Date Log
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
Seabed Geoacoustic Analysis Using Scientific Single Beam Echosounder
Corresponding Author(s) : Henry M. Manik Manik
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 17 No. 1 (2025): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Highlight Research
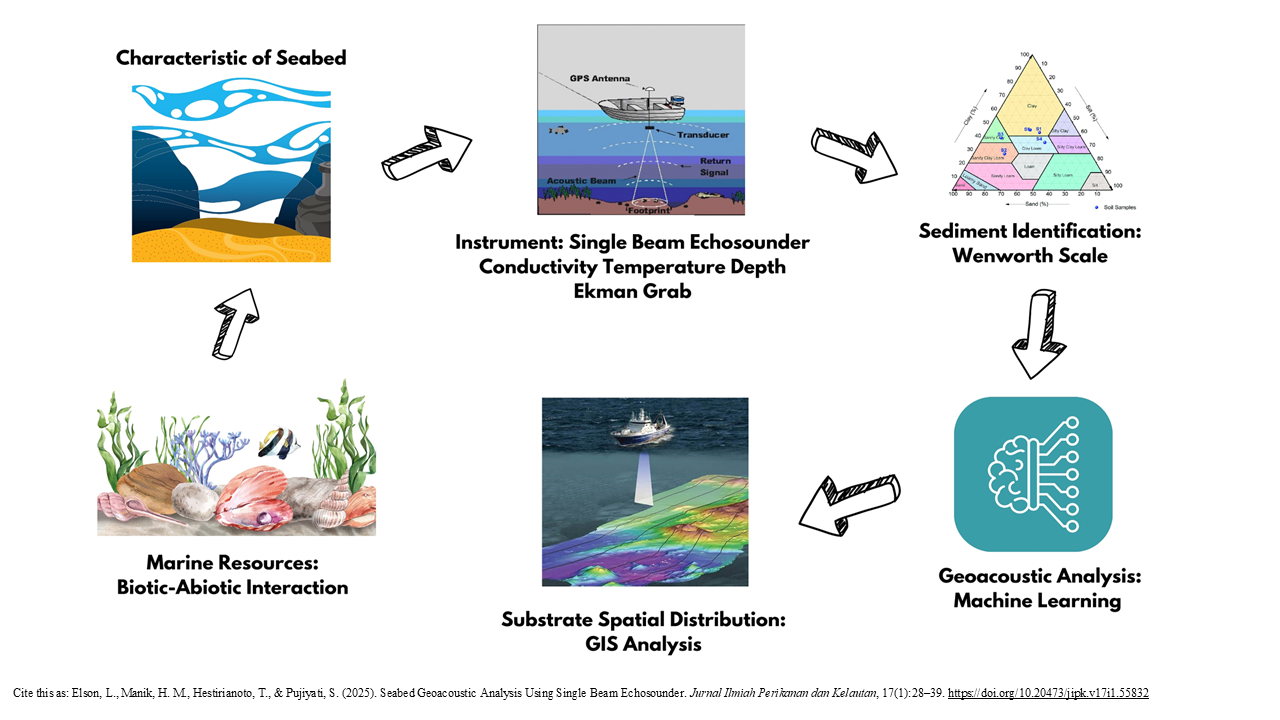
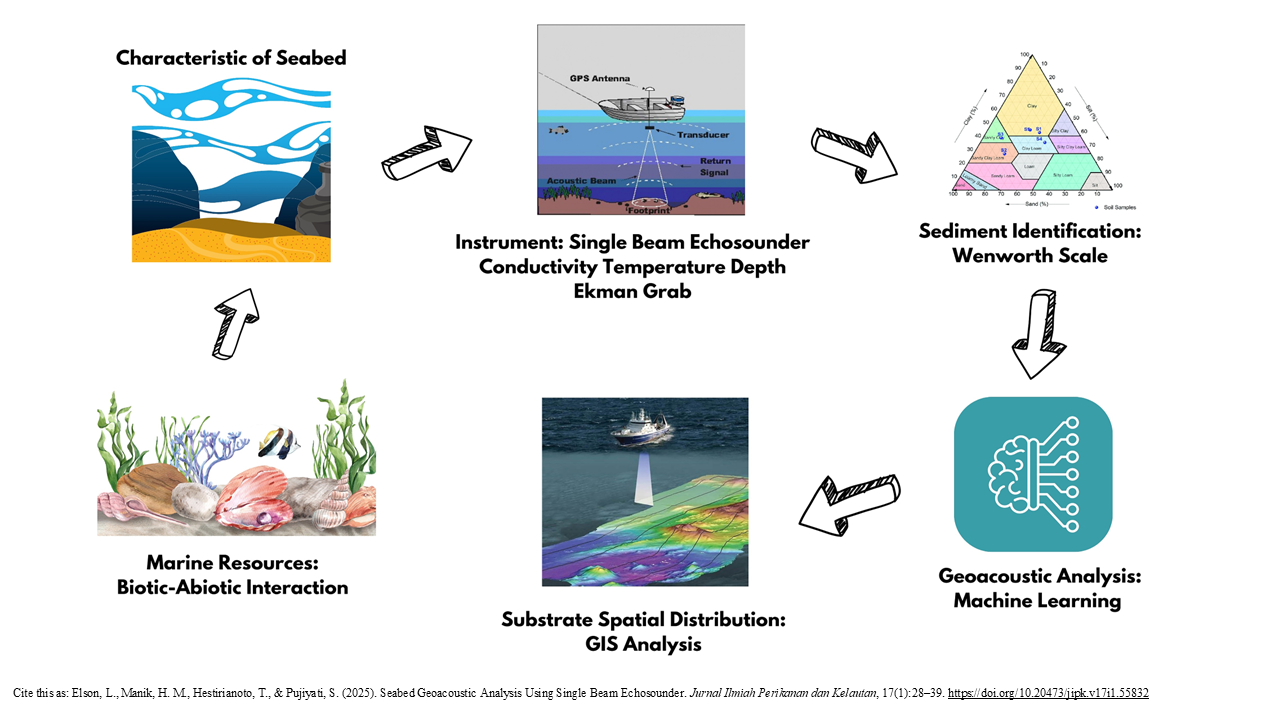
- Hydroacoustic technology was used to identify seabed substrates in real-time with the Simrad EK-15 Single Beam Echosounder.
- Acoustic backscatter analysis classified seabed substrates into 9 sediment types, with reflection values ranging from -28.03 dB to -20.02 dB.
- Machine learning models (k-NN and Random Forest) achieved 98.21% and 96.43% accuracy, enabling faster sediment classification than conventional methods.
- Geoacoustic analysis revealed sound speed, sediment density, acoustic impedance, and reflection coefficients, defining the physical properties of the seabed.
- This study supports coastal engineering, marine habitat conservation, and underwater geological mapping more effectively and efficiently.
Abstract
Hydroacoustic technology was able to quantify the seabed substrate and can be estimated accurately and near real time on the acoustic characters of each substrate. The purpose of the research was to identify the geoacoustic characteristics and spatial mapping of the seabed substrate in Lancang Island. Acoustic data was acquired using a Simrad EK-15 Single Beam Echosounder instrument operating at 200 kHz. Sediment samples were taken using an Ekman grab, which will be used to validate the acoustic data. The results of this study indicated that the acoustic backscatter values of the seabed substrate based on the surface backscattering strength value and sediment particle size at fourteen sampling stations are -28.03 decibels to -20.02 decibels divided into 9 sediment type groups, namely medium and very coarse sand mixture; medium sand; medium, fine and coarse sand mixture; medium and fine sand mixture; fine and medium sand mixture; medium and very fine sand mixture; very fine and medium sand mixture; fine and very fine sand mixture; and fine sand. The accuracy level of k-Nearest Neighbour and Random Forest computational used has very good accuracy of 98.21 % and 96.43 % and Naevi Bayes has a lower accuracy of 58.93 %. The identified geoacoustic characteristics included the mean grain size, sound speed, density, acoustic impedance, and reflection coefficient. Faster, more effective, and efficient computational processes with high accuracy make k-Nearest Neighbour and Random Forest models the best alternative to be used as geoacoustic computational models of seafloor substrates.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Anderson, J. T., Van Holliday, D., Kloser, R., Reid, D. G., & Simard, Y. (2008). Acoustic seabed classification: Current practice and future directions. International Council for the Exploration of the Sea Journal of Marine Science, 65(6):1004-1011.
- Bae, S. H., Kim, D. C., Lee, G. S., Kim, G. Y., Kim, S. P., Seo, Y. K., & Kim, J. C. (2014). Physical and acoustic properties of inner shelf sediments in the South Sea, Korea. Quaternary International, 344(1):125-142.
- Ballard, M. S., Lee, K. M., McNeese, A. R., Wilson, P. S., Chaytor, J. D., Goff, J. A., & Reed, A. H. (2020). In situ measurements of compressional wave speed during gravity coring operations in the New England Mud Patch. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 45(1):26-38.
- Buscombe, D., & Brams, E. P. (2018). Probabilistic substrate classification with multispectral acoustic backscatter: A comparison of discriminative and generative models. Journal of Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Geosciences. 8(11):1-21.
- Chakraborty, B., Mahale, V., Navelkar, G., Rao, B. R., Prabhudesai, R. G., Ingole, B., & Janakiraman, G. (2007). Acoustic characterization of seafloor habitats on the western continental shelf of India. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 64(3):551-558.
- Chaytor, J. D., Ballard, M. S., Buczkowski, B. J., Goff, J. A., Lee, K. M., Reed, A. H., & Boggess, A. A. (2022). Measurements of geologic characteristics and geophysical properties of sediments from the New England Mud Patch. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 47(3):503-530.
- Chotiros, N. P. (2017). Acoustics of the seabed as a poroelastic medium. New York: Springer Briefs in Oceanography.
- Dall’Osto, D. R., & Tang, D. (2022). Acoustic resonances within the surficial layer of a muddy seabed. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 151(5):3473-3480.
- Farihah, R. A., Manik, H. M., & Harsono, G. (2020). Measurement and analysis of acoustic scattering using multibeam echosounder technology for sediment classification in Palu Bay. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 12(2):439-455.
- Frederick, K., Vilar, S., & Michalopoulou, Z. H. (2020). Seabed classification using physics-based modeling and machine learning. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 148(2):859-872.
- Hamilton, E. L. (1980). Geoacoustic modeling of the sea floor. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 68(5):1313-1340.
- Hamuna, B., Pujiyat, S., Natih, N. M. N., & Dimara, L. (2018). Acoustic backscatter analysis for classification and mapping of aquatic bottom substrates in Yos Sudarso Bay, Jayapura City. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 10(2):291-300.
- Indonesia National Standard 7646. (2010). Hydrographic survey using single beam echosounder.
- Jackson, D. R. & Richardson M. D. (2007). High frequency seafloor acoustics. New York: Springer Science+Business Media, LLC.
- Kim, G. Y., Kim, D. C., Yoo, D. G., & Shin, B. K. (2011). Physical and geoacoustic properties of surface sediments off eastern Geoje Island, South Sea of Korea. Quaternary International, 230(1-2):21-33.
- Kim, G. Y., Narantsetseg, B., Lee, J. Y., Chang, T. S., Lee, G. S., Yoo, D. G., & Kim, S. P. (2018). Physical and geotechnical properties of drill core sediments in the Heuksan Mud Belt off SW Korea. Quaternary International, 468(1):33-48.
- Kusrini, K. & Luthfi, E.T. (2009). Algoritma data mining. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Andi.
- Li, G., Wang, J., Liu, B., Meng, X., Kan, G., & Pei, Y. (2019). Measurement and modeling of high‐frequency acoustic properties in Fine Sandy sediments. Earth and Space Science, 6(11):2057-2070.
- Liu, B., Han, T., Kan, G., & Li, G. (2013). Correlations between the in situ acoustic properties and geotechnical parameters of sediments in the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 77(1):83-90.
- Lu, B., Liu, Q., & Li, G. (2010). Grain and pore factors in acoustic response to seafloor sediments. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 28(2):115-129.
- Lurton, X. (2002). An introduction to underwater acoustics: Principles and applications. Chichester: Praxis Publishing.
- Manik, H. M. (2012). Seabed identification and characterization using sonar. Advances in Acoustics and Vibration, 2012(1):1-5.
- Manik, H. M., Furusawa, M., & Amakasu, K. (2006). Measurement of sea bottom surface backscattering strength by quantitative echo sounder. Fisheries Science, 72(3):503-512.
- Prasetyo, E. (2013). Data mining-processing data into information using matlab. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Andi.
- Pujiyati, S. (2008). Hydroacoustic method approach for the analysis of the relationship between aquatic bottom substrate types and demersal fish communities. Disertation. Bogor, Indonesia: Institut Pertanian Bogor.
- Pujiyati, S., Hartati, S., & Priyono, W. (2010). Effects of grain size, roughness, and hardness of sea floor on back scattering value based on hydroacoustic detection. [in English]. E-Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 2(1):59-67.
- Snellen, M., Siemes, K., & Simons, D. G. (2011). Model-based sediment classification using single-beam echosounder signals. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 129(5):2878-2888.
- [SNI] Standar Nasional Indonesia 7646. (2010). Hydrographic survey using single beam echosounder. Jakarta: Badan Standardisasi Nasional.
- Solikin, S. (2020). Development of a classification method for seafloor substrates using multibeam echsounder data. Disertation. Bogor, Indonesia: Institut Pertanian Bogor.
- Sternlicht, D. D., & de Moustier, C. P. (2003). Time-dependent seafloor acoustic backscatter (10–100 kHz).
- Walree, P. A., Ainslie, M. A., & Simons, D. G. (2006). Mean grain size mapping with single-beam echo sounders. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 120(5):2555-2566.
- Wang, J., Kan, G., Li, G., Meng, X., Zhang, L., Chen, M., Liu, C., & Liu, B. (2023). Physical properties and in situ geoacoustic properties of seafloor surface sediments in the East China Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10(1):1-11.
- Xhemali, D, Hinde, C. J., & Store, R. G. (2009). Naive bayes vs decision trees vs neural network in the classification of training web pages. International Journal of Computer Science, 14(1):16-23.
- Yusuf, M. I., Iqbal, M., & Jaya, I. (2020). Real-time reef fishes identification using deep learning. IOP Conference Series: Iinternational Conference in Marine Science, 429(1):1-8.
- Zailani, A., & Hanun, N. L. (2020). Application of random forest classification algorithm to determine the feasibility of credit in Mitra Sejahtera cooperatives. Journal of Technology Information, 6(1):7-14.
- Zhang, Y., Guo, C., Wang, J., Hou, Z., & Chen, W. (2017). Relationship between in situ sound velocity and granular characteristics of seafloor sediments in the Qingdao offshore region. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 35(3):704-711.
- Zou, D., Williams, K. L., & Thorsos, E. I. (2015). Influence of temperature on acoustic sound speed and attenuation of seafloor sand sediment. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 40(4):969-980.
References
Anderson, J. T., Van Holliday, D., Kloser, R., Reid, D. G., & Simard, Y. (2008). Acoustic seabed classification: Current practice and future directions. International Council for the Exploration of the Sea Journal of Marine Science, 65(6):1004-1011.
Bae, S. H., Kim, D. C., Lee, G. S., Kim, G. Y., Kim, S. P., Seo, Y. K., & Kim, J. C. (2014). Physical and acoustic properties of inner shelf sediments in the South Sea, Korea. Quaternary International, 344(1):125-142.
Ballard, M. S., Lee, K. M., McNeese, A. R., Wilson, P. S., Chaytor, J. D., Goff, J. A., & Reed, A. H. (2020). In situ measurements of compressional wave speed during gravity coring operations in the New England Mud Patch. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 45(1):26-38.
Buscombe, D., & Brams, E. P. (2018). Probabilistic substrate classification with multispectral acoustic backscatter: A comparison of discriminative and generative models. Journal of Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Geosciences. 8(11):1-21.
Chakraborty, B., Mahale, V., Navelkar, G., Rao, B. R., Prabhudesai, R. G., Ingole, B., & Janakiraman, G. (2007). Acoustic characterization of seafloor habitats on the western continental shelf of India. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 64(3):551-558.
Chaytor, J. D., Ballard, M. S., Buczkowski, B. J., Goff, J. A., Lee, K. M., Reed, A. H., & Boggess, A. A. (2022). Measurements of geologic characteristics and geophysical properties of sediments from the New England Mud Patch. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 47(3):503-530.
Chotiros, N. P. (2017). Acoustics of the seabed as a poroelastic medium. New York: Springer Briefs in Oceanography.
Dall’Osto, D. R., & Tang, D. (2022). Acoustic resonances within the surficial layer of a muddy seabed. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 151(5):3473-3480.
Farihah, R. A., Manik, H. M., & Harsono, G. (2020). Measurement and analysis of acoustic scattering using multibeam echosounder technology for sediment classification in Palu Bay. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 12(2):439-455.
Frederick, K., Vilar, S., & Michalopoulou, Z. H. (2020). Seabed classification using physics-based modeling and machine learning. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 148(2):859-872.
Hamilton, E. L. (1980). Geoacoustic modeling of the sea floor. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 68(5):1313-1340.
Hamuna, B., Pujiyat, S., Natih, N. M. N., & Dimara, L. (2018). Acoustic backscatter analysis for classification and mapping of aquatic bottom substrates in Yos Sudarso Bay, Jayapura City. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 10(2):291-300.
Indonesia National Standard 7646. (2010). Hydrographic survey using single beam echosounder.
Jackson, D. R. & Richardson M. D. (2007). High frequency seafloor acoustics. New York: Springer Science+Business Media, LLC.
Kim, G. Y., Kim, D. C., Yoo, D. G., & Shin, B. K. (2011). Physical and geoacoustic properties of surface sediments off eastern Geoje Island, South Sea of Korea. Quaternary International, 230(1-2):21-33.
Kim, G. Y., Narantsetseg, B., Lee, J. Y., Chang, T. S., Lee, G. S., Yoo, D. G., & Kim, S. P. (2018). Physical and geotechnical properties of drill core sediments in the Heuksan Mud Belt off SW Korea. Quaternary International, 468(1):33-48.
Kusrini, K. & Luthfi, E.T. (2009). Algoritma data mining. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Andi.
Li, G., Wang, J., Liu, B., Meng, X., Kan, G., & Pei, Y. (2019). Measurement and modeling of high‐frequency acoustic properties in Fine Sandy sediments. Earth and Space Science, 6(11):2057-2070.
Liu, B., Han, T., Kan, G., & Li, G. (2013). Correlations between the in situ acoustic properties and geotechnical parameters of sediments in the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 77(1):83-90.
Lu, B., Liu, Q., & Li, G. (2010). Grain and pore factors in acoustic response to seafloor sediments. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 28(2):115-129.
Lurton, X. (2002). An introduction to underwater acoustics: Principles and applications. Chichester: Praxis Publishing.
Manik, H. M. (2012). Seabed identification and characterization using sonar. Advances in Acoustics and Vibration, 2012(1):1-5.
Manik, H. M., Furusawa, M., & Amakasu, K. (2006). Measurement of sea bottom surface backscattering strength by quantitative echo sounder. Fisheries Science, 72(3):503-512.
Prasetyo, E. (2013). Data mining-processing data into information using matlab. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Andi.
Pujiyati, S. (2008). Hydroacoustic method approach for the analysis of the relationship between aquatic bottom substrate types and demersal fish communities. Disertation. Bogor, Indonesia: Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Pujiyati, S., Hartati, S., & Priyono, W. (2010). Effects of grain size, roughness, and hardness of sea floor on back scattering value based on hydroacoustic detection. [in English]. E-Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan Tropis, 2(1):59-67.
Snellen, M., Siemes, K., & Simons, D. G. (2011). Model-based sediment classification using single-beam echosounder signals. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 129(5):2878-2888.
[SNI] Standar Nasional Indonesia 7646. (2010). Hydrographic survey using single beam echosounder. Jakarta: Badan Standardisasi Nasional.
Solikin, S. (2020). Development of a classification method for seafloor substrates using multibeam echsounder data. Disertation. Bogor, Indonesia: Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Sternlicht, D. D., & de Moustier, C. P. (2003). Time-dependent seafloor acoustic backscatter (10–100 kHz).
Walree, P. A., Ainslie, M. A., & Simons, D. G. (2006). Mean grain size mapping with single-beam echo sounders. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 120(5):2555-2566.
Wang, J., Kan, G., Li, G., Meng, X., Zhang, L., Chen, M., Liu, C., & Liu, B. (2023). Physical properties and in situ geoacoustic properties of seafloor surface sediments in the East China Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10(1):1-11.
Xhemali, D, Hinde, C. J., & Store, R. G. (2009). Naive bayes vs decision trees vs neural network in the classification of training web pages. International Journal of Computer Science, 14(1):16-23.
Yusuf, M. I., Iqbal, M., & Jaya, I. (2020). Real-time reef fishes identification using deep learning. IOP Conference Series: Iinternational Conference in Marine Science, 429(1):1-8.
Zailani, A., & Hanun, N. L. (2020). Application of random forest classification algorithm to determine the feasibility of credit in Mitra Sejahtera cooperatives. Journal of Technology Information, 6(1):7-14.
Zhang, Y., Guo, C., Wang, J., Hou, Z., & Chen, W. (2017). Relationship between in situ sound velocity and granular characteristics of seafloor sediments in the Qingdao offshore region. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 35(3):704-711.
Zou, D., Williams, K. L., & Thorsos, E. I. (2015). Influence of temperature on acoustic sound speed and attenuation of seafloor sand sediment. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 40(4):969-980.