Date Log
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
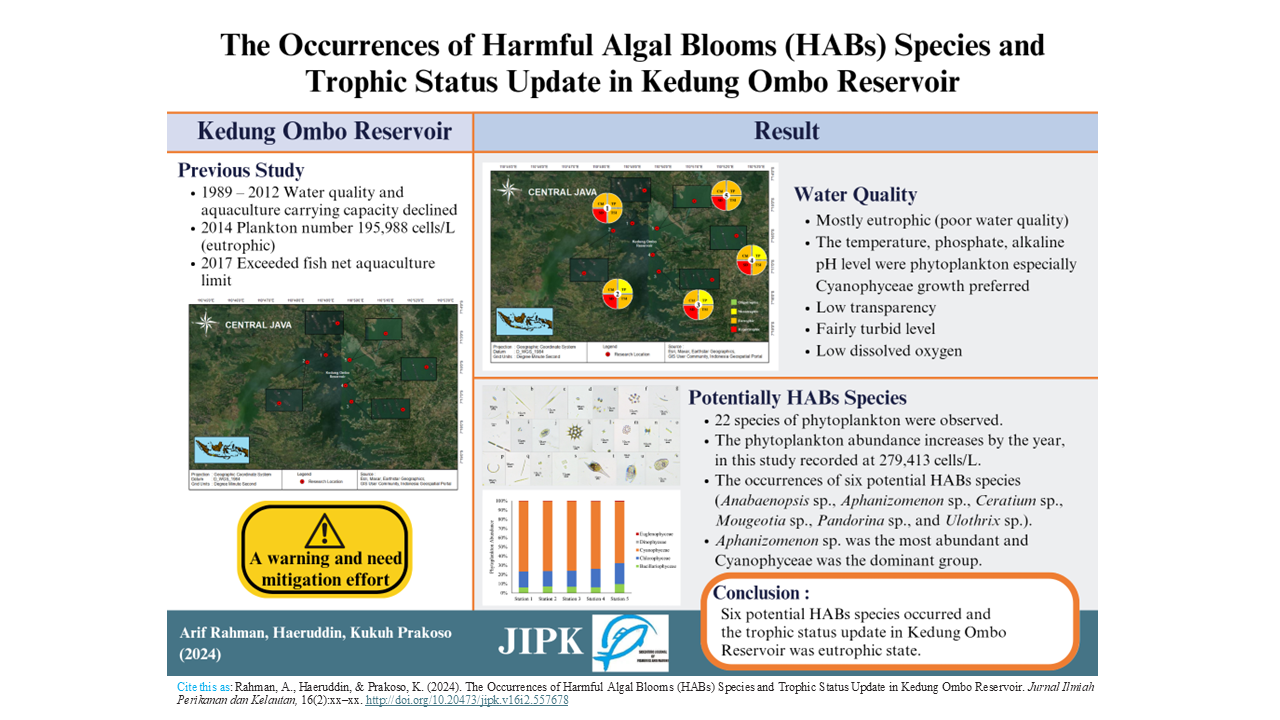
The Occurrences of Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) Species and Trophic Status Update in Kedung Ombo Reservoir
Corresponding Author(s) : Arif Rahman
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 17 No. 1 (2025): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
Graphical Abstract

Highlight Research
- Six harmful algal species were identified, with Aphanizomenon sp. being the most dominant, primarily from Cyanophyceae (blue-green algae).
- Kedung Ombo Reservoir is eutrophic, with low transparency, low dissolved oxygen (DO), and high phosphate levels (0.10–0.88 mg/L) contributing to HABs.
- Anthropogenic activities, including aquaculture, agriculture, and sewage, accelerate nutrient enrichment and phytoplankton overgrowth.
- Trophic State Index (TSI) confirmed eutrophic conditions, with HABs abundance linked to high phosphate concentrations.
- Urgent mitigation efforts like nutrient control, biomanipulation, and regular monitoring are needed to prevent further HABs outbreaks.
Abstract
Anthropogenic inputs affect the quality of freshwater ecosystems which causes ecological and health problems to aquatic ecosystems. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) associated with cyanotoxins often occur in nutrient-rich or eutrophic freshwater ecosystems. Kedung Ombo Reservoir in Indonesia has been previously classified as eutrophic to hypertrophic. Therefore, this study aimed to identify the occurrences of potential HABs species, measure the bio-physico-chemical water quality parameters, and update the trophic status of Kedung Ombo Reservoir. Sampling was done thrice during the dry season in 2022 from 5 stations. Twenty-two species of phytoplankton were observed in Kedung Ombo Reservoir. Anabaenopsis sp., Aphanizomenon sp., Ceratium sp., Mougeotia sp., Pandorina sp., and Ulothrix sp. were identified as potentially harmful species. Among those, the potentially HABs species, Aphanizomenon sp. was the most abundant (179,344 cells/L) and Cyanophyceae (205,539 cells/L) was the dominant group of phytoplankton. Kedung Ombo Reservoir had a water temperature of 29.49±0.41°C, phosphate of 0.27±0.25 mg/L, and alkaline pH of 7.90±0.39. Kedung Ombo Reservoir also had low transparency coupled with low dissolved oxygen concentration. The occurrences of HABs species were correlated with transparency and dissolved inorganic nutrients, especially phosphate concentrations. Kedung Ombo Reservoir showed eutrophic conditions based on Secchi depth, chlorophyll-a, total phosphorus, and TSI. Based on research findings, control and mitigation efforts are needed to overcome the eutrophication problems which disrupt the balance of the aquatic ecosystem in the Kedung Ombo Reservoir.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Álvarez, X., Valero, E., Santos, R. M. B., Varandas, S. G. P., Sanches Fernandes, L. F., & Pacheco, F. A. L. (2017). Anthropogenic nutrients and eutrophication in multiple land use watersheds: Best management practices and policies for the protection of water resources. Land Use Policy, 69(2017):1-11.
- Anabtawi, H. M., Lee, W. H., Al-Anazi, A., Mohamed, M. M., & Aly Hassan, A. (2024). Advancements in biological strategies for controlling harmful algal blooms (HABs). Water, 16(2):1-26.
- APHA (American Public Health Association). (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. E. W. Rice & L. Bridgewater (Eds.), 21st ed. the American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and the Water Environment Federation (WEF).
- Assmy, P., & Smetacek, V. (2009). Algal blooms. in environmental microbiology and ecology. New York, USA: Elsevier.
- Azis, A., Yusuf, H., Faisal, Z., & Suradi, M. (2015). Water turbidity impact on discharge decrease of groundwater recharge in recharge reservoir. Procedia Engineering, 125(27):199-206.
- Baleta, F. N., & Bolaños, J. M. (2016). Phytoplankton identification and water quality monitoring along the fish-cage belt at Magat dam reservoir, Philippines. International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies, 4(3):254-260.
- Bartozek, E. C. R., Bueno, N. C., Feiden, A., & Rodrigues, L. C. (2016). Response of phytoplankton to an experimental fish culture in net cages in a subtropical reservoir. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 76(4):824-833.
- Beaulieu, M., Pick, F., Palmer, M., Watson, S., Winter, J., Zurawell, R., & Gregory-Eaves, I. (2014). Comparing predictive cyanobacterial models from temperate regions. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 71(12):1830-1839.
- Becker, V., Caputo, L., Ordonez, J., Marce, R., Armengol, J., Crossetti, L. O., & Huszar, V. L. M. (2010). Driving factors of the phytoplankton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean reservoir. Water Research, 44(11):3345-3354.
- Bellinger, E. G., & Sigee, D. C. (2010). Freshwater algae: Identification and use as bioindicators. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- Boivin-Rioux, A., Starr, M., Chassé, J., Scarratt, M., Perrie, W., Long, Z., & Lavoie, D. (2022). Harmful algae and climate change on the Canadian East Coast: Exploring occurrence predictions of Dinophysis acuminata, D. norvegica, and Pseudo-nitzschia seriata. Harmful Algae, 112(2):1-17.
- Briddon, C. L., Szekeres, E., Hegedüs, A., Nicoară, M., Chiriac, C., Stockenreiter, M., & Drugă, B. (2022). The combined impact of low temperatures and shifting phosphorus availability on the competitive ability of cyanobacteria. Scientific Reports, 12(1):1-13.
- Burkholder, J. M., Glasgow Jr, H. B., & Hobbs, C. W. (1995). Fish kills linked to a toxic ambush-predator dinoflagellate: Distribution and environmental conditions. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 124:43-61.
- Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(2):361-369.
- Chakraborty, S., Karmaker, D., Rahman, M. A., Bali, S. C., Das, S. K., & Hossen, R. (2021). Impacts of pH and salinity on community composition, growth and cell morphology of three freshwater phytoplankton. Plant Science Today, 8(3):655-661.
- Du, H. T., Hieu, N. M., & Kunzmann, A. (2022). Negative effects of fish cages on coral reefs through nutrient enrichment and eutrophication in Nha Trang Bay, Viet Nam. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 55(2022):1-7.
- Fang, F., Gao, Y., Gan, L., He, X., & Yang, L. (2018). Effects of different initial pH and irradiance levels on cyanobacterial colonies from Lake Taihu, China. Journal of Applied Phycology, 30(3):1777-1793.
- Gao, H., Zhao, Z., Zhang, L., & Ju, F. (2022). Cyanopeptides restriction and degradation co-mediate microbiota assembly during a freshwater cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom (CyanoHAB). Water Research, 220(118674).
- Glibert, P. M. (2020). Harmful algae at the complex nexus of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae, 91(1):1-15.
- Håkanson, L., & Blenckner, T. (2014). A review on operational bioindicators for sustainable coastal management-criteria, motives and relationships. Ocean & Coastal Management, 51(1):43-72.
- Hidayah, T., Ridho, M. R., & Suheryanto. (2014). Phytoplankton community structure in Kedungombo Reservoir. Maspari Journal, 6(2):104-112.
- Igwaran, A., Kayode, A. J., Moloantoa, K. M., Khetsha, Z. P., & Unuofin, J. O. (2024). Cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Causes, impacts, and risk management. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 235(71):1-26.
- Karydis, M. (2009). Eutrophication assessment of coastal waters based on indicators: A literature review. Global NEST Journal, 11(4):373-390.
- Kimambo, O. N., Chikoore, H., Gumbo, J. R., & Msagati, T. A. M. (2019). Retrospective analysis of chlorophyll-a and its correlation with climate and hydrological variations in Mindu Dam, Morogoro, Tanzania. Heliyon, 5(11):1-14.
- Krismono, & Sugianti, Y. (2007). Plankton distribution in Kedungombo Reservoir. Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 19(1):108-115.
- Legono, D., Wahono, E. P., Kusumastuti, D. I., & Harset, D. (2022). Dynamics of reservoir environment carrying capacity (case of Kedungombo Reservoir, Central Java, Indonesia). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1105(1):1-7.
- Liu, Z., Wang, X., Jia, S., & Mao, B. (2023). Eutrophication causes analysis under the influencing of anthropogenic activities in China’s largest freshwater lake (Poyang Lake): Evidence from hydrogeochemistry and reverse simulation methods. Journal of Hydrology, 625(14):1-13.
- Malone, T. C., & Newton, A. (2020). The globalization of cultural eutrophication in the coastal ocean: Causes and consequences. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7(670):1-30.
- Metcalf, J. S., Tischbein, M., Cox, P. A., & Stommel, E. W. (2021). Cyanotoxins and the nervous system. Toxins, 13(9):1-19.
- Minakova, E. A., Shlichkov, A. P., & Arinina, A. V. (2019). Approaches to management of anthropogenic eutrophication caused by loading from mineral fertilizers. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 272(3):1-6.
- Moraes, M. A. B., Rodrigues, R. A. M., Schlüter, L., Podduturi, R., Jørgensen, N. O. G., & Calijuri, M. C. (2021). Influence of environmental factors on occurrence of cyanobacteria and abundance of saxitoxin-producing cyanobacteria in a subtropical drinking water reservoir in Brazil. Water, 13(12):1-19.
- Na, L., Shaoyang, C., Zhenyan, C., Xing, W., Yun, X., Li, X., Yanwei, G., Tingting, W., Xuefeng, Z., & Siqi, L. (2022). Long-term prediction of sea surface chlorophyll-a concentration based on the combination of spatio-temporal features. Water Research, 211(4):1-15.
- Oberholster, P. J., & Botha, A.-M. (2011). Dynamics of phytoplankton and phytobenthos in Lake Loskop (South Africa) and downstream irrigation canals. Fundamental and Applied Limnology, 179(3):169-178.
- Park, K.-W., Chung, M.-H., Yoo, M.-H., O, K.-S., Kim, K.-Y., Park, T.-G., & Youn, S.-H. (2023). Impact of phytoplankton community structure changes in the South Sea of Korea on Marine ecosystems due to climate change. Water, 15(23):1-16.
- Prasad, A. G. D., & Siddaraju. (2012). Carlson’s trophic state index for the assessment of trophic status of two lakes in Mandya District. Pelagia Research Library Advances, 3(5):2992-2996.
- Purwana, Y. M., Dananjaya, R. H., & Hartono, W. A. (2019). Pre-evaluation of Kedung Ombo Dam safety based on probabilistic seismic hazard analysis. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2114(1):1-12.
- Rahayu, N. W. S. T., Hendrawan, I. G., & Suteja, Y. (2018). Spatial and temporal distribution of nitrate and phosphate during the West Monsoon on the surface of the waters of Benoa Bay, Bali. Journal of Marine and Aquatic Sciences, 4(1):1-13.
- Ridho, M. R., Patriono, E., & Mulyani, Y. S. (2020). Correlation among phytoplankton abundance, chlorophyll-a, and water quality of Sungsang Coastal Waters, South Sumatera. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 12(1):1-8.
- Sahoo, D., & Anandhi, A. (2023). Conceptualizing turbidity for aquatic ecosystems in the context of sustainable development goals. Environmental Science: Advances, 2(9):1220-1234.
- Sidabutar, T., Srimariana, E. S., Cappenberg, H., & Wouthuyzen, S. (2024). Comprehensive analysis of harmful algal blooms in indonesia: from occurrence to impact. BIO Web Conferences, 87(10):1-12.
- Simanjuntak, I. C. B. H., & Muhammad, F. (2018). Carrying capacity of Kedungombo reservoir for net cage culture. E3S Web of Conferences, 73(03018):1-5.
- Smayda, T. J. (1997). Harmful algal blooms: Their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnology and Oceanography, 42(5):1137-1153.
- Smyth, A., Laughinghouse, H. D., Havens, K., & Frazer, T. (2022). Rethinking the role of nitrogen and phosphorus in the eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems. EDIS, 2022(1):1-15.
- Sulastri. (2018). Phytoplankton of lakes on the Island of Java: Diversity and their role as aquatic bioindicators. LIPI Press.
- Sulastri, Henny, C., Nomosatryo, S., Susanti, E., & Sulawesty, F. (2023). Monitoring planktonic cyanobacteria in Lake Maninjau, West Sumatra, Indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1260(2):1-13.
- Suteja, Y., Dirgayusa, I. G. N. P., Afdal, Cordova, M. R., Rachman, A., Rintaka, W. E., Takarina, N. D., Putri, W. A. E., Isnaini, & Purwiyanto, A. I. S. (2021). Identification of potentially harmful microalgal species and eutrophication status update in Benoa Bay, Bali, Indonesia. Ocean and Coastal Management, 210(12):1-15.
- Syakti, A. D., Idris, F., Koenawan, C. J., Asyhar, R., & Apriadi, T. (2019). Biological pollution potential in the water of Bintan-Riau Islands Province, Indonesia: First appearance of harmful algal bloom species. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 45:117-122.
- Tabrett, S., Ramsay, I., Dias, F. S., Burford, M., Claus, S., & Sheidler, C. (2024). Review of nutrient release from aquaculture activities. Final Report. State of Queensland, Australia.
- Thawabteh, A. M., Naseef, H. A., Karaman, D., Bufo, S. A., Scrano, L., & Karaman, R. (2023). Understanding the risks of diffusion of cyanobacteria toxins in rivers, lakes, and potable water. Toxins, 15(9):1-38.
- Turner, M. A., Howell, E. T., Summerby, M., Hesslein, R. H., Findlay, D. L., & Jackson, M. B. (1991). Changes in epilithon and epiphyton associated with experimental acidification of a lake to pH 5. Limnology and Oceanography, 36(7):1390-1405.
- Turner, A. D., Turner, F. R. I., White, M., Hartnell, D., Crompton, C. G., Bates, N., Egginton, J., Branscombe, L., Lewis, A. M., & Maskrey, B. H. (2022). Confirmation using triple quadrupole and high-resolution mass spectrometry of a fatal canine neurotoxicosis following exposure to anatoxins at an inland reservoir. Toxins, 14(11):1-19.
- van Vuuren, S. J., Taylor, J., van Ginkel, C., & Gerber, A. (2006). Easy identification of the most common freshwater algae: A guide for the identification of microscopic algae in South African freshwaters. North-West University and Department of Water Affairs and Forestry.
- Vidyarathna, N. K., Papke, E., Coyne, K. J., Cohen, J. H., & Warner, M. E. (2020). Functional trait thermal acclimation differs across three species of mid-Atlantic harmful algae. Harmful Algae, 94(4):1-11.
- Vollenweider, R. (1968). Scientific fundamentals of the eutrophication of lakes and flowing waters, with particular reference to nitrogen and phosphorus as factors in eutrophication. Paris, France: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
- Vundo, A., Matsushita, B., Jiang, D., Gondwe, M., Hamzah, R., Setiawan, F., & Fukushima, T. (2019). An overall evaluation of water transparency in Lake Malawi from MERIS Data. Remote Sensing, 11(279):1-18.
- Wang, J., Sharaf, F., & Kanwal, A. (2023). Nitrate pollution and its solutions with special emphasis on electrochemical reduction removal. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(4):9290-9310.
- Watson, S. B., & Molot, L. (2013). Harmful algal blooms. In J.-F. Férard & C. Blaise (Eds.), Encyclopedia of aquatic ecotoxicology. (pp. 575-596). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
- Watson, S. B., Whitton, B. A., Higgins, S. N., Paerl, H. W., Brooks, B. W., & Wehr, J. D. (2015). Harmful algal blooms. In J. Wehr, R. Sheath & J. P. Kociolek (Eds.), Freshwater Algae of North America. (pp. 873-920). San Diego: Academic Press.
- Weigelhofer, G., Hein, T., & Bondar-Kunze, E. (2018). Phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in riverine systems: Human impacts and management options. In S. Schmutz & J. Sendzimir (Eds.), Riverine ecosystem management: Science for governing towards a sustainable future. (pp. 187-202). Springer International Publishing.
- Xu, S., Lyu, P., Zheng, X., Yang, H., Xia, B., Li, H., Zhang, H., & Ma, S. (2022). Monitoring and control methods of harmful algal blooms in Chinese freshwater system: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 29(38):56908-56927.
- Zhou, Y., Wang, L., Zhou, Y., & Mao, X. (2020). Eutrophication control strategies for highly anthropogenic influenced coastal waters. Science of the Total Environment, 705(8):1–11.
References
Álvarez, X., Valero, E., Santos, R. M. B., Varandas, S. G. P., Sanches Fernandes, L. F., & Pacheco, F. A. L. (2017). Anthropogenic nutrients and eutrophication in multiple land use watersheds: Best management practices and policies for the protection of water resources. Land Use Policy, 69(2017):1-11.
Anabtawi, H. M., Lee, W. H., Al-Anazi, A., Mohamed, M. M., & Aly Hassan, A. (2024). Advancements in biological strategies for controlling harmful algal blooms (HABs). Water, 16(2):1-26.
APHA (American Public Health Association). (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. E. W. Rice & L. Bridgewater (Eds.), 21st ed. the American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and the Water Environment Federation (WEF).
Assmy, P., & Smetacek, V. (2009). Algal blooms. in environmental microbiology and ecology. New York, USA: Elsevier.
Azis, A., Yusuf, H., Faisal, Z., & Suradi, M. (2015). Water turbidity impact on discharge decrease of groundwater recharge in recharge reservoir. Procedia Engineering, 125(27):199-206.
Baleta, F. N., & Bolaños, J. M. (2016). Phytoplankton identification and water quality monitoring along the fish-cage belt at Magat dam reservoir, Philippines. International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies, 4(3):254-260.
Bartozek, E. C. R., Bueno, N. C., Feiden, A., & Rodrigues, L. C. (2016). Response of phytoplankton to an experimental fish culture in net cages in a subtropical reservoir. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 76(4):824-833.
Beaulieu, M., Pick, F., Palmer, M., Watson, S., Winter, J., Zurawell, R., & Gregory-Eaves, I. (2014). Comparing predictive cyanobacterial models from temperate regions. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 71(12):1830-1839.
Becker, V., Caputo, L., Ordonez, J., Marce, R., Armengol, J., Crossetti, L. O., & Huszar, V. L. M. (2010). Driving factors of the phytoplankton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean reservoir. Water Research, 44(11):3345-3354.
Bellinger, E. G., & Sigee, D. C. (2010). Freshwater algae: Identification and use as bioindicators. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Boivin-Rioux, A., Starr, M., Chassé, J., Scarratt, M., Perrie, W., Long, Z., & Lavoie, D. (2022). Harmful algae and climate change on the Canadian East Coast: Exploring occurrence predictions of Dinophysis acuminata, D. norvegica, and Pseudo-nitzschia seriata. Harmful Algae, 112(2):1-17.
Briddon, C. L., Szekeres, E., Hegedüs, A., Nicoară, M., Chiriac, C., Stockenreiter, M., & Drugă, B. (2022). The combined impact of low temperatures and shifting phosphorus availability on the competitive ability of cyanobacteria. Scientific Reports, 12(1):1-13.
Burkholder, J. M., Glasgow Jr, H. B., & Hobbs, C. W. (1995). Fish kills linked to a toxic ambush-predator dinoflagellate: Distribution and environmental conditions. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 124:43-61.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(2):361-369.
Chakraborty, S., Karmaker, D., Rahman, M. A., Bali, S. C., Das, S. K., & Hossen, R. (2021). Impacts of pH and salinity on community composition, growth and cell morphology of three freshwater phytoplankton. Plant Science Today, 8(3):655-661.
Du, H. T., Hieu, N. M., & Kunzmann, A. (2022). Negative effects of fish cages on coral reefs through nutrient enrichment and eutrophication in Nha Trang Bay, Viet Nam. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 55(2022):1-7.
Fang, F., Gao, Y., Gan, L., He, X., & Yang, L. (2018). Effects of different initial pH and irradiance levels on cyanobacterial colonies from Lake Taihu, China. Journal of Applied Phycology, 30(3):1777-1793.
Gao, H., Zhao, Z., Zhang, L., & Ju, F. (2022). Cyanopeptides restriction and degradation co-mediate microbiota assembly during a freshwater cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom (CyanoHAB). Water Research, 220(118674).
Glibert, P. M. (2020). Harmful algae at the complex nexus of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae, 91(1):1-15.
Håkanson, L., & Blenckner, T. (2014). A review on operational bioindicators for sustainable coastal management-criteria, motives and relationships. Ocean & Coastal Management, 51(1):43-72.
Hidayah, T., Ridho, M. R., & Suheryanto. (2014). Phytoplankton community structure in Kedungombo Reservoir. Maspari Journal, 6(2):104-112.
Igwaran, A., Kayode, A. J., Moloantoa, K. M., Khetsha, Z. P., & Unuofin, J. O. (2024). Cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Causes, impacts, and risk management. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 235(71):1-26.
Karydis, M. (2009). Eutrophication assessment of coastal waters based on indicators: A literature review. Global NEST Journal, 11(4):373-390.
Kimambo, O. N., Chikoore, H., Gumbo, J. R., & Msagati, T. A. M. (2019). Retrospective analysis of chlorophyll-a and its correlation with climate and hydrological variations in Mindu Dam, Morogoro, Tanzania. Heliyon, 5(11):1-14.
Krismono, & Sugianti, Y. (2007). Plankton distribution in Kedungombo Reservoir. Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 19(1):108-115.
Legono, D., Wahono, E. P., Kusumastuti, D. I., & Harset, D. (2022). Dynamics of reservoir environment carrying capacity (case of Kedungombo Reservoir, Central Java, Indonesia). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1105(1):1-7.
Liu, Z., Wang, X., Jia, S., & Mao, B. (2023). Eutrophication causes analysis under the influencing of anthropogenic activities in China’s largest freshwater lake (Poyang Lake): Evidence from hydrogeochemistry and reverse simulation methods. Journal of Hydrology, 625(14):1-13.
Malone, T. C., & Newton, A. (2020). The globalization of cultural eutrophication in the coastal ocean: Causes and consequences. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7(670):1-30.
Metcalf, J. S., Tischbein, M., Cox, P. A., & Stommel, E. W. (2021). Cyanotoxins and the nervous system. Toxins, 13(9):1-19.
Minakova, E. A., Shlichkov, A. P., & Arinina, A. V. (2019). Approaches to management of anthropogenic eutrophication caused by loading from mineral fertilizers. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 272(3):1-6.
Moraes, M. A. B., Rodrigues, R. A. M., Schlüter, L., Podduturi, R., Jørgensen, N. O. G., & Calijuri, M. C. (2021). Influence of environmental factors on occurrence of cyanobacteria and abundance of saxitoxin-producing cyanobacteria in a subtropical drinking water reservoir in Brazil. Water, 13(12):1-19.
Na, L., Shaoyang, C., Zhenyan, C., Xing, W., Yun, X., Li, X., Yanwei, G., Tingting, W., Xuefeng, Z., & Siqi, L. (2022). Long-term prediction of sea surface chlorophyll-a concentration based on the combination of spatio-temporal features. Water Research, 211(4):1-15.
Oberholster, P. J., & Botha, A.-M. (2011). Dynamics of phytoplankton and phytobenthos in Lake Loskop (South Africa) and downstream irrigation canals. Fundamental and Applied Limnology, 179(3):169-178.
Park, K.-W., Chung, M.-H., Yoo, M.-H., O, K.-S., Kim, K.-Y., Park, T.-G., & Youn, S.-H. (2023). Impact of phytoplankton community structure changes in the South Sea of Korea on Marine ecosystems due to climate change. Water, 15(23):1-16.
Prasad, A. G. D., & Siddaraju. (2012). Carlson’s trophic state index for the assessment of trophic status of two lakes in Mandya District. Pelagia Research Library Advances, 3(5):2992-2996.
Purwana, Y. M., Dananjaya, R. H., & Hartono, W. A. (2019). Pre-evaluation of Kedung Ombo Dam safety based on probabilistic seismic hazard analysis. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2114(1):1-12.
Rahayu, N. W. S. T., Hendrawan, I. G., & Suteja, Y. (2018). Spatial and temporal distribution of nitrate and phosphate during the West Monsoon on the surface of the waters of Benoa Bay, Bali. Journal of Marine and Aquatic Sciences, 4(1):1-13.
Ridho, M. R., Patriono, E., & Mulyani, Y. S. (2020). Correlation among phytoplankton abundance, chlorophyll-a, and water quality of Sungsang Coastal Waters, South Sumatera. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 12(1):1-8.
Sahoo, D., & Anandhi, A. (2023). Conceptualizing turbidity for aquatic ecosystems in the context of sustainable development goals. Environmental Science: Advances, 2(9):1220-1234.
Sidabutar, T., Srimariana, E. S., Cappenberg, H., & Wouthuyzen, S. (2024). Comprehensive analysis of harmful algal blooms in indonesia: from occurrence to impact. BIO Web Conferences, 87(10):1-12.
Simanjuntak, I. C. B. H., & Muhammad, F. (2018). Carrying capacity of Kedungombo reservoir for net cage culture. E3S Web of Conferences, 73(03018):1-5.
Smayda, T. J. (1997). Harmful algal blooms: Their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnology and Oceanography, 42(5):1137-1153.
Smyth, A., Laughinghouse, H. D., Havens, K., & Frazer, T. (2022). Rethinking the role of nitrogen and phosphorus in the eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems. EDIS, 2022(1):1-15.
Sulastri. (2018). Phytoplankton of lakes on the Island of Java: Diversity and their role as aquatic bioindicators. LIPI Press.
Sulastri, Henny, C., Nomosatryo, S., Susanti, E., & Sulawesty, F. (2023). Monitoring planktonic cyanobacteria in Lake Maninjau, West Sumatra, Indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1260(2):1-13.
Suteja, Y., Dirgayusa, I. G. N. P., Afdal, Cordova, M. R., Rachman, A., Rintaka, W. E., Takarina, N. D., Putri, W. A. E., Isnaini, & Purwiyanto, A. I. S. (2021). Identification of potentially harmful microalgal species and eutrophication status update in Benoa Bay, Bali, Indonesia. Ocean and Coastal Management, 210(12):1-15.
Syakti, A. D., Idris, F., Koenawan, C. J., Asyhar, R., & Apriadi, T. (2019). Biological pollution potential in the water of Bintan-Riau Islands Province, Indonesia: First appearance of harmful algal bloom species. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 45:117-122.
Tabrett, S., Ramsay, I., Dias, F. S., Burford, M., Claus, S., & Sheidler, C. (2024). Review of nutrient release from aquaculture activities. Final Report. State of Queensland, Australia.
Thawabteh, A. M., Naseef, H. A., Karaman, D., Bufo, S. A., Scrano, L., & Karaman, R. (2023). Understanding the risks of diffusion of cyanobacteria toxins in rivers, lakes, and potable water. Toxins, 15(9):1-38.
Turner, M. A., Howell, E. T., Summerby, M., Hesslein, R. H., Findlay, D. L., & Jackson, M. B. (1991). Changes in epilithon and epiphyton associated with experimental acidification of a lake to pH 5. Limnology and Oceanography, 36(7):1390-1405.
Turner, A. D., Turner, F. R. I., White, M., Hartnell, D., Crompton, C. G., Bates, N., Egginton, J., Branscombe, L., Lewis, A. M., & Maskrey, B. H. (2022). Confirmation using triple quadrupole and high-resolution mass spectrometry of a fatal canine neurotoxicosis following exposure to anatoxins at an inland reservoir. Toxins, 14(11):1-19.
van Vuuren, S. J., Taylor, J., van Ginkel, C., & Gerber, A. (2006). Easy identification of the most common freshwater algae: A guide for the identification of microscopic algae in South African freshwaters. North-West University and Department of Water Affairs and Forestry.
Vidyarathna, N. K., Papke, E., Coyne, K. J., Cohen, J. H., & Warner, M. E. (2020). Functional trait thermal acclimation differs across three species of mid-Atlantic harmful algae. Harmful Algae, 94(4):1-11.
Vollenweider, R. (1968). Scientific fundamentals of the eutrophication of lakes and flowing waters, with particular reference to nitrogen and phosphorus as factors in eutrophication. Paris, France: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Vundo, A., Matsushita, B., Jiang, D., Gondwe, M., Hamzah, R., Setiawan, F., & Fukushima, T. (2019). An overall evaluation of water transparency in Lake Malawi from MERIS Data. Remote Sensing, 11(279):1-18.
Wang, J., Sharaf, F., & Kanwal, A. (2023). Nitrate pollution and its solutions with special emphasis on electrochemical reduction removal. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(4):9290-9310.
Watson, S. B., & Molot, L. (2013). Harmful algal blooms. In J.-F. Férard & C. Blaise (Eds.), Encyclopedia of aquatic ecotoxicology. (pp. 575-596). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Watson, S. B., Whitton, B. A., Higgins, S. N., Paerl, H. W., Brooks, B. W., & Wehr, J. D. (2015). Harmful algal blooms. In J. Wehr, R. Sheath & J. P. Kociolek (Eds.), Freshwater Algae of North America. (pp. 873-920). San Diego: Academic Press.
Weigelhofer, G., Hein, T., & Bondar-Kunze, E. (2018). Phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in riverine systems: Human impacts and management options. In S. Schmutz & J. Sendzimir (Eds.), Riverine ecosystem management: Science for governing towards a sustainable future. (pp. 187-202). Springer International Publishing.
Xu, S., Lyu, P., Zheng, X., Yang, H., Xia, B., Li, H., Zhang, H., & Ma, S. (2022). Monitoring and control methods of harmful algal blooms in Chinese freshwater system: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 29(38):56908-56927.
Zhou, Y., Wang, L., Zhou, Y., & Mao, X. (2020). Eutrophication control strategies for highly anthropogenic influenced coastal waters. Science of the Total Environment, 705(8):1–11.