula Clownfish, Amphiprion percula (Lacepede, 1802). SpringerPlus, 4(1):1–7
D'Alba, L., & Shawkey, M. D. (2019). Melanosomes: Biogenesis, properties, and evolution of an ancient organelle. Physiological Reviews, 99(1):1–19.
Díaz-Jiménez, L., Hernández-Vergara, M. P., Pérez-Rostro, C. I., & Olvera-Novoa, M. Á. (2021). The effect of two carotenoid sources, background colour, and light spectrum on the body pigmentation of the clownfish Amphiprion ocellaris. Aquaculture Research, 52(7):3052–3061.
DjurdjeviÄ, I., Kreft, M. E., & Bajec, S. S. (2015). Comparison of pigment cell ultrastructure and organization in the dermis of marble trout and brown trout, and the first description of erythrophore ultrastructure in salmonids. Journal of Anatomy, 227(5):583–595.
Ebeneezar, S., Prabu, D. L., Chandrasekar, S., Tejpal, C. S., Madhu, K., Sayooj, P., & Vijayagopal, P. (2020). Evaluation of feed oleoresins on the enhancement of skin coloration and growth in the marine ornamental clown fish, Amphiprion ocellaris (Cuvier, 1830). Aquaculture, 529:735728.
Fang, W., Huang, J., Li, S., & Lu, J. (2022). Identification of pigment genes (melanin, carotenoid, and pteridine) associated with skin color variant in red tilapia using transcriptome analysis. Aquaculture, 547:737429.
Gedi, M. A., Magee, K. J., Darwish, R., Eakpetch, P., Young, I., & Gray, D. A. (2019). Impact of the partial replacement of fish meal with a chloroplast rich fraction on the growth and selected nutrient profile of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Food & Function, 10(2):733–745.
Ghosh, S., Kumar, T. A., Vinoth, R., Balasubramanian, T., Dabbagh, A. R., & Keshavarz, M. (2011). Effect of short-term enrichment of wild zooplankton on survival of larval maroon Clownfish (Premnas biaculeatus). Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 7(5):674–677.
Guo, H., Huang, B., Qi, F., & Zhang, S. (2007). Distribution and ultrastructure of pigment cells in the skins of normal and albino adult turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 25(2):199–208.
Grether, G. F., Kolluru, G. R., & Nersissian, K. (2004). Individual colour patches as multicomponent signals. Biological Reviews, 79(3):583-610.
Hamre, L. A., Oldham, T., Oppedal, F., Nilsen, F., & Glover, K. A. (2021). The potential for cleaner fish-driven evolution in the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis: Genetic or environmental control of pigmentation? Ecology and Evolution, 11(12):7865–7878.
Hirata, M., Nakamura, K., Kanemaru, T., Shibata, Y., & Kondo, S. (2003). Pigment cell organization in the hypodermis of zebrafish. Developmental Dynamics, 227(4):497–503.
Kumar, A., Kumar, V., Gull, A., & Nayik, G. A. (2020). Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicon). In G. A. Nayik and A. Gull (Ed.), Antioxidants in vegetables and nuts-properties and health benefits. (pp. 191–207). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
Kumar, S., Kumar, R., Diksha, Kumari, A., & Panwar, A. (2022). Astaxanthin: A super antioxidant from microalgae and its therapeutic potential. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 62(9):1064–1082.
Liang, Y., Meyer, A., & Kratochwil, C. F. (2020). Neural innervation as a potential trigger of morphological color change and sexual dimorphism in cichlid fish. Scientific Reports, 10(12329):1-16.
Ligon, R. A., & McCartney, K. L. (2016). Biochemical regulation of pigment motility in vertebrate chromatophores: A review of physiological color change mechanisms. Current Zoology, 62(3):237–252.
Lim, K. C., Yusoff, F. M., Karim, M., & Natrah, F. M. (2023). Carotenoids modulate stress tolerance and immune responses in aquatic animals. Reviews in Aquaculture, 15(2):872–894.
Liu, C., Liu, H., Zhu, X., Han, D., Jin, J., Yang, Y., & Xie, S. (2022). The effects of dietary Arthrospira platensis on oxidative stress response and pigmentation in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Antioxidants, 11(6):1100.
Luo, M., Lu, G., Yin, H., Wang, L., Atuganile, M., & Dong, Z. (2021). Fish pigmentation and coloration: Molecular mechanisms and aquaculture perspectives. Reviews in Aquaculture, 13(4):2395–2412.
Makri, V., Feidantsis, K., Papadopoulos, D., Lattos, A., Georgoulis, I., Michaelidis, B., & Giantsis, I. A. (2021). Natural-like pigmentation in cultured fish stocks, not only a matter of nutrition. A review of Salmonidae and Sparidae families, with a particular focus on the red porgy Pagrus pagrus. Aquaculture Research, 52(7):2942–2953.
Maoka, T. (2020). Carotenoids as natural functional pigments. Journal of Natural Medicines, 74(1):1–16.
Marudhupandi, T., Dhayanithi, N. B., Jeyaprakashsabari, S., Deepa, S. D., & Kumar, T. T. A. (2022). Effect of lipid supplementation, using oil extracted from Nannochloropsis salina on growth indices and expression of gene associated lipid metabolism in clownfish, Amphiprion ocellaris. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1–10.
Micah, A. D., Wen, B., Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Yusuf, A., Thierry, N. N. B., Tokpanou, O. S., Onimisi, M. M., Adeyemi, S. O., & Gao, J.-Z. (2022). Effect of dietary astaxanthin on growth, body color, biochemical parameters and transcriptome profiling of juvenile blood parrotfish (Vieja melanurus ♀ x Amphilophus citrinellus ♂). Aquaculture Reports, 24:101142.
Meléndez-Martínez, A. J. (2019). An overview of carotenoids, apocarotenoids, and vitamin A in agro-food, nutrition, health, and disease. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 63(15):1801045.
Merhan, O. (2017). The biochemistry and antioxidant properties of carotenoids. In D. J. Cvetkovic and G. S. Nikolic (Ed.), Carotenoids. (pp. 51). Croatia: InTech.
Moore, B., Herrera, M., Gairin, E., Li, C., Miura, S., Jolly, J., Mercader, M., Izumiyama, M., Kawai, E., & Ravasi, T. (2023). The chromosome-scale genome assembly of the yellowtail clownfish Amphiprion Clarkii provides insights into the melanic pigmentation of anemonefish. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 13(3)1-12.
Nakano, T. (2020). Stress in Fish and application of carotenoid for aquafeed as an antistress supplement. Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology, 2999–3019.
Navarro, R. E., Ramos-Balderas, J. L., Guerrero, I., Pelcastre, V., & Maldonado, E. (2008). Pigment dilution mutants from fish models with connection to lysosome-related organelles and vesicular traffic genes. Zebrafish, 5(4):309–318.
Nhan, H. T., Minh, T. X., Liew, H. J., Hien, T. T. T., & Jha, R. (2019). Effects of natural feed carotenoids on skin coloration of false Clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris Cuvier, 1830). Aquaculture Nutrition, 25(3):662–668.
Nüsslein-Volhard, C., & Singh, A. P. (2017). How fish color their skin: A paradigm for development and evolution of adult patterns. BioEssays, 39(3):1600231.
Pataro, G., Carullo, D., & Ferrari, G. (2019). Effect of PEF pre-treatment and extraction temperature on the recovery of carotenoids from tomato wastes. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 75:139–144.
Pietoyo, A., Hidayat, K. W., Nurazizah, S., Arifin, I. F. Z., Prabowo, D. G., Widianto, F. T., & Mustakim, I. (2020). The effect of stocking density on the growth of Ocellaris clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris Cuvier, 1830) with recirculation. Journal of Aquaculture and Fish Health, 9(3):189–193.
Pinela, J., Oliveira, M., & Ferreira, I. (2016). Bioactive compounds of tomatoes as health promoters. In L. R. da Silva and B. M. Silva (Ed.), Natural bioactive compounds from fruits and vegetables as health promotors: Part II. (pp. 48–91). Sharjah, UAE: Bentham Science Publisher.
Purnomo, T. A. B., Kurniawan, Y. S., Kesuma, R. F., & Yuliati, L. (2020). Selection of maceration solvent for natural pigment extraction from red fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam). Indonesian Journal of Natural Pigments, 2(1):8–12.
Pratiwi, R., Mulyono, M., Saputra, A., Farkan, M., Samsuharapan, S. B., & Panjaitan, A. S. (2022). Enhancement of color brightness on clown fish (Amphiprion percula) with addition of tomato powder extract. Asian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Research, 20(6):117–124.
Rebelo, B. A., Farrona, S., Ventura, M. R., & Abranches, R. (2020). Canthaxanthin, a red-hot carotenoid: applications, synthesis, and biosynthetic evolution. Plants, 9(8):1039.
Renko, G., DjurdjeviÄ, I., & Bajec, S. S. (2022). Isolation of chromatophores from brown trout (Salmo trutta) skin. Fishes, 7(2):72.
Riaz, M., Zia-Ul-Haq, M., & Dou, D. (2021). Chemistry of carotenoids. In M. Zia-Ul-Haq, S. Dewanjee, and M. Riaz (Ed.), Carotenoids: structure and function in the human body. (pp. 43–76). Cham: Springer Cham.
Sheng, J., Guan, L., Sheng, B., Geng, S., Wu, D., Hu, B., Li, Z., Le, S., & Hong, Y. (2021). Analysis of pigment cell composition, pigment content, tyrosinase content, and activity of three kinds of loaches Misgurnus anguillicaudatus from Poyang Lake. Journal of Fish Biology, 100(2):366–377.
Sinha, A. (2022). Pigmentation in fishes. In P. K. Pandey and J. Parhi (Ed.), Advances in fisheries biotechnology. (pp. 245–261). Singapore: Springer.
Stahl, W., & Sies, H. (2003). Antioxidant activity of carotenoids. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 24(6):345–351.
Tian, X., Peng, N., Ma, X., Wu, L., Shi, X., Liu, H., Song, H., Wu, Q., Meng, X., & Li, X. (2022). MicroRNA-430b targets scavenger receptor class B member 1 (scarb1) and inhibits coloration and carotenoid synthesis in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquaculture, 546:737334.
Toomey, M. B., Marques, C. I., Araújo, P. M., Huang, D., Zhong, S., Liu, Y., Schreiner, G. D., Myers, C. A., Pereira, P., & Afonso, S. (2022). A mechanism for red coloration in vertebrates. Current Biology, 32(19):4201–4214.
Tran, D. V., Dang, T. T., Cao, T. T., Hua, N. T., & Pham, H. Q. (2022). Natural astaxanthin extracted from shrimp waste for pigment improvement in the orange clownfish, Amphiprion percula. Aquaculture Research, 53(11):4190–4198.
Vissio, P. G., Darias, M. J., Di Yorio, M. P., Sirkin, D. I. P., & Delgadin, T. H. (2021). Fish skin pigmentation in aquaculture: The influence of rearing conditions and its neuroendocrine regulation. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 301:113662.
Zhang, Y., Wang, T., Zhang, X., Wei, Y., Chen, P., Zhang, S., Guo, Z., Xiong, Y., Jiang, J., & Huang, X. (2022). Observation of body color formation and pigment cells in grey-black and golden Paramisgumus dabryanus. Aquaculture Research, 53(7):2657–2669.
Zhao, T., Yan, X., Sun, L., Yang, T., Hu, X., He, Z., Liu, F., & Liu, X. (2019). Research progress on extraction, biological activities, and delivery systems of natural astaxanthin. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 91:354–361.
Zia-Ul-Haq, M. (2021). Historical and introductory aspects of carotenoids. In M. Zia-Ul-Haq, S. Dewanjee, and M. Riaz (Ed.), Carotenoids: Structure and function in the human body. (pp. 1–42). Cham: Springer Cham.