Date Log
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
Quality and Shelf Life Assessment of Modified Pekasam Ale-ale (Meretrix meretrix)
Corresponding Author(s) : Risa Nofiani
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 17 No. 1 (2025): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
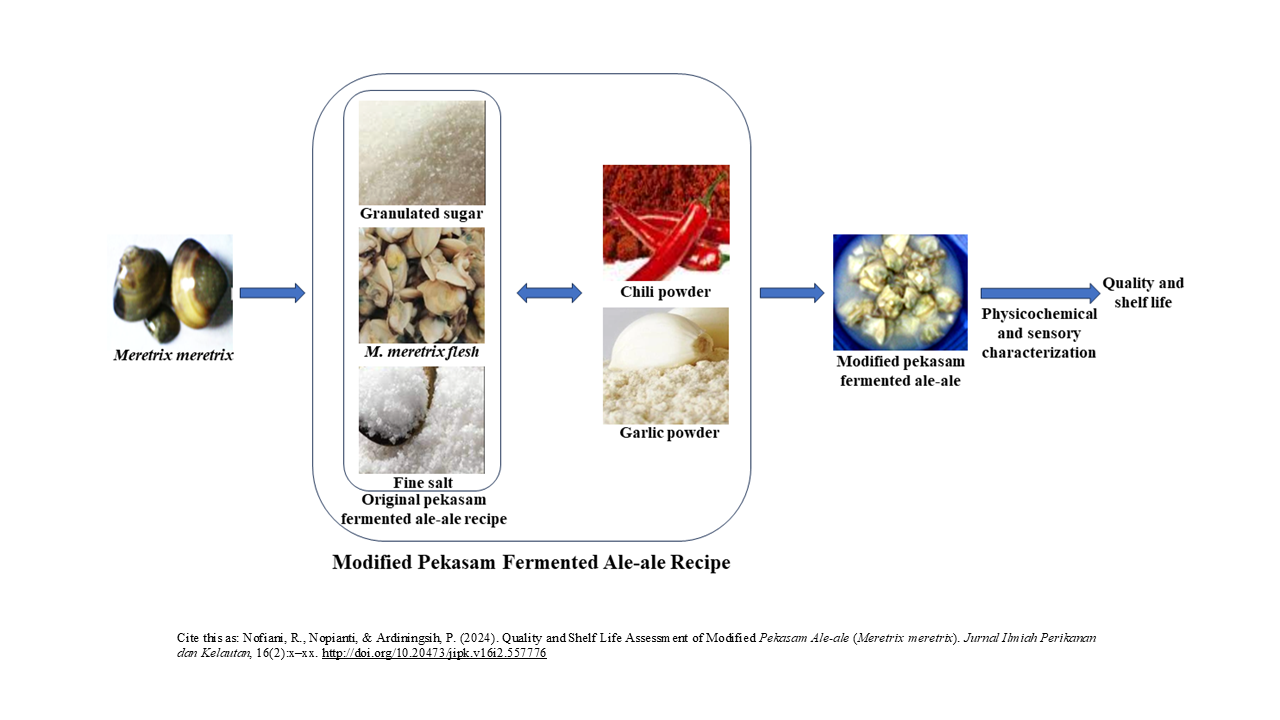
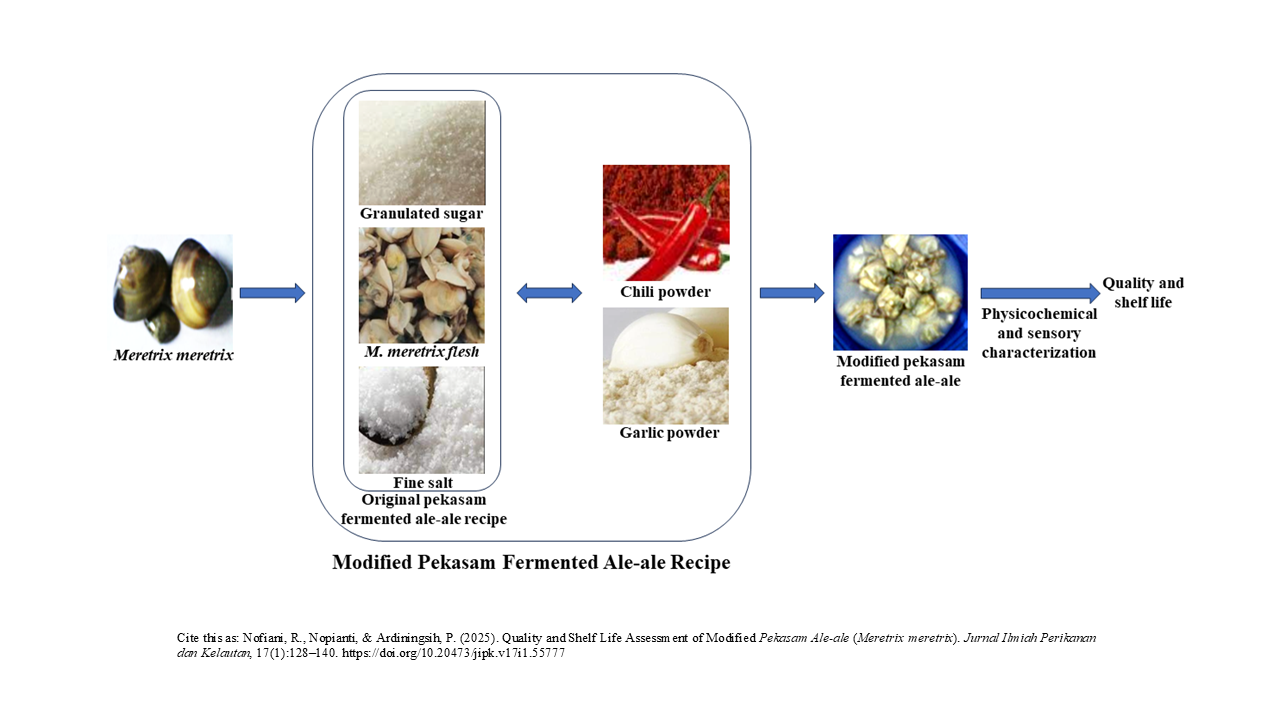
Graphical Abstract
Highlight Research
- Pekasam ale-ale is spontaneously fermented ale-ale (Meretrix meretrix) flesh with fine salt and incubated for 3-7 days.
- Modified pekasam ale-ale prepared by adding 155 g of garlic powder into the original pekasam ale-ale showed the best acceptability and had a different quality than the original pekasam ale-ale.
- The best maturity time and the predicted shelf life for modified pekasam ale-ale fell on days 40 and 60, respectively.
- Garlic powder has successfully improved the taste and aroma of modified pekasam ale-ale.
Abstract
Pekasam ale-ale is spontaneously fermented ale-ale (Meretrix meretrix) flesh with fine salt and carbohydrates, such as sugar, rice porridge or angkak (red fermented rice) followed by incubation for 3-7 days. This product has a slightly fishy odour based on the communities’ opinion at Ketapang and its unknown shelf life. The original recipe added granulated sugar and garlic powder might be able to remove the fishy odour. The effects of the addition of both ingredients are still unknown for the quality, consumer acceptability and shelf life. The objective of the study was to evaluate the quality and shelf life of pekasam ale-ale added granulated sugar and garlic powder based on sensory, physicochemical and microbiological profiles. Three recipes for this study were A (1 kg of fresh ale-ale flesh, 400 g of fine salt), B (recipe A, 200 g of granulated sugar, 55 g of garlic powder), and C (recipe A, 200 g of granulated sugar, 125 g of garlic powder) then tested physicochemical, microbiological and sensory properties. The water content, pH, and free fatty acids of A, B, and C differ significantly except for the ash content. All recipes were safe for consumption based on their physicochemical and microbiological properties. The best taste and aroma were awarded to C and B, respectively. The best acceptance score was awarded for C, with days 40 and 60 for the best maturity and shelf life, respectively. In conclusion, garlic powder successfully enhances the taste and aroma and reduces the fishy aroma of pekasam ale-ale.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Al-Sheikh, H., & Abdelzaher, H. M. . (2012). Occurrence, Identification and Pathogenicity of Phytium aphanidermatum, P. diclinum, P. dissotocum and Phytium “Group P” Isolated from Dawmat Al-Jandal Lake, Saudi Arabia. Research Journal of Environmental Science, 6(6):196–209.
- Alonso, J. A., & Lamata, M. T. (2006). Consistency in the analytic hierarchy process: A new approach. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowlege-Based Systems, 14(4):445–459.
- AOAC. (2000). Official Methods for Analysis of AOAC. Gaithersburg, MD, USA: The Association of Official Analytical Chemist, Inc.
- Bao, Z., Xiong, J., Lin, W., & Ye, J. (2016). Profiles of free fatty acids, free amino acids, and volatile compounds of milk bases fermented by Lactobacillus casei GBHM-21 with different fat levels. CYTA - Journal of Food, 14(1):10–17.
- Bekhit, A. E. A., Hopkins, D. L., Giteru, S. G., & Holman, B. W. B. (2021). Total volatile basic nitrogen and trimethylamine in muscle foods : Potential formation pathways and effects on human health. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 20(4):3620–3666.
- Bernadez, M., Pastoriza, L., Sampedro, G., Herrera, J. J., & Cabo, M. L. (2005). Modified method for the analysis of free fatty acids in fish. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(6):1903–1906.
- Castro, P., Padrón, J. C. P., Cansino, M. J. C., Velázquez, E. S., & Larriva, R. M. De. (2006). Total volatile base nitrogen and its use to assess freshness in European sea bass stored in ice. Food Control, 17(4):245–248.
- Chowdhury, J., Islam Sarkar, M., Khan, M., & Bhuyan, M. (2019). Biochemical composition of Meretrix meretrix in the Bakkhali River Estuary, Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Annals of Marine Science, 3(1):018–024.
- Conway, E. J., & Bryne, A. (1933). An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances: Biochemical Journal, 27(2):419–429.
- Corzo-Martinez, M., Corzo, N., Villamiel, M., & Castillo, M. Dolores, D. (2012). Food Biochemistry and Food Processing. In B. K. Simpson, L. M. . Nolet, F. Toldra, S. Benjakul, G. Paliyath, & Y. Hui (Eds.), John Wiley & Sons, Inc (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Daliri, E. B. M., Choi, S. Il, Cho, B. Y., Jo, H. Y., Kim, S. H., Chelliah, R., Rubab, M., Kim, J. H., Oh, H. T., Lee, O. H., & Oh, D. H. (2019). Biological activities of a garlicCirsium setidens Nakai blend fermented with Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Food Science and Nutrition, 7(6):2024–2032.
- Gao, P., Li, L., Xia, W., Xu, Y., & Liu, S. (2020). Valorization of nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fish head for a novel fish sauce by fermentation with selected lactic acid bacteria. Lwt, 129(13):109539-109546.
- Gram, L., Ravn, L., Rasch, M., Bruhn, J. B., Christensen, A. B., & Givskov, M. (2002). Food spoilage - Interactions between food spoilage bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 78(1–2):79–97.
- Guo, X., Yu, L., Lu, Q., Ding, W., Zhong, J., Zhang, L., & Wang, X. (2023). Quality evaluation and shelf-life prediction model establishment of frozen Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Lwt, 173(1):114250-114260.
- Han, B. Z., Beumer, R. R., Rombouts, F. M., & Robert Nout, M. J. (2001). Microbiological safety and quality of commercial sufu - A Chinese fermented soybean food. Food Control, 12(8):541–547.
- Holt, J. G., Krieg, N. ., Sneath, P. H. ., Staley, J. ., & Williams, S. (1994). Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology (9th ed.). William and Wilkins.
- Hossain, M., Adhikary, R., Mahbub, K., Begum, M., & Islam, M. (2012). Effect of 10% concentration of salt, garlic and coriander on the quality of smoked hilsa fish (Tenualosa ilisha). American Journal of Food Technology, 7(8):501–505.
- Hughes, B. G., & Lawson, L. D. (1991). Antimicrobial effects of Allium sativum L. ( Garlic ), Allium ampeloprasum L. ( Elephant Garlic ), and Allium cepa L. ( Onion ), garlic compounds and commercial garlic supplement products. Phytotheraphy Research, 5(4):154–158.
- Indonesian National Standard. (1992). Methods of food and drink tests. In SNI 01-2891-1992. National Standardization Agency.
- Kilinc, B., Cakli, S., Tolasa, S., & Dincer, T. (2006). Chemical, microbiological and sensory changes associated with fish sauce processing. European Food Research and Technology, 222(5–6):604–613.
- Kim, J. Y., Bae, Y. M., & Lee, S. Y. (2021). Combined effect of various salt concentrations and lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes in white kimchi at different temperatures. Food Science and Biotechnology, 30(12):1593–1600.
- Kim, Y. S., Baek, H. H., Chung, I. M., Kwon, B., & Ji, G. E. (2009). Garlic fermentation by lactic acid bacteria. Food Science and Biotechnology, 18(5):1279–1283.
- Lee, K. W., Shim, J. M., Kim, D. W., Yao, Z., Kim, J. A., Kim, H. J., & Kim, J. H. (2018). Effects of different types of salts on the growth of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts during kimchi fermentation. Food Science and Biotechnology, 27(2):489–498.
- Li, J. lin, Tu, Z. cai, Zhang, L., Sha, X. mei, Wang, H., Pang, J. Juan, & Tang, P. Ping. (2016). The effect of ginger and garlic addition during cooking on the volatile profile of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) soup. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(8):3253–3270.
- Li, X., Teng, W., Liu, G., Guo, F., Xing, H., Zhu, Y., & Li, J. (2022). Allicin promoted reducing effect of garlic powder through acrylamide formation stage. Foods, 11(16):1–12.
- Liao, E., Xu, Y., Jiang, Q., & Xia, W. (2019). Effects of inoculating autochthonous starter cultures on N-nitrosodimethylamine and its precursors formation during fermentation of Chinese traditional fermented fish. Food Chemistry, 271(3):174–181.
- Lim, S. B., Shin, S. Y., Moon, J. S., Otgonbayar, G. E., Joo, W., Lee, S. J., Jeon, C. O., & Han, N. S. (2015). Garlic is a source of major lactic acid bacteria for early-stage fermentation of cabbage-kimchi. Food Science and Biotechnology, 24(4):1437–1441.
- Mariutti, L. R. B., & Bragagnolo, N. (2017). Influence of salt on lipid oxidation in meat and seafood products: A review. Food Research International, 94(4):90–100.
- McFeeters, R. F. (2004). Fermentation microorganisms and flavor changes in fermented foods. Journal of Food Science, 69(1):2002–2004.
- Mondal, A., Banerjee, S., Bose, S., Mazumder, S., Haber, R. A., Farzaei, M. H., & Bishayee, A. (2022). Garlic constituents for cancer prevention and therapy: From phytochemistry to novel formulations. Pharmacological Research, 175(1):105837-105859.
- Monika, Savitri, Kumar, V., Kumari, A., Angmo, K., & Bhalla, T. C. (2017). Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from traditional pickles of Himachal Pradesh, India. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 54(7):1945–1952.
- Moschopoulou, E., Moatsou, G., Syrokou, M. K., Paramithiotis, S., & Drosinos, E. H. (2019). Food quality changes during shelf life. In Food Quality and Shelf Life. Elsevier Inc.
- Nair, M. K. M., Joy, J., Vasudevan, P., Hinckley, L., Hoagland, T. A., & Venkitanarayanan, K. S. (2005). Antibacterial effect of caprylic acid and monocaprylin on major bacterial mastitis pathogens. Journal of Dairy Science, 88(10):3488–3495.
- Nofiani, R, Elminah, E., & Ardiningsih, P. (2019). Chemical and microbiological properties of buduk , A commercial fish sauce from West Kalimantan. Jurnah Pengolaha Hasil Perikanan Indonesia, 22(3):601–608.
- Nofiani, R, Kalbar, M., & Ardiningsih, P. (2010). Chemical characteristics and microbiological safety of commercial fermented ale-ale from West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 5(6):483–493.
- Nofiani, R, Syahmurdiandi, N. M., & Ardiningsih, P. (2021). The effects of garlic and red chilli pepper powder on physicochemical, microbiological, and sensory properties of cincalok. International Journal of Food Science, 2021(1):1-11.
- Nofiani, Risa, Ardiningsih, P., Adhitiyawarman, & Sarwiyati. (2022). Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional fermented fish. Biodiversitas, 23(11):5662–5669.
- Nursyam, H. (2011). Pengolahan sosis fermentasi ikan tuna (Thunnus sp.) menggunakan kultur starter Lactobacillus plantarum terhadap nilai pH, total asam, N-total, dan N-amino. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan Dan Kelautan, 3(2):221–228.
- Paludan-Müller, C., Valyasevi, R., Huss, H. H., & Gram, L. (2002). Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of garlic-fermenting lactic acid bacteria isolated from som-fak, a Thai low-salt fermented fish product. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 92(2):307–314.
- Paludan-Müller, Christine, Henrik Huss, H., & Gram, L. (1999). Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a Thai low-salt fermented fish product and the role of garlic as substrate for fermentation. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 46(3):219–229.
- Persulessy, C. B., Kusdiyantini, E., Ferniah, R. S., Agustini, T. W., & Budiharjo, A. (2020). Ina sua: The traditional food fermentation from teon nila serua, Central of Maluku, Indonesia. Journal of Ethnic Foods, 7(1):1–6.
- Qiu, Z., Zheng, Z., Zhang, B., Sun-Waterhouse, D., & Qiao, X. (2020). Formation, nutritional value, and enhancement of characteristic components in black garlic: A review for maximizing the goodness to humans. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 19(2):801–834.
- Rasane, P., Jha, A., & Sharma, N. (2015). Predictive modelling for shelf life determination of nutricereal based fermented baby food. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(8):5003–5011.
- Sari, R. A., Nofiani, R., & Ardiningsih, P. (2012). Characterization of lactic acid bacteria, Leuconostoc sp. isolated from pekasam ale-ale formulation at laboratory scale. Jurnal Kimia, 1(1):14–20.
- Sawant, P. P., & Mohite, S. A. (2013). Study of proximate composition of Meretrix meretrix (Linnaeus, 1758) of the Ratnagiri coast, Maharashtra, India. Biosciences Biotechnology Research Asia, 10(1):311–317.
- Smit, G., Smit, B. A., & Engels, W. J. M. (2005). Flavour formation by lactic acid bacteria and biochemical flavour profiling of cheese products. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 29(3):591–610.
- Solms, J. (1969). The taste of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 17(4):686–688.
- Tao, A., Zhang, H., Duan, J., Xiao, Y., Liu, Y., Li, J., Huang, J., Zhong, T., & Yu, X. (2022). Mechanism and application of fermentation to remove beany flavor from plant-based meat analogs: A mini review. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13:1070773-1070784.
- Tirillini, B., Maggi, F., Venanzoni, R., & Angelini, P. (2019). Enhanced duration of truffle sauce preservation due to addition of linoleic acid. Journal of Food Quality, 2019(1):1-10.
- Watanabe, T. (2010). Pictorial atlas of soil and seed fungi. In Pictorial Atlas of Soil and Seed Fungi.
- Wen, X., Chen, A., Wu, Y., Yang, Y., Xu, Y., Xia, W., Zhang, Y., Cao, Y., & Chen, S. (2020). Comparative evaluation of proximate compositions and taste attributes of three Asian hard clams (Meretrix meretrix) with different shell colors. International Journal of Food Properties, 23(1):400–411.
- Wieczorek, M. N., & Drabińska, N. (2022). Flavour generation during lactic acid fermentation of Brassica vegetables—Literature Review. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 12(11):5598-5617.
- Xu, Y., Li, L., Xia, W., Zang, J., & Gao, P. (2019). The role of microbes in free fatty acids release and oxidation in fermented fish paste. Lwt, 101(7):323–330.
- Xu, Y., Xia, W., Yang, F., & Nie, X. (2010). Physical and chemical changes of silver carp sausages during fermentation with Pediococcus pentosaceus. Food Chemistry, 122(3):633–637.
- Young, N. W. G., & O’Sullivan, G. R. (2011). The influence of ingredients on product stability and shelf life. Food and Beverage Stability and Shelf Life. Woodhead Publishing Limited.
- Zhang, K., Zhang, T. T., Guo, R. R., Ye, Q., Zhao, H. L., & Huang, X. H. (2023). The regulation of key flavor of traditional fermented food by microbial metabolism: A review. Food Chemistry: X, 19(4):100871-100883.
- Zhao, C. J., Schieber, A., & Gänzle, M. G. (2016). Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations – A review. Food Research International, 89(12):39–47.
References
Al-Sheikh, H., & Abdelzaher, H. M. . (2012). Occurrence, Identification and Pathogenicity of Phytium aphanidermatum, P. diclinum, P. dissotocum and Phytium “Group P” Isolated from Dawmat Al-Jandal Lake, Saudi Arabia. Research Journal of Environmental Science, 6(6):196–209.
Alonso, J. A., & Lamata, M. T. (2006). Consistency in the analytic hierarchy process: A new approach. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowlege-Based Systems, 14(4):445–459.
AOAC. (2000). Official Methods for Analysis of AOAC. Gaithersburg, MD, USA: The Association of Official Analytical Chemist, Inc.
Bao, Z., Xiong, J., Lin, W., & Ye, J. (2016). Profiles of free fatty acids, free amino acids, and volatile compounds of milk bases fermented by Lactobacillus casei GBHM-21 with different fat levels. CYTA - Journal of Food, 14(1):10–17.
Bekhit, A. E. A., Hopkins, D. L., Giteru, S. G., & Holman, B. W. B. (2021). Total volatile basic nitrogen and trimethylamine in muscle foods : Potential formation pathways and effects on human health. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 20(4):3620–3666.
Bernadez, M., Pastoriza, L., Sampedro, G., Herrera, J. J., & Cabo, M. L. (2005). Modified method for the analysis of free fatty acids in fish. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(6):1903–1906.
Castro, P., Padrón, J. C. P., Cansino, M. J. C., Velázquez, E. S., & Larriva, R. M. De. (2006). Total volatile base nitrogen and its use to assess freshness in European sea bass stored in ice. Food Control, 17(4):245–248.
Chowdhury, J., Islam Sarkar, M., Khan, M., & Bhuyan, M. (2019). Biochemical composition of Meretrix meretrix in the Bakkhali River Estuary, Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Annals of Marine Science, 3(1):018–024.
Conway, E. J., & Bryne, A. (1933). An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances: Biochemical Journal, 27(2):419–429.
Corzo-Martinez, M., Corzo, N., Villamiel, M., & Castillo, M. Dolores, D. (2012). Food Biochemistry and Food Processing. In B. K. Simpson, L. M. . Nolet, F. Toldra, S. Benjakul, G. Paliyath, & Y. Hui (Eds.), John Wiley & Sons, Inc (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Daliri, E. B. M., Choi, S. Il, Cho, B. Y., Jo, H. Y., Kim, S. H., Chelliah, R., Rubab, M., Kim, J. H., Oh, H. T., Lee, O. H., & Oh, D. H. (2019). Biological activities of a garlicCirsium setidens Nakai blend fermented with Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Food Science and Nutrition, 7(6):2024–2032.
Gao, P., Li, L., Xia, W., Xu, Y., & Liu, S. (2020). Valorization of nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fish head for a novel fish sauce by fermentation with selected lactic acid bacteria. Lwt, 129(13):109539-109546.
Gram, L., Ravn, L., Rasch, M., Bruhn, J. B., Christensen, A. B., & Givskov, M. (2002). Food spoilage - Interactions between food spoilage bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 78(1–2):79–97.
Guo, X., Yu, L., Lu, Q., Ding, W., Zhong, J., Zhang, L., & Wang, X. (2023). Quality evaluation and shelf-life prediction model establishment of frozen Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Lwt, 173(1):114250-114260.
Han, B. Z., Beumer, R. R., Rombouts, F. M., & Robert Nout, M. J. (2001). Microbiological safety and quality of commercial sufu - A Chinese fermented soybean food. Food Control, 12(8):541–547.
Holt, J. G., Krieg, N. ., Sneath, P. H. ., Staley, J. ., & Williams, S. (1994). Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology (9th ed.). William and Wilkins.
Hossain, M., Adhikary, R., Mahbub, K., Begum, M., & Islam, M. (2012). Effect of 10% concentration of salt, garlic and coriander on the quality of smoked hilsa fish (Tenualosa ilisha). American Journal of Food Technology, 7(8):501–505.
Hughes, B. G., & Lawson, L. D. (1991). Antimicrobial effects of Allium sativum L. ( Garlic ), Allium ampeloprasum L. ( Elephant Garlic ), and Allium cepa L. ( Onion ), garlic compounds and commercial garlic supplement products. Phytotheraphy Research, 5(4):154–158.
Indonesian National Standard. (1992). Methods of food and drink tests. In SNI 01-2891-1992. National Standardization Agency.
Kilinc, B., Cakli, S., Tolasa, S., & Dincer, T. (2006). Chemical, microbiological and sensory changes associated with fish sauce processing. European Food Research and Technology, 222(5–6):604–613.
Kim, J. Y., Bae, Y. M., & Lee, S. Y. (2021). Combined effect of various salt concentrations and lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes in white kimchi at different temperatures. Food Science and Biotechnology, 30(12):1593–1600.
Kim, Y. S., Baek, H. H., Chung, I. M., Kwon, B., & Ji, G. E. (2009). Garlic fermentation by lactic acid bacteria. Food Science and Biotechnology, 18(5):1279–1283.
Lee, K. W., Shim, J. M., Kim, D. W., Yao, Z., Kim, J. A., Kim, H. J., & Kim, J. H. (2018). Effects of different types of salts on the growth of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts during kimchi fermentation. Food Science and Biotechnology, 27(2):489–498.
Li, J. lin, Tu, Z. cai, Zhang, L., Sha, X. mei, Wang, H., Pang, J. Juan, & Tang, P. Ping. (2016). The effect of ginger and garlic addition during cooking on the volatile profile of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) soup. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(8):3253–3270.
Li, X., Teng, W., Liu, G., Guo, F., Xing, H., Zhu, Y., & Li, J. (2022). Allicin promoted reducing effect of garlic powder through acrylamide formation stage. Foods, 11(16):1–12.
Liao, E., Xu, Y., Jiang, Q., & Xia, W. (2019). Effects of inoculating autochthonous starter cultures on N-nitrosodimethylamine and its precursors formation during fermentation of Chinese traditional fermented fish. Food Chemistry, 271(3):174–181.
Lim, S. B., Shin, S. Y., Moon, J. S., Otgonbayar, G. E., Joo, W., Lee, S. J., Jeon, C. O., & Han, N. S. (2015). Garlic is a source of major lactic acid bacteria for early-stage fermentation of cabbage-kimchi. Food Science and Biotechnology, 24(4):1437–1441.
Mariutti, L. R. B., & Bragagnolo, N. (2017). Influence of salt on lipid oxidation in meat and seafood products: A review. Food Research International, 94(4):90–100.
McFeeters, R. F. (2004). Fermentation microorganisms and flavor changes in fermented foods. Journal of Food Science, 69(1):2002–2004.
Mondal, A., Banerjee, S., Bose, S., Mazumder, S., Haber, R. A., Farzaei, M. H., & Bishayee, A. (2022). Garlic constituents for cancer prevention and therapy: From phytochemistry to novel formulations. Pharmacological Research, 175(1):105837-105859.
Monika, Savitri, Kumar, V., Kumari, A., Angmo, K., & Bhalla, T. C. (2017). Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from traditional pickles of Himachal Pradesh, India. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 54(7):1945–1952.
Moschopoulou, E., Moatsou, G., Syrokou, M. K., Paramithiotis, S., & Drosinos, E. H. (2019). Food quality changes during shelf life. In Food Quality and Shelf Life. Elsevier Inc.
Nair, M. K. M., Joy, J., Vasudevan, P., Hinckley, L., Hoagland, T. A., & Venkitanarayanan, K. S. (2005). Antibacterial effect of caprylic acid and monocaprylin on major bacterial mastitis pathogens. Journal of Dairy Science, 88(10):3488–3495.
Nofiani, R, Elminah, E., & Ardiningsih, P. (2019). Chemical and microbiological properties of buduk , A commercial fish sauce from West Kalimantan. Jurnah Pengolaha Hasil Perikanan Indonesia, 22(3):601–608.
Nofiani, R, Kalbar, M., & Ardiningsih, P. (2010). Chemical characteristics and microbiological safety of commercial fermented ale-ale from West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 5(6):483–493.
Nofiani, R, Syahmurdiandi, N. M., & Ardiningsih, P. (2021). The effects of garlic and red chilli pepper powder on physicochemical, microbiological, and sensory properties of cincalok. International Journal of Food Science, 2021(1):1-11.
Nofiani, Risa, Ardiningsih, P., Adhitiyawarman, & Sarwiyati. (2022). Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional fermented fish. Biodiversitas, 23(11):5662–5669.
Nursyam, H. (2011). Pengolahan sosis fermentasi ikan tuna (Thunnus sp.) menggunakan kultur starter Lactobacillus plantarum terhadap nilai pH, total asam, N-total, dan N-amino. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan Dan Kelautan, 3(2):221–228.
Paludan-Müller, C., Valyasevi, R., Huss, H. H., & Gram, L. (2002). Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of garlic-fermenting lactic acid bacteria isolated from som-fak, a Thai low-salt fermented fish product. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 92(2):307–314.
Paludan-Müller, Christine, Henrik Huss, H., & Gram, L. (1999). Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a Thai low-salt fermented fish product and the role of garlic as substrate for fermentation. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 46(3):219–229.
Persulessy, C. B., Kusdiyantini, E., Ferniah, R. S., Agustini, T. W., & Budiharjo, A. (2020). Ina sua: The traditional food fermentation from teon nila serua, Central of Maluku, Indonesia. Journal of Ethnic Foods, 7(1):1–6.
Qiu, Z., Zheng, Z., Zhang, B., Sun-Waterhouse, D., & Qiao, X. (2020). Formation, nutritional value, and enhancement of characteristic components in black garlic: A review for maximizing the goodness to humans. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 19(2):801–834.
Rasane, P., Jha, A., & Sharma, N. (2015). Predictive modelling for shelf life determination of nutricereal based fermented baby food. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(8):5003–5011.
Sari, R. A., Nofiani, R., & Ardiningsih, P. (2012). Characterization of lactic acid bacteria, Leuconostoc sp. isolated from pekasam ale-ale formulation at laboratory scale. Jurnal Kimia, 1(1):14–20.
Sawant, P. P., & Mohite, S. A. (2013). Study of proximate composition of Meretrix meretrix (Linnaeus, 1758) of the Ratnagiri coast, Maharashtra, India. Biosciences Biotechnology Research Asia, 10(1):311–317.
Smit, G., Smit, B. A., & Engels, W. J. M. (2005). Flavour formation by lactic acid bacteria and biochemical flavour profiling of cheese products. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 29(3):591–610.
Solms, J. (1969). The taste of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 17(4):686–688.
Tao, A., Zhang, H., Duan, J., Xiao, Y., Liu, Y., Li, J., Huang, J., Zhong, T., & Yu, X. (2022). Mechanism and application of fermentation to remove beany flavor from plant-based meat analogs: A mini review. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13:1070773-1070784.
Tirillini, B., Maggi, F., Venanzoni, R., & Angelini, P. (2019). Enhanced duration of truffle sauce preservation due to addition of linoleic acid. Journal of Food Quality, 2019(1):1-10.
Watanabe, T. (2010). Pictorial atlas of soil and seed fungi. In Pictorial Atlas of Soil and Seed Fungi.
Wen, X., Chen, A., Wu, Y., Yang, Y., Xu, Y., Xia, W., Zhang, Y., Cao, Y., & Chen, S. (2020). Comparative evaluation of proximate compositions and taste attributes of three Asian hard clams (Meretrix meretrix) with different shell colors. International Journal of Food Properties, 23(1):400–411.
Wieczorek, M. N., & Drabińska, N. (2022). Flavour generation during lactic acid fermentation of Brassica vegetables—Literature Review. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 12(11):5598-5617.
Xu, Y., Li, L., Xia, W., Zang, J., & Gao, P. (2019). The role of microbes in free fatty acids release and oxidation in fermented fish paste. Lwt, 101(7):323–330.
Xu, Y., Xia, W., Yang, F., & Nie, X. (2010). Physical and chemical changes of silver carp sausages during fermentation with Pediococcus pentosaceus. Food Chemistry, 122(3):633–637.
Young, N. W. G., & O’Sullivan, G. R. (2011). The influence of ingredients on product stability and shelf life. Food and Beverage Stability and Shelf Life. Woodhead Publishing Limited.
Zhang, K., Zhang, T. T., Guo, R. R., Ye, Q., Zhao, H. L., & Huang, X. H. (2023). The regulation of key flavor of traditional fermented food by microbial metabolism: A review. Food Chemistry: X, 19(4):100871-100883.
Zhao, C. J., Schieber, A., & Gänzle, M. G. (2016). Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations – A review. Food Research International, 89(12):39–47.