Date Log
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
Isolation of H2S-generating Bacterium (Desulfovibrio sp.) and Vibrio parahaemolyticus From Aquatic Farming and In Vitro Evaluation of the Ability of Bacteriophages as Biocontrol
Corresponding Author(s) : Truong Thi Bich Van
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan,
Vol. 17 No. 1 (2025): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Highlight Research
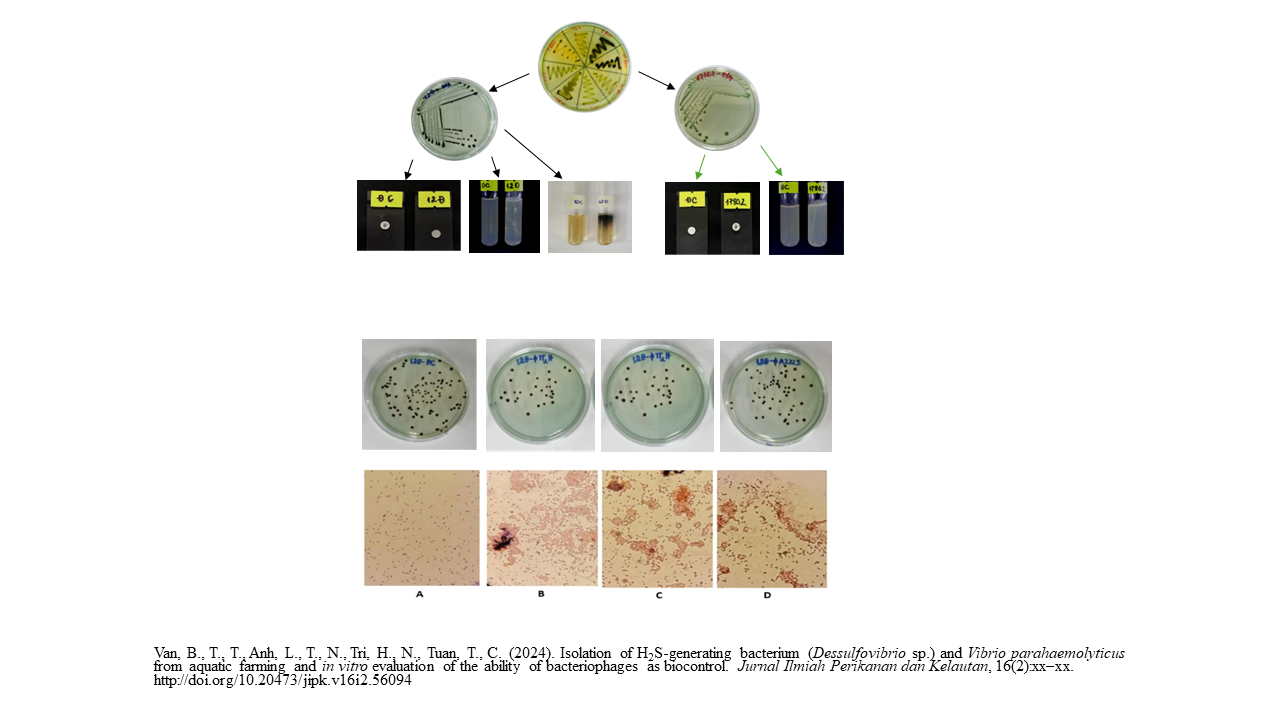
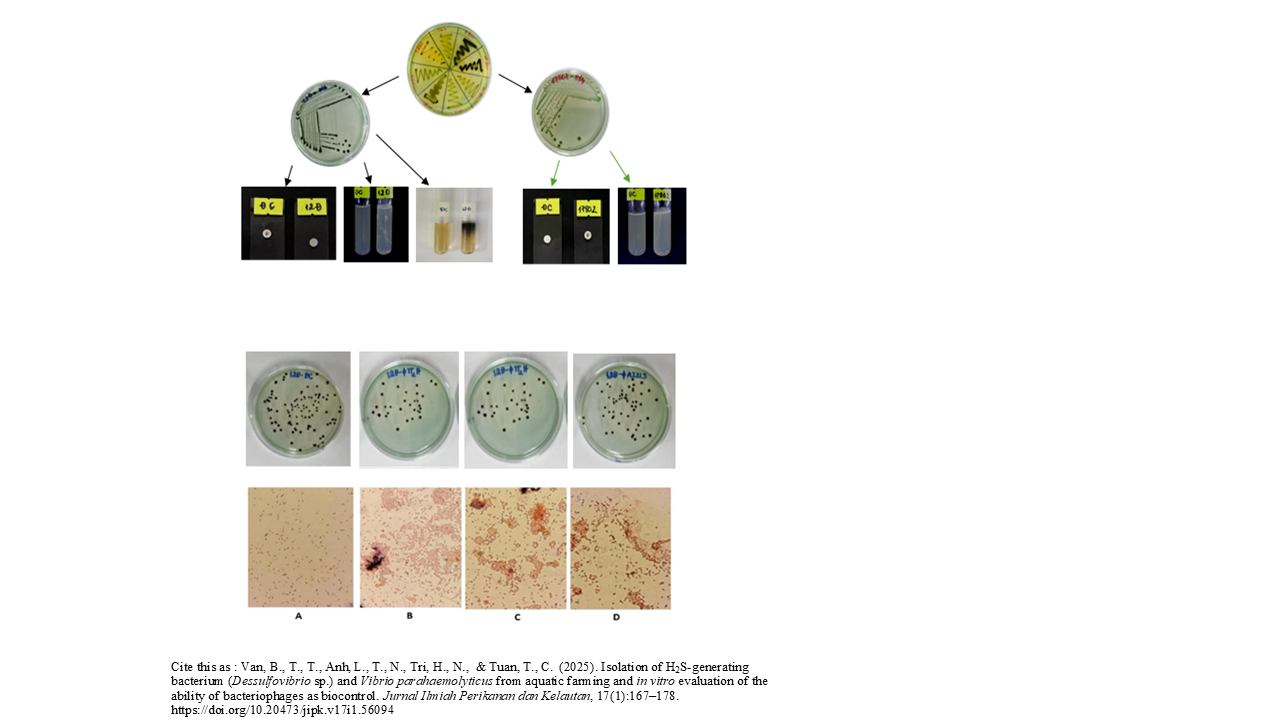
- H2S-generating bacterium (Desulfovibrio) and Vibrio sp. Were idenfied and surveyed its charecteristics.
- Bacteriophages, ɸTT1H, ɸTT2H, and ɸA2223, could reduce Desulfovibrio vulgaris and Vibrio parahaemolyticus colony sizes and change the bacterial shapes.
- The bacteriophages could not reduce Desulfovibrio vulgaris and Vibrio parahaemolyticus colony quantity.
- The bacteriophages affected neither the nucleotide sequence ToxR genes of Vibrio parahaemolyticus nor the 16S rRNA of Desulfovibrio vulgaris.
Abstract
Shrimp farming is an important industry in many countries. However, the leftover feed in shrimp ponds can create harmful compounds like H2S and provide a breeding ground for Vibrio bacteria, which causes acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Antibiotics are commonly used to treat this disease, but they can lead to bacterial resistance and environmental pollution. Therefore, using bacteriophages as a treatment option is a more sustainable approach. The present study aimed to isolate H2S-generating bacteria and bacteriophages capable of inhibiting Vibrio sp. and Desulfovibrio sp. from shrimp pond water. Bacteria were identified through biochemical and molecular biology tests. The study utilized plaque and spread methods to observe changes in bacterial number and colony morphology. The study successfully isolated the bacterial strain Desulfovibrio vulgaris (12D) from shrimp ponds. Three potential bacteriophage strains, ɸTT1H, ɸTT2H, and ɸA2223, were identified that have the ability to inhibit Desulfovibrio vulgaris and V. parahaemolyticus bacteria by altering the size, shape, and number of colonies in treatments supplemented with phages. Although they do not alter the nucleotide sequence of these two bacterial strains, they still have a significant effect on controlling the bacterial population. Among the three potential bacteriophage lineages, ɸTT2H was able to inhibit Desulfovibrio vulgaris, reducing the colony quantity by 2.9%. This research allowed researchers to apply bacteriophages to shrimp culture.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- A. Al-Tayyar, T., A. Al-Allaf, M., & A. Mohammad, G. (2018). Isolation and Identification of Desulfovibrio spp. From Hammam Al-Alel and Study some of the Environmental Properties of the Water in This Region. Rafidain Journal of Science, 27(2):1–11.
- Abdelaziz, M., Ibrahem, M. D., Ibrahim, M. A., Abu-Elala, N. M., & Abdel-moneam, D. A. (2017). Monitoring of different vibrio species affecting marine fishes in Lake Qarun and Gulf of Suez: Phenotypic and molecular characterization. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 43(2):141–146.
- Alcaide, E., Amaro, C., Todolí, R., & Oltra, R. (1999). Isolation and characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing infection in Iberian toothcarp Aphanius iberus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 35(1):77–80.
- Aryal, S. (2015a, June 24). Catalase Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Result Interpretation with Precautions. Microbiology Info.Com.
- Aryal, S. (2015b, July 1). Oxidase Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Types, Result Interpretation... Microbiology Info.Com.
- Dutta, D., Kaushik, A., Kumar, D., & Bag, S. (2021). Foodborne Pathogenic Vibrios: Antimicrobial Resistance. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12(1):1-10.
- Dy, R. L., Richter, C., Salmond, G. P. C., & Fineran, P. C. (2014). Remarkable Mechanisms in Microbes to Resist Phage Infections. Annual Review of Virology, 1(1):307–331.
- Fujihara T., Kimura K., Matsuo H., Sada R. M., Hamaguchi S., Yamamoto G., Yamakura T., & Kutsuna S. (n.d.). Aneurysm Infection Caused by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans 29(8):1680-1681. Emerging Infectious Diseases journal—CDC.
- Gummalla, V. S., Zhang, Y., Liao, Y.-T., & Wu, V. C. H. (2023). The Role of Temperate Phages in Bacterial Pathogenicity. Microorganisms, 11(3):541-554.
- Gxalo, O., Digban, T. O., Igere, B. E., Olapade, O. A., Okoh, A. I., & Nwodo, U. U. (2021). Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Characteristics of Vibrio Isolates From Rustic Environmental Freshwaters. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 11(1):1-12.
- Hao, O. J., Chen, J. M., Huang, L., & Buglass, R. L. (1996). Sulfate‐reducing bacteria. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 26(2):155–187.
- Himanshu, R. Prudencio, C., da Costa, A. C., Leal, E., Chang, C.-M., & Pandey, R. P. (2022). Systematic Surveillance and Meta-Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance and Food Sources from China and the USA. Antibiotics, 11(11):1-15.
- Hsu, T.-K., Shih, H.-Y., Huang, H.-J., Hsu, J. C.-K., Wang, H.-C., Chen, Y.-Y., & Chen, L.-L. (2024). Isolation and characterization of the novel phage BP14 for lysing Vibrio parahaemolyticus and reducing virulence proteins. Aquaculture, 581(5):1-16.
- Huynh, T. G., Vu, H. H., Phan, T. C. T., Pham, T. T. N., & Vu, N. U. (2021). Characterizations of sulfur oxidizing bacteria from extensive shrimp ponds. Can Tho University Journal of Science, 13(2):1–10.
- Koonjan, S., Cardoso Palacios, C., & Nilsson, A. S. (2022). Population Dynamics of a Two Phages–One Host Infection System Using Escherichia coli Strain ECOR57 and Phages vB_EcoP_SU10 and vB_EcoD_SU57. Pharmaceuticals, 15(3):1-20.
- Labrie, S. J., Samson, J. E., & Moineau, S. (2010). Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 8(5):317–327.
- Lee, J. H., Oh, M., & Kim, B. S. (2023). Phage biocontrol of zoonotic food-borne pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus for seafood safety. Food Control, 144(2):1-11.
- Li, Z., Ren, Y., Wang, Z., Qi, Z., Murtaza, B., & Ren, H. (2023). Characterization and genomic analysis of the vibrio phage R01 lytic to Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture Reports, 30(3):1-7.
- Mancini, M. E., Alessiani, A., Donatiello, A., Didonna, A., D’Attoli, L., Faleo, S., Occhiochiuso, G., Carella, F., Di Taranto, P., Pace, L., Rondinone, V., Damato, A. M., Coppola, R., Pedarra, C., & Goffredo, E. (2023). Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms, 11(450):1-14.
- Montieri, S., Suffredini, E., Ciccozzi, M., & Croci, L. (2010). Phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus isolates based on toxR gene sequence. New Microbiology, 33(4):359-372.
- Nguyen, K. C. T., Truong, P. H., Thi, H. T., Ho, X. T., & Nguyen, P. V. (2024). Prevalence, multidrug resistance, and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives, 15(1):56–67.
- Pelzek, A. J., Schuch, R., Schmitz, J. E., & Fischetti, V. A. (2013). Isolation, Culture, and Characterization of Bacteriophages. Current Protocols Essential Laboratory Techniques, 7(1):441-4433.
- Pepi, M., & Focardi, S. (2021). Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Aquaculture and Climate Change: A Challenge for Health in the Mediterranean Area. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(11):1-31.
- Rostøl, J. T., & Marraffini, L. (2019). (Ph)ighting phages – how bacteria resist their parasites. Cell Host & Microbe, 25(2):184–194.
- Schwechheimer, C., & Kuehn, M. J. (2015). Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: Biogenesis and functions. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 13(10):605–619.
- Simmons, E. L., Drescher, K., Nadell, C. D., & Bucci, V. (2018). Phage mobility is a core determinant of phage–bacteria coexistence in biofilms. The ISME Journal, 12(2):532–543.
- Spriewald, S., Stadler, E., Hense, B. A., Münch, P. C., McHardy, A. C., Weiss, A. S., Obeng, N., Müller, J., & Stecher, B. (2020). Evolutionary Stabilization of Cooperative Toxin Production through a Bacterium-Plasmid-Phage Interplay. mBio, 11(4):1-18.
- Tan, C. W., Rukayadi, Y., Hasan, H., Thung, T. Y., Lee, E., Rollon, W. D., Hara, H., Kayali, A. Y., Nishibuchi, M., & Radu, S. (2020). Prevalence and antibiotic resistance patterns of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from different types of seafood in Selangor, Malaysia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 27(6):1602–1608.
- Van, T. T. B., & Thu, T. V. M. (2023). Isolation of toxic gas-producing bacteria (Desulfovibrio spp.) from shrimp ponds and potential of bacteriophages as biocontrol. Journal of Applied Biology and Biotechnology, 11(6):59–65.
- Warren, Y. A., Citron, D. M., Merriam, C. V., & Goldstein, E. J. C. (2005). Biochemical Differentiation and Comparison of Desulfovibrio Species and Other Phenotypically Similar Genera. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 43(8):4041–4045.
- Xu, Y., Sun, J., Hu, J., Bao, Z., & Wang, M. (2023). Characterization and Preliminary Application of a Novel Lytic Vibrio parahaemolyticus Bacteriophage vB_VpaP_SJSY21. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24):1-15.
References
A. Al-Tayyar, T., A. Al-Allaf, M., & A. Mohammad, G. (2018). Isolation and Identification of Desulfovibrio spp. From Hammam Al-Alel and Study some of the Environmental Properties of the Water in This Region. Rafidain Journal of Science, 27(2):1–11.
Abdelaziz, M., Ibrahem, M. D., Ibrahim, M. A., Abu-Elala, N. M., & Abdel-moneam, D. A. (2017). Monitoring of different vibrio species affecting marine fishes in Lake Qarun and Gulf of Suez: Phenotypic and molecular characterization. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 43(2):141–146.
Alcaide, E., Amaro, C., Todolí, R., & Oltra, R. (1999). Isolation and characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing infection in Iberian toothcarp Aphanius iberus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 35(1):77–80.
Aryal, S. (2015a, June 24). Catalase Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Result Interpretation with Precautions. Microbiology Info.Com.
Aryal, S. (2015b, July 1). Oxidase Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Types, Result Interpretation... Microbiology Info.Com.
Dutta, D., Kaushik, A., Kumar, D., & Bag, S. (2021). Foodborne Pathogenic Vibrios: Antimicrobial Resistance. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12(1):1-10.
Dy, R. L., Richter, C., Salmond, G. P. C., & Fineran, P. C. (2014). Remarkable Mechanisms in Microbes to Resist Phage Infections. Annual Review of Virology, 1(1):307–331.
Fujihara T., Kimura K., Matsuo H., Sada R. M., Hamaguchi S., Yamamoto G., Yamakura T., & Kutsuna S. (n.d.). Aneurysm Infection Caused by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans 29(8):1680-1681. Emerging Infectious Diseases journal—CDC.
Gummalla, V. S., Zhang, Y., Liao, Y.-T., & Wu, V. C. H. (2023). The Role of Temperate Phages in Bacterial Pathogenicity. Microorganisms, 11(3):541-554.
Gxalo, O., Digban, T. O., Igere, B. E., Olapade, O. A., Okoh, A. I., & Nwodo, U. U. (2021). Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Characteristics of Vibrio Isolates From Rustic Environmental Freshwaters. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 11(1):1-12.
Hao, O. J., Chen, J. M., Huang, L., & Buglass, R. L. (1996). Sulfate‐reducing bacteria. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 26(2):155–187.
Himanshu, R. Prudencio, C., da Costa, A. C., Leal, E., Chang, C.-M., & Pandey, R. P. (2022). Systematic Surveillance and Meta-Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance and Food Sources from China and the USA. Antibiotics, 11(11):1-15.
Hsu, T.-K., Shih, H.-Y., Huang, H.-J., Hsu, J. C.-K., Wang, H.-C., Chen, Y.-Y., & Chen, L.-L. (2024). Isolation and characterization of the novel phage BP14 for lysing Vibrio parahaemolyticus and reducing virulence proteins. Aquaculture, 581(5):1-16.
Huynh, T. G., Vu, H. H., Phan, T. C. T., Pham, T. T. N., & Vu, N. U. (2021). Characterizations of sulfur oxidizing bacteria from extensive shrimp ponds. Can Tho University Journal of Science, 13(2):1–10.
Koonjan, S., Cardoso Palacios, C., & Nilsson, A. S. (2022). Population Dynamics of a Two Phages–One Host Infection System Using Escherichia coli Strain ECOR57 and Phages vB_EcoP_SU10 and vB_EcoD_SU57. Pharmaceuticals, 15(3):1-20.
Labrie, S. J., Samson, J. E., & Moineau, S. (2010). Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 8(5):317–327.
Lee, J. H., Oh, M., & Kim, B. S. (2023). Phage biocontrol of zoonotic food-borne pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus for seafood safety. Food Control, 144(2):1-11.
Li, Z., Ren, Y., Wang, Z., Qi, Z., Murtaza, B., & Ren, H. (2023). Characterization and genomic analysis of the vibrio phage R01 lytic to Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture Reports, 30(3):1-7.
Mancini, M. E., Alessiani, A., Donatiello, A., Didonna, A., D’Attoli, L., Faleo, S., Occhiochiuso, G., Carella, F., Di Taranto, P., Pace, L., Rondinone, V., Damato, A. M., Coppola, R., Pedarra, C., & Goffredo, E. (2023). Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms, 11(450):1-14.
Montieri, S., Suffredini, E., Ciccozzi, M., & Croci, L. (2010). Phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus isolates based on toxR gene sequence. New Microbiology, 33(4):359-372.
Nguyen, K. C. T., Truong, P. H., Thi, H. T., Ho, X. T., & Nguyen, P. V. (2024). Prevalence, multidrug resistance, and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives, 15(1):56–67.
Pelzek, A. J., Schuch, R., Schmitz, J. E., & Fischetti, V. A. (2013). Isolation, Culture, and Characterization of Bacteriophages. Current Protocols Essential Laboratory Techniques, 7(1):441-4433.
Pepi, M., & Focardi, S. (2021). Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Aquaculture and Climate Change: A Challenge for Health in the Mediterranean Area. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(11):1-31.
Rostøl, J. T., & Marraffini, L. (2019). (Ph)ighting phages – how bacteria resist their parasites. Cell Host & Microbe, 25(2):184–194.
Schwechheimer, C., & Kuehn, M. J. (2015). Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: Biogenesis and functions. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 13(10):605–619.
Simmons, E. L., Drescher, K., Nadell, C. D., & Bucci, V. (2018). Phage mobility is a core determinant of phage–bacteria coexistence in biofilms. The ISME Journal, 12(2):532–543.
Spriewald, S., Stadler, E., Hense, B. A., Münch, P. C., McHardy, A. C., Weiss, A. S., Obeng, N., Müller, J., & Stecher, B. (2020). Evolutionary Stabilization of Cooperative Toxin Production through a Bacterium-Plasmid-Phage Interplay. mBio, 11(4):1-18.
Tan, C. W., Rukayadi, Y., Hasan, H., Thung, T. Y., Lee, E., Rollon, W. D., Hara, H., Kayali, A. Y., Nishibuchi, M., & Radu, S. (2020). Prevalence and antibiotic resistance patterns of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from different types of seafood in Selangor, Malaysia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 27(6):1602–1608.
Van, T. T. B., & Thu, T. V. M. (2023). Isolation of toxic gas-producing bacteria (Desulfovibrio spp.) from shrimp ponds and potential of bacteriophages as biocontrol. Journal of Applied Biology and Biotechnology, 11(6):59–65.
Warren, Y. A., Citron, D. M., Merriam, C. V., & Goldstein, E. J. C. (2005). Biochemical Differentiation and Comparison of Desulfovibrio Species and Other Phenotypically Similar Genera. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 43(8):4041–4045.
Xu, Y., Sun, J., Hu, J., Bao, Z., & Wang, M. (2023). Characterization and Preliminary Application of a Novel Lytic Vibrio parahaemolyticus Bacteriophage vB_VpaP_SJSY21. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24):1-15.