Date Log
Copyright (c) 2024 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
Purification of Phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents with Varied Hydrogen Bond Donor
Corresponding Author(s) : Eirene Tentua
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 17 No. 1 (2025): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
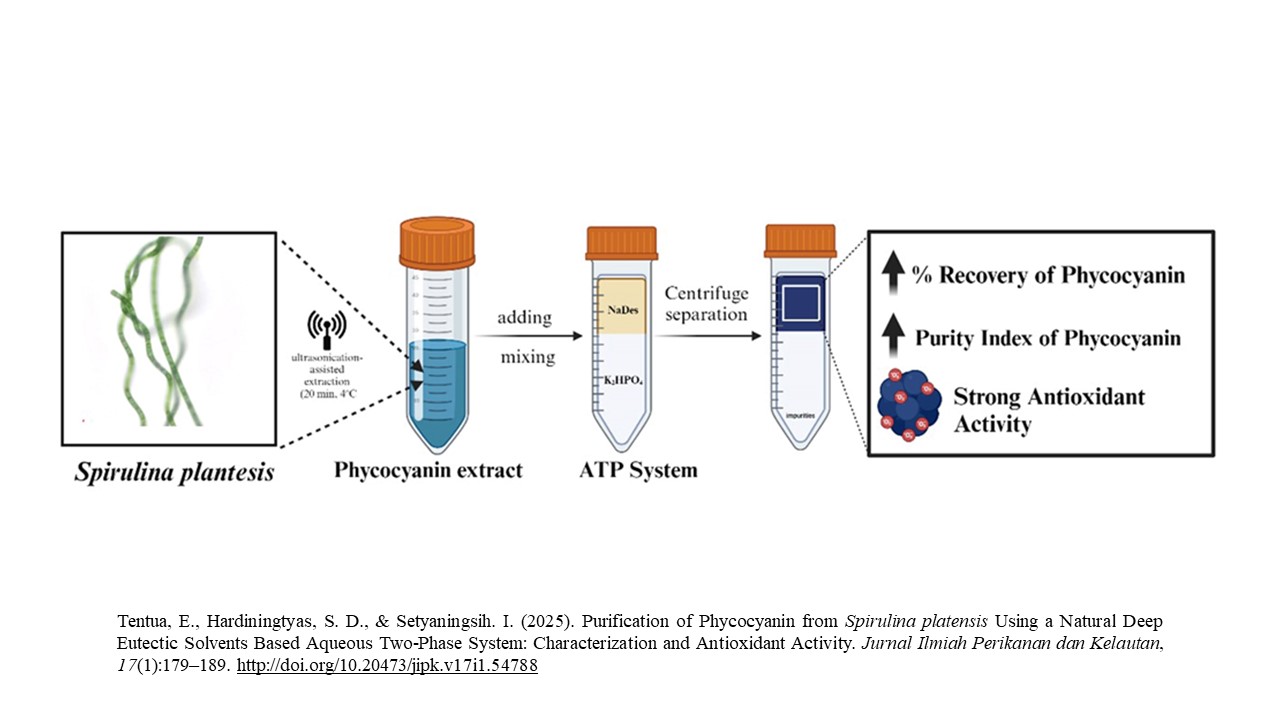
Graphical Abstract
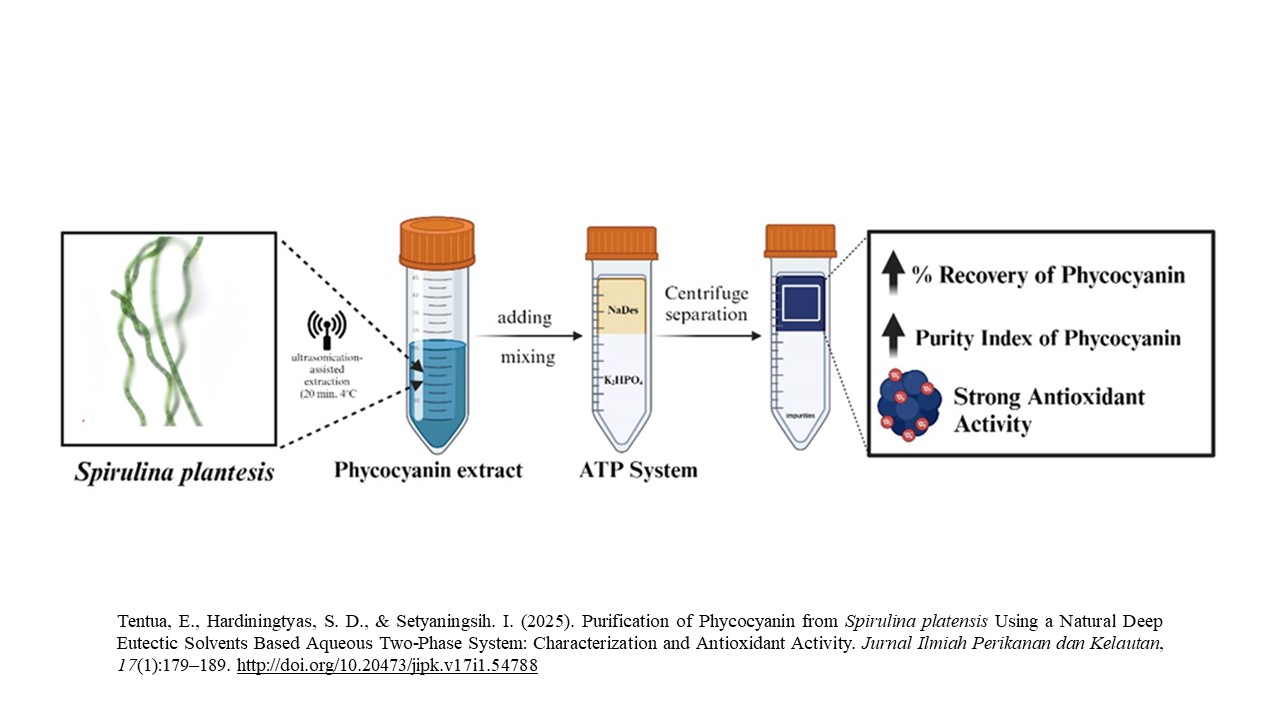
Highlight Research
- NaDES-based purification offers a sustainable and cost-effective method for extracting phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis.
- ChCl:Citric Acid (NaDES) achieved 2.3-fold purity (71.83%), surpassing ammonium sulfate precipitation (70.15%).
- Phycocyanin retained its structural integrity, with enhanced antioxidant activity (IC50 = 40.54 ppm) post-purification.
- The aqueous two-phase system (ATPs) efficiently separated impurities, improving extraction scalability.
- This method supports applications in nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and functional food industries as a green alternative.
Abstract
Phycocyanin, a pharmacologically potent blue pigment extracted from Spirulina platensis, requires optimal purity for effective utilization. Traditional purification methods, although effective, are impeded by time and cost constraints. Addressing this challenge, aqueous two-phase systems (ATPs) incorporating natural deep eutectic solvents (NaDES) emerge as promising alternatives. These systems offer operational simplicity and cost-effectiveness, ensuring efficient purification with high purity and optimal recovery of phycocyanin. This study investigated the impact of various types of hydrogen bond donors (HBD) within choline chloride-based natural deep eutectic solvents (NaDES) on the purification of phycocyanin. Phycocyanin was extracted from Spirulina platensis biomass through ultrasonication and purified using an aqueous two-phase system with various HBD of NaDES, including urea, glycerol, and citric acid. The experimental design adhered to a completely randomized design. The initial purity index and yield of crude extract phycocyanin were 0.54±0.02 and 12.79±0.27%, respectively. The NaDES system with ChCl:citric acid exhibited superior performance, demonstrating a high purity index and recovery (2.3-fold, 71.83±2.36%) compared to ammonium sulfate (1.5-fold, 70.15±4.10%). The obtained phycocyanin was partially pure compared to commercial phycocyanin (purity index: 1.60), as indicated by SDS-PAGE. Moreover, the antioxidant activity of phycocyanin was enhanced post-purification, evident in the IC50 value of 40.54 ppm. In summary, organic acid-based NaDES has proven effective in increasing the purity and achieving a significant recovery percentage of phycocyanin compared to conventional ammonium sulfate methods. The antioxidant activity of phycocyanin was enhanced after purification. These results indicate the promising potential of NaDES-based ATP systems for producing functional protein-based ingredients, exemplified by phycocyanin.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Adjali, A., Clarot, I., Chen, Z., Marchioni, E., & Boudier, A. (2022). Physicochemical degradation of phycocyanin and means to improve its stability: A short review. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 12(3):406–414.
- Afriani, S., Uju, & Setyaningsih, I. (2018). Chemical Composition of Spirulina platensis which Cultivated in Photobioreactors with Different Photoperiodes. Jurnal Pengolahan Hasil Perikanan Indonesia, 21(3):471–479.
- Agrawal, M., Bansal, S., & Chopra, K. (2021). Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo antioxidant potentials of food grade Phycocyanin. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58(2):4382–4390.
- Ahmed, T., Yamanishi, C., Kojima, T., & Takayama, S. (2021). Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Microfluidics for Microscale Assays and Analytical Measurements. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 14(3):231–255.
- Almarza, J., Rincon, L., Bahsas, A., & Brito, F. (2009). Molecular Mechanism for the Denaturation of Proteins by Urea. Biochemistry, 48(32):7608–7613.
- Bennett, A., & Bogobad, L. (1973). Complementary chromatic adaptation in a filamentous blue-green alga. Journal of Cell Biology, 58(2):419–435.
- Bowen, H., Durrani, R., Delavault, A., Durand, E., Chenyu, J., Yiyang, L., Lili, S., Jian, S., Weiwei, H., & Fei, G. (2022). Application of deep eutectic solvents in protein extraction and purification. Frontiers in Chemistry, 10:1–10.
- Cannavacciuolo, C., Pagliari, S., Frigerio, J., Giustra, C. M., Labra, M., & Campone, L. (2023). Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs) Combined with Sustainable Extraction Techniques: A Review of the Green Chemistry Approach in Food Analysis. Foods, 12(1):1-9.
- Chen, Q., Chaihu, L., Yao, X., Cao, X., Bi, W., Lin, J., & Chen, D. D. Y. (2021). Molecular Property-Tailored Soy Protein Extraction Process Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 9(30):10083–10092.
- da Silva Figueira, F., Moraes, C. C., & Kalil, S. J. (2018). C-phycocyanin purification: Multiple processes for different applications. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 35(3):1117–1128.
- Duangsee, R., Phoopat, N., & Ningsanond, S. (2009). Phycocyanin extraction from Spirulina platensis and extract stability under various pH and temperature. Asian Journal of Food and Agro-Industry, 2(4):819–826.
- Farias, F. O., Pereira, J. F., Coutinho, J. A., Igarashi-Mafra, L., & Mafra, M. R. (2020). Fluid Phase Equilibria Understanding the role of the hydrogen bond donor of the deep eutectic solvents in the formation of the aqueous biphasic systems. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 503.
- Freire, M. G., Pereira, J. F. B., Francisco, M., Rodriguez, H., Rebelo, L. P. N., Rogers, R. D., & Coutinho, J. A. P. (2012). Insight into the Interactions That Control the Phase Behaviour of New Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Polyethylene Glycol Polymers and Ionic Liquids. Chem. Eur. J, 35487, 1831–1839.
- Grover, P., Bhatnagar, A., Kumari, N., Bhatt, A. N., & Nishad, D. K. (2021). Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences C-Phycocyanin-a novel protein from Spirulina platensis - In vivo toxicity , antioxidant and immunomodulatory studies. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(3):1853–1859.
- Gustiningtyas, A., Setyaningsih, I., Hardiningtyas, S. D., & Susila, A. A. R. (2020). Improvement stability of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis encapsulated by water soluble chitosan nanoparticles. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 414(1):1-9.
- Hardiningtyas, S. D., Putri, F. A., & Setyaningsih, I. (2022). Antibacterial activity of ethanolic Spirulina platensis extract-water soluble chitosan nanoparticles. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1033(1):1-11.
- Iqbal, M., Tao, Y., Xie, S., Zhu, Y., Chen, D., Wang, X., Huang, L., Peng, D., Sattar, A., Shabbir, M. A. B., Hussain, H. I., Ahmed, S., & Yuan, Z. (2016). Aqueous two-phase system (ATPS): an overview and advances in its applications. Biological Procedures Online, 18(1):1–18.
- Jurić, T., Uka, D., Holló, B. B., Jović, B., Kordić, B., & Popović, B. M. (2021). Comprehensive physicochemical evaluation of choline chloride-based natural deep eutectic solvents. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 343(3):1-11.
- Kumar, D., Dhar, D. W., Walia, S. P., Kumar, N., & Suresh. (2014). Extraction and purification of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina. Ind J Plant Physiol, 19(6):184–188.
- Liao, X., Zhang, B., & Wang, X. (2011). Purification of C-Phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis by Single-Step Ion-Exchange Chromatography. Chromatographia, 73(3):291–296.
- Mjalli, F. S., & Naser, J. (2015). Viscosity model for choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. Chemical Engineering, 10(2):273–281.
- Mr, M. B. S., Mr, V. S. K., Chaudhary, M., & Singh, P. (2021). A mini review on synthesis, properties and applications of deep eutectic solvents. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 98(11):1-10.
- Nege, A. S., Masithah, E. D., & Khotib, J. (2020). Trends in the uses of spirulina microalga: A mini-review. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan Dan Kelautan, 12(1):149–166.
- Nie, L., Zheng, Z., Lu, M., Yao, S., & Guo, D. (2022). Phase Behavior of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20):1-12.
- Patil, G., & Raghavarao, K. S. M. S. (2007). Aqueous two phase extraction for purification of C-phycocyanin. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 34(2):156–164.
- Pez Jaeschke, D., Rocha Teixeira, I., Damasceno Ferreira Marczak, L., & Domeneghini Mercali, G. (2021). Phycocyanin from Spirulina: A review of extraction methods and stability. Food Research International, 143(11)1-12.
- Prabakaran, G., Sampathkumar, P., Kavisri, M., & Moovendhan, M. (2020). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Extraction and characterization of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis and evaluation of its anticancer , antidiabetic and antiin fl ammatory effect. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 153(3):256–263.
- Renugadevi, K., Nachiyar, C. V., Sowmiya, P., & Sunkar, S. (2018). Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology Antioxidant activity of phycocyanin pigment extracted from marine fi lamentous cyanobacteria Geitlerinema sp TRV57. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 16(2):237–242.
- Sharma, O. P., & Bhat, T. K. (2009). DPPH antioxidant assay revisited. Food Chemistry, 113(4):1202–1205.
- Stefanovic, R., Ludwig, M., Webber, G. B., Atkin, R., & Page, A. J. (2017). Nanostructure, hydrogen bonding and rheology in choline chloride deep eutectic solvents as a function of the hydrogen bond donor. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 19(4):3297–3306.
- Suzery, M., Hadiyanto, Majid, D., Setyawan, D., & Sutanto, H. (2017). Improvement of Stability and Antioxidant Activities by Using Phycocyanin - Chitosan Encapsulation Technique. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 55(2):1-9.
- Wada, N., Sakamoto, T., & Matsugo, S. (2013). Multiple Roles of Photosynthetic and Sunscreen Pigments in Cyanobacteria Focusing on the Oxidative Stress. Metabolites, 3(2):463–483.
- Wang, Q., Wei, N., Wang, Y., Hou, Y., Ren, X., & Wei, Q. (2020). Single-step purification of C-phycocyanin from Arthrospira platensis using aqueous two-phase system based on natural deep eutectic solvents. Journal of Applied Phycology, 32(6):3873–3883.
- Xu, K., Wang, Y., Huang, Y., Li, N., & Wen, Q. (2015). A green deep eutectic solvent-based aqueous two-phase system for protein extracting. Analytica Chimica Acta, 864(2):9–20.
- Xu, Y., Wang, Q., & Hou, Y. (2020). Efficient purification of R-phycoerythrin from marine algae (Porphyra yezoensis) based on a deep eutectic solvents aqueous two-phase system. Marine Drugs, 18(12):1–14.
- Yao, T., Huang, X., Zang, H., Song, H., & Yao, S. (2017). Measurement and correlation of phase equilibria in aqueous two-phase systems containing functionalized magnetic ionic liquids and K2HPO4/K2CO3/Na2CO3 at 298.15 K. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 231(3):411–418.
References
Adjali, A., Clarot, I., Chen, Z., Marchioni, E., & Boudier, A. (2022). Physicochemical degradation of phycocyanin and means to improve its stability: A short review. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 12(3):406–414.
Afriani, S., Uju, & Setyaningsih, I. (2018). Chemical Composition of Spirulina platensis which Cultivated in Photobioreactors with Different Photoperiodes. Jurnal Pengolahan Hasil Perikanan Indonesia, 21(3):471–479.
Agrawal, M., Bansal, S., & Chopra, K. (2021). Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo antioxidant potentials of food grade Phycocyanin. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58(2):4382–4390.
Ahmed, T., Yamanishi, C., Kojima, T., & Takayama, S. (2021). Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Microfluidics for Microscale Assays and Analytical Measurements. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 14(3):231–255.
Almarza, J., Rincon, L., Bahsas, A., & Brito, F. (2009). Molecular Mechanism for the Denaturation of Proteins by Urea. Biochemistry, 48(32):7608–7613.
Bennett, A., & Bogobad, L. (1973). Complementary chromatic adaptation in a filamentous blue-green alga. Journal of Cell Biology, 58(2):419–435.
Bowen, H., Durrani, R., Delavault, A., Durand, E., Chenyu, J., Yiyang, L., Lili, S., Jian, S., Weiwei, H., & Fei, G. (2022). Application of deep eutectic solvents in protein extraction and purification. Frontiers in Chemistry, 10:1–10.
Cannavacciuolo, C., Pagliari, S., Frigerio, J., Giustra, C. M., Labra, M., & Campone, L. (2023). Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs) Combined with Sustainable Extraction Techniques: A Review of the Green Chemistry Approach in Food Analysis. Foods, 12(1):1-9.
Chen, Q., Chaihu, L., Yao, X., Cao, X., Bi, W., Lin, J., & Chen, D. D. Y. (2021). Molecular Property-Tailored Soy Protein Extraction Process Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 9(30):10083–10092.
da Silva Figueira, F., Moraes, C. C., & Kalil, S. J. (2018). C-phycocyanin purification: Multiple processes for different applications. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 35(3):1117–1128.
Duangsee, R., Phoopat, N., & Ningsanond, S. (2009). Phycocyanin extraction from Spirulina platensis and extract stability under various pH and temperature. Asian Journal of Food and Agro-Industry, 2(4):819–826.
Farias, F. O., Pereira, J. F., Coutinho, J. A., Igarashi-Mafra, L., & Mafra, M. R. (2020). Fluid Phase Equilibria Understanding the role of the hydrogen bond donor of the deep eutectic solvents in the formation of the aqueous biphasic systems. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 503.
Freire, M. G., Pereira, J. F. B., Francisco, M., Rodriguez, H., Rebelo, L. P. N., Rogers, R. D., & Coutinho, J. A. P. (2012). Insight into the Interactions That Control the Phase Behaviour of New Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Polyethylene Glycol Polymers and Ionic Liquids. Chem. Eur. J, 35487, 1831–1839.
Grover, P., Bhatnagar, A., Kumari, N., Bhatt, A. N., & Nishad, D. K. (2021). Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences C-Phycocyanin-a novel protein from Spirulina platensis - In vivo toxicity , antioxidant and immunomodulatory studies. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(3):1853–1859.
Gustiningtyas, A., Setyaningsih, I., Hardiningtyas, S. D., & Susila, A. A. R. (2020). Improvement stability of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis encapsulated by water soluble chitosan nanoparticles. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 414(1):1-9.
Hardiningtyas, S. D., Putri, F. A., & Setyaningsih, I. (2022). Antibacterial activity of ethanolic Spirulina platensis extract-water soluble chitosan nanoparticles. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1033(1):1-11.
Iqbal, M., Tao, Y., Xie, S., Zhu, Y., Chen, D., Wang, X., Huang, L., Peng, D., Sattar, A., Shabbir, M. A. B., Hussain, H. I., Ahmed, S., & Yuan, Z. (2016). Aqueous two-phase system (ATPS): an overview and advances in its applications. Biological Procedures Online, 18(1):1–18.
Jurić, T., Uka, D., Holló, B. B., Jović, B., Kordić, B., & Popović, B. M. (2021). Comprehensive physicochemical evaluation of choline chloride-based natural deep eutectic solvents. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 343(3):1-11.
Kumar, D., Dhar, D. W., Walia, S. P., Kumar, N., & Suresh. (2014). Extraction and purification of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina. Ind J Plant Physiol, 19(6):184–188.
Liao, X., Zhang, B., & Wang, X. (2011). Purification of C-Phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis by Single-Step Ion-Exchange Chromatography. Chromatographia, 73(3):291–296.
Mjalli, F. S., & Naser, J. (2015). Viscosity model for choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. Chemical Engineering, 10(2):273–281.
Mr, M. B. S., Mr, V. S. K., Chaudhary, M., & Singh, P. (2021). A mini review on synthesis, properties and applications of deep eutectic solvents. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 98(11):1-10.
Nege, A. S., Masithah, E. D., & Khotib, J. (2020). Trends in the uses of spirulina microalga: A mini-review. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan Dan Kelautan, 12(1):149–166.
Nie, L., Zheng, Z., Lu, M., Yao, S., & Guo, D. (2022). Phase Behavior of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20):1-12.
Patil, G., & Raghavarao, K. S. M. S. (2007). Aqueous two phase extraction for purification of C-phycocyanin. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 34(2):156–164.
Pez Jaeschke, D., Rocha Teixeira, I., Damasceno Ferreira Marczak, L., & Domeneghini Mercali, G. (2021). Phycocyanin from Spirulina: A review of extraction methods and stability. Food Research International, 143(11)1-12.
Prabakaran, G., Sampathkumar, P., Kavisri, M., & Moovendhan, M. (2020). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Extraction and characterization of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis and evaluation of its anticancer , antidiabetic and antiin fl ammatory effect. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 153(3):256–263.
Renugadevi, K., Nachiyar, C. V., Sowmiya, P., & Sunkar, S. (2018). Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology Antioxidant activity of phycocyanin pigment extracted from marine fi lamentous cyanobacteria Geitlerinema sp TRV57. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 16(2):237–242.
Sharma, O. P., & Bhat, T. K. (2009). DPPH antioxidant assay revisited. Food Chemistry, 113(4):1202–1205.
Stefanovic, R., Ludwig, M., Webber, G. B., Atkin, R., & Page, A. J. (2017). Nanostructure, hydrogen bonding and rheology in choline chloride deep eutectic solvents as a function of the hydrogen bond donor. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 19(4):3297–3306.
Suzery, M., Hadiyanto, Majid, D., Setyawan, D., & Sutanto, H. (2017). Improvement of Stability and Antioxidant Activities by Using Phycocyanin - Chitosan Encapsulation Technique. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 55(2):1-9.
Wada, N., Sakamoto, T., & Matsugo, S. (2013). Multiple Roles of Photosynthetic and Sunscreen Pigments in Cyanobacteria Focusing on the Oxidative Stress. Metabolites, 3(2):463–483.
Wang, Q., Wei, N., Wang, Y., Hou, Y., Ren, X., & Wei, Q. (2020). Single-step purification of C-phycocyanin from Arthrospira platensis using aqueous two-phase system based on natural deep eutectic solvents. Journal of Applied Phycology, 32(6):3873–3883.
Xu, K., Wang, Y., Huang, Y., Li, N., & Wen, Q. (2015). A green deep eutectic solvent-based aqueous two-phase system for protein extracting. Analytica Chimica Acta, 864(2):9–20.
Xu, Y., Wang, Q., & Hou, Y. (2020). Efficient purification of R-phycoerythrin from marine algae (Porphyra yezoensis) based on a deep eutectic solvents aqueous two-phase system. Marine Drugs, 18(12):1–14.
Yao, T., Huang, X., Zang, H., Song, H., & Yao, S. (2017). Measurement and correlation of phase equilibria in aqueous two-phase systems containing functionalized magnetic ionic liquids and K2HPO4/K2CO3/Na2CO3 at 298.15 K. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 231(3):411–418.