Date Log
Copyright (c) 2023 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
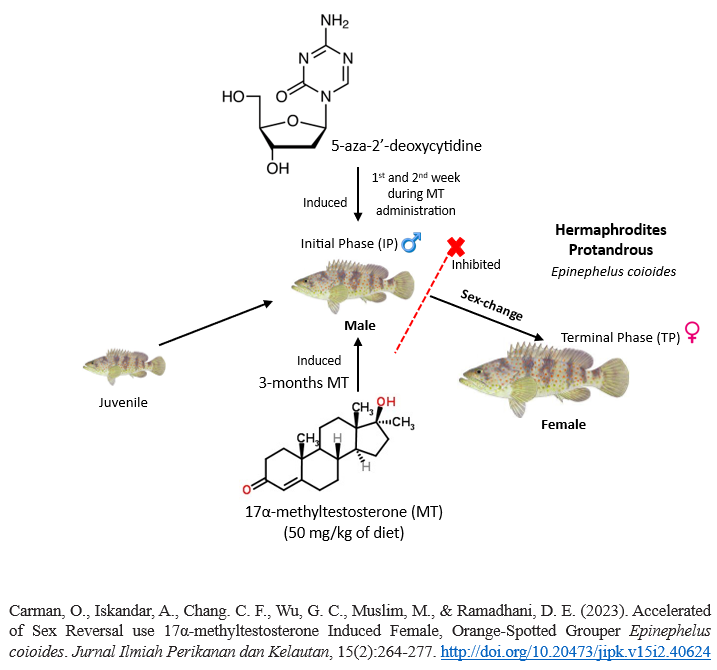
Accelerated of Sex Reversal use 17α-methyltestosterone Induced Female, Orange-Spotted Grouper Epinephelus coioides
Corresponding Author(s) : Odang Carman
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 15 No. 2 (2023): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
Highlight Research
- Sex reversal for orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides
- The application of 17α-methyltestosterone induce sex change
- The stability of sex change need more investigation
Abstract
The occurance of hermaphrodites in grouper fish causes a scarcity of male parents, so an alternative is needed to accelerate sexchange to male at a young age. The present study was expected to scrutinize the mechanisms of sex-change in fish in the early change process, and whether the testis converted from immature ovary using 17α-methyltestosterone (MT) would recover after the termination of MT treatment. MT-induced sex-change and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-Aza) were connected as DNA methylation inhibitors to comprehend the alternation of gonadal soma cells. The orange-spotted groupers were used at the developmental ages and fed a diet containing MT at 50 mg/kg for three months and then a normal diet for a month. In the first week and second week fish injected with 5-Aza intraperitoneally during the MT-oral administration. Most of the fishes in the control group had immature ovaries, but all the females fed with MT, had immature spermatogenesis. However, one month after the withdrawal of MT treatment, the sex of the fish returned to female-like even though the fish have undergone MT-induced masculinization. This outcome demonstrates precocious sex-change from under yearling, orange-spotted grouper utilizing oral MT treatment is impermanent. All the females of 5-aza treatments showed no spermatogenic cells. In this study, lower growth rates were demonstrated by the MT-treated groups. The impact of this metabolic change was clear after the end of the hormone oral administration since the decreased growth of the groups treated for three months.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Aarabi, M., Modarressi, M. H., Soltanghoraee, H., Behjati, R., Amirjannati, N., & Akhondi, M. M. (2006). Testicular expression of synaptonemal complex protein 3 (SYCP3) messenger ribonucleic acid in 110 patients with nonobstructive azoospermia. Fertility and Sterility, 86(2):325-331.
- Achmad, D. S., Gani, S., Ardiansyah, W., Mokognita, M. M., Nurdin, M. S., Jompa, J., Indrianti, M. A., Achmad, N. (2022). Population dynamics of reef fish in the Kwandang Bay, Sulawesi Sea, Indonesia. Biodiversitas, 23(10):5217-5226.
- Ajani, P. A., Henriquez-Nunez, H. F., Verma, A., Nagai, S., Uchida, H., Tesoriero, M. J., Farrell, H., Zammit, A., Brett, S., & Murray, S. A. (2022). Mapping the development of a Dinophysis bloom in a shellfish aquaculture area using a novel molecular qPCR assay. Harmful Algae, 116:102253.
- Alonso-Fernandez, A., Also, J., Grau, A., Dominguez-Petit, R., Saborido-Rey, F. (2011). The use of histological technuques to study the reproductive biology of the hermaphroditic Mediterranean fishes Coris julis, Serranus scriba, and Diplodus annularis. Marine and Coastal Fisheries: Dynamics, Management, and Ecosystem Science, 3(1):145-159.
- Aoki, Y., Nakamura, S., Ishikawa, Y., & Tanaka, M. (2009). Expression and syntenic analyses of four nanos genes in medaka. Zoological Science, 26(2):112-118.
- Bancroft, J. D., & Cook, H. C. (1994). Manual of histological techniques and their diagnostic application. London: Churchill Livingstone.
- Bellaiche, J., Lareyre, J.-J., Cauty, C., Yano, A., Allemand, I., & Le Gac, F. (2014). Spermatogonial stem cell quest: nanos2, marker of a subpopulation of undifferentiated A spermatogonia in trout testis. Biology of Reproduction, 90(4):71-79.
- Bhandari, R. K., Nakamura, M., Kobayashi, T., & Nagahama, Y. (2006). Suppression of steroidogenic enzyme expression during androgen-induced sex reversal in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 145(1):20-24.
- Blazer, V. S. (2002). Histopathological assessment of gonadal tissue in wild fishes. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 26:85-101.
- Blázquez, M., Piferrer, F., Zanuy, S., Carrillo, M., & Donaldson, E. M. (1995). Development of sex control techniques for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) aquaculture: Effects of dietary 17 α-methyltestosterone prior to sex differentiation. Aquaculture, 135(4):329-342.
- Cardwell, J. R., & Liley, N. R. (1991). Hormonal control of sex and color change in the stoplight parrotfish, Sparisoma viride. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 81(1):7-20.
- Chan, S. T. H., & Yeung, W. S. B. (1983). 4 sex control and sex reversal in fish under natural conditions. Fish Physiology, 9(Part B):171-222.
- Chang, C. F., Lau, E. L., & Lin, B. Y. (1995). Estradiol-17β suppresses testicular development and stimulates sex reversal in protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 14(6):481-488.
- Chen, F. Y., Chow, M., Chao, T. M., & Lim, R. (1977). Artificial spawning and larval rearing of the grouper, Epinephelus tauvina (Forskal) in Singapore. Singapore Journal of Primary Industries, 5(1):1-21.
- Devlin, R. H., & Nagahama, Y. (2002). Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture, 208(3–4):191-364.
- Donaldson, E. M., Fagerlund, U. H. M., Higgs, D. A., & McBride, J. R. (1979). Hormonal enhancement of growth. In W. S. Hoar, D. J. Randall, & J. R. Brett (Ed.), Fish Physiology, Vol. VIII: Bioenergetics and Growth. (pp. 455-597). New York: Academic Press.
- Forbes, A., & Lehmann, R. (1998). Nanos and Pumilio have critical roles in the development and function of Drosophila germline stem cells. Development, 125(4):679-690.
- Frisch, A. (2004). Sex-change and gonadal steroids in sequentially-hermaphroditic teleost fish. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 14(4):481-499.
- Han, Y., Peng, C., Wang, L., Guo, J., Lu, M., Chen, J., Liu, Y., Li, S., Zhao, M., Zhang, Y., & Lin, H. (2018). Female-to-male sex reversal in orang-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) caused by overexpressing of Amh in vivo. Biology of Reproduction, 99(6):1205-1215.
- Heemstra, P. C., & Randall, J. E. (1993). FAO species catalogue: Vol. 16 groupers of the world (family Serranidae, subfamily Epinephelinae). Rome: FAO.
- Huang, S., Wu, Y., Chen, K., Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Luo, Q., Liu, H., Wang, F., Li, K., Fei, S., Zhang, X., & Ou, M. (2023). Gene expression and epigenetic modification of aromatase during sex reversal and gonadal development in blotched snakehead (Channa maculate). Fishes, 8(129):1-16.
- Huang, T., Gu, W., Liu, E., Shi, X., Wang, B., Wu, W, Dong, F., & Xu, G. (2021). Comprehensive analysis of miRNA-mRNA/IncRNA during gonadal development of triploid female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Genomics, 113(6):3533-3543.
- Humason, G. L. (1979). Animal tissue techniques. San Fransisco: W.H. Freeman and Company.
- Iwai, T., Yoshii, A., Yokota, T., Sakai, C., Hori, H., Kanamori, A., & Yamashita, M. (2006). Structural components of the synaptonemal complex, SYCP1 and SYCP3, in the medaka fish Oryzias latipes. Experimental Cell Research, 312(13):2528-2537.
- Kajiura"Kobayashi, H., Kobayashi, T., & Nagahama, Y. (2005). Cloning of cDNAs and the differential expression of A"type cyclins and Dmc1 during spermatogenesis in the Japanese eel, a teleost fish. Developmental Dynamics: An Official Publication of the American Association of Anatomists, 232(4):1115-1123.
- Kitano, T., Takamune, K., Nagahama, Y., & Abe, S. (2000). Aromatase inhibitor and 17α"methyltestosterone cause sex"reversal from genetical females to phenotypic males and suppression of P450 aromatase gene expression in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Molecular Reproduction and Development: Incorporating Gamete Research, 56(1):1-5.
- Koulish, S., & Kramer, C. R. (1989). Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) induces gonad reversal in a protogynous fish, the bluehead wrasse, Thalassoma bifasciatum (Teleostei, Labridae). Journal of Experimental Zoology, 252(2):156-168.
- Kramer, C. R., Koulish, S., & Bertacchi, P. L. (1988). The effects of testosterone implants on ovarian morphology in the bluehead wrasse, Thalassoma bifasciatum (Bloch) (Teleostei: Labridae). Journal of Fish Biology, 32(3):397-407.
- Kroon, F. J., & Liley, N. R. (2000). The role of steroid hormones in protogynous sex change in the blackeye goby, Coryphopterus nicholsii (Teleostei: Gobiidae). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 118(2):273-283.
- Kuo, C. M., Ting, Y. Y., & Yeh, S. L. (1988). Induced sex reversal and spawning of blue-spotted grouper, Epinephelus fario. Aquaculture, 74(1–2):113-126.
- Li, Y., Liu, F. (2021). DNA methylation rehapes sex development in zebrafish. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 19: 44-47.
- Li, G. L., Liu, X. C., & Lin, H. R. (2006). Effects of aromatizable and nonaromatizable androgens on the sex inversion of red-spotted grouper (Epinephelus akaara). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 32(1):25-33.
- Liu, M., & Sadovy, Y. J. (2008). Grouper mariculture in mainland China and Hong Kong. Hongkong: World Aquaculture Society.
- Muniasamy, S., Benziger, P. S. S, Kumar, Y. A, Haniffa, M. A, Paray, B. A, Albeshr, M. F., & Al-Umri, S. (2019). Effect of 17-α-methyl testosterone incorporated diets on growth of spotted snakehead, Channa punctatus and white carp, Cirrihinus mrigala. Saudi Journal of Biological Science, 26(3):541-546.
- Murata, R., Kobayashi, Y., Karimata, H., Kishimoto, K., Kimura, M., & Nakamura, M. (2014). Transient sex change in the immature Malabar grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus, androgen treatment. Biology of Reproduction, 91(1):21-25.
- Nakamura, M., Alam, M. A., Kobayashi, Y., & Bhandari, R. K. (2007). Role of sex hormones in sex change of grouper. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 15:23-27.
- Nakamura, M., Bhandari, R. K., & Higa, M. (2003). The role estrogens play in sex differentiation and sex changes of fish. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 28(1):113-117.
- Nakamura, S., Kobayashi, K., Nishimura, T., Higashijima, S., & Tanaka, M. (2010). Identification of germline stem cells in the ovary of the teleost medaka. Science, 328(5985):1561-1563.
- Navarro-Martin, L., Vinas, J., Ribas, L., Diaz, N., Gutierrez, A., Croce, L. D., Piferrer, F. (2011). DNA methylation of the gonadal aromatase (cyp19a) promotor is involved in temperature-dependent sex ratio shifts in the European sea bass. PloS Genetics, 12:1002447.
- Nirmala, A. R. C., & Pandian, T. J. (1983). Effect of steroid injection on food utilization in Channa striatus. Proceedings: Animal Science, 92:221-229.
- Oh, S. R., Kang, H. C., Lee, C. H., Hur, S. W., & Lee, Y. D. (2013). Sex reversal and masculinization according to growth in longtooth grouper Epinephelus bruneus. Development & Reproduction, 17(2):79-85.
- Overturf, K. (2009). Molecular research in aquaculture. New Jersey: Blackwell Publishing.
- Parra, M. T., Viera, A., Gómez, R., Page, J., Benavente, R., Santos, J. L., Rufas, J. S., & Suja, J. A. (2004). Involvement of the cohesin Rad21 and SCP3 in monopolar attachment of sister kinetochores during mouse meiosis I. Journal of Cell Science, 117(7):1221-1234.
- Qin, Q., Zhou, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, M., Qin, H., Zhao, C., & Liu, S. (2019). Analysis on the meiosis-related gene (Dmc1, Ph1) expression in autotriploid Carassius auratus. Marine Biotechnology, 21(6):754-761.
- Quinitio, G. F., Caberoy, N. B., & Reyes, D. M. (1997). Induction of sex change in female Epinephelus coioides by social control. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture - Bamidgeh, 49(2):77-83.
- Ribas, L., Vanezis, K., Imues, M. A., Piferrer, F. (2017). Treatment with a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor feminizes zebrafish and induces long-term expression changes in the gonads. Epigenetic & Chromatin, 10(59):1-16.
- Roeder, G. S. (1997). Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango. Genes & Development, 11(20):2600-2621.
- Sada, A., Suzuki, A., Suzuki, H., & Saga, Y. (2009). The RNA-binding protein NANOS2 is required to maintain murine spermatogonial stem cells. Science, 325(5946):1394-1398.
- Sundaray, J. K., Dixit, S., Rather, A., Rasal, K. D., & Sahoo, L. (2022). Aquaculture omics: An update on the current status of research and data analysis. Marine Genomics, 64:100967.
- Tan-Fermin, J. D. (1992). Withdrawal of exogenous 17-alpha methyltestosterone causes reversal of sex-inversed male grouper Epinephelus suillus (Valenciennes). The Philippine Scientist, 29:33-39.
- Tan-Fermin, J. D., Garcia, L. M. B., & Castillo, A. R. (1994). Induction of sex inversion in juvenile grouper, Epinephelus suillus (Valenciennes) by injections of 17α-methyltestosterone. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology, 40(4):413-420.
- Tao, Y. X., Lin, H. R., Van Der Kraak, G., & Peter, R. E. (1993). Hormonal induction of precocious sex reversal in the ricefield eel, Monopterus albus. Aquaculture, 118(1–2):131-140.
- Tsuda, M., Sasaoka, Y., Kiso, M., Abe, K., Haraguchi, S., Kobayashi, S., & Saga, Y. (2003). Conserved role of nanos proteins in germ cell development. Science, 301(5637):1239-1241.
- Vatheeswaran, S., & Ali, S. A. (1986). Evaluation certain Substances as growth – promoting agents drawn Penaeus indicus. Indian Journal of Fisheries, 33:95-100.
- Wang Q, Liu Y, Peng C, Wang X, Xiao L, Wang D, Chen J, Zhang H, Zhao H, Li S, Zhang Y, & Lin H. (2017). Molecular regulation of sex change induced by methyltestosterone-feeding and methyltestosterone-feeding withdrawal in the protogynous orange-spotted grouper. Biology of Reproduction, 97(2):324-333.
- Wu, G. C., Tey, W. G., Li, H. W., & Chang, C. F. (2015). Sexual fate reprogramming in the steroid-induced bi-directional sex change in the protogynous orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. PLoS One, 10(12):e0145438.
- Yeh, S. L., Kuo, C. M., Ting, Y. Y., & Chang, C. F. (2003). Androgens stimulate sex change in protogynous grouper, Epinephelus coioides: spawning performance in sex-changed males. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 135(3):375-382.
- Yamazaki, I. (1976). Application of hormones in fish culture. Journal of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 33(4):948-958.
- You, X., Shan, X., & Shi, Q. (2020). Research advances in the genomics and applications for molecular breeding of aquaculture animals. Aquaculture, 526:735357.
- Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, L., Zhu, T., Tian, J., Li, X., & Lin, H. (2004). Two distinct cytochrome P450 aromatases in the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides): cDNA cloning and differential mRNA expression. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 92(1–2):39-50.
- Zhu, Q., Han, C., Liu, S., Ouyang, S., Liu, D., Zhang, Z., Huang, J., Han, L., Li, S., Li, G., Lin, H., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Development and gene expression analysis of gonad during 17α-methyltestosterone-induced sex reversal in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquaculture Reports, 23:101049.
References
Aarabi, M., Modarressi, M. H., Soltanghoraee, H., Behjati, R., Amirjannati, N., & Akhondi, M. M. (2006). Testicular expression of synaptonemal complex protein 3 (SYCP3) messenger ribonucleic acid in 110 patients with nonobstructive azoospermia. Fertility and Sterility, 86(2):325-331.
Achmad, D. S., Gani, S., Ardiansyah, W., Mokognita, M. M., Nurdin, M. S., Jompa, J., Indrianti, M. A., Achmad, N. (2022). Population dynamics of reef fish in the Kwandang Bay, Sulawesi Sea, Indonesia. Biodiversitas, 23(10):5217-5226.
Ajani, P. A., Henriquez-Nunez, H. F., Verma, A., Nagai, S., Uchida, H., Tesoriero, M. J., Farrell, H., Zammit, A., Brett, S., & Murray, S. A. (2022). Mapping the development of a Dinophysis bloom in a shellfish aquaculture area using a novel molecular qPCR assay. Harmful Algae, 116:102253.
Alonso-Fernandez, A., Also, J., Grau, A., Dominguez-Petit, R., Saborido-Rey, F. (2011). The use of histological technuques to study the reproductive biology of the hermaphroditic Mediterranean fishes Coris julis, Serranus scriba, and Diplodus annularis. Marine and Coastal Fisheries: Dynamics, Management, and Ecosystem Science, 3(1):145-159.
Aoki, Y., Nakamura, S., Ishikawa, Y., & Tanaka, M. (2009). Expression and syntenic analyses of four nanos genes in medaka. Zoological Science, 26(2):112-118.
Bancroft, J. D., & Cook, H. C. (1994). Manual of histological techniques and their diagnostic application. London: Churchill Livingstone.
Bellaiche, J., Lareyre, J.-J., Cauty, C., Yano, A., Allemand, I., & Le Gac, F. (2014). Spermatogonial stem cell quest: nanos2, marker of a subpopulation of undifferentiated A spermatogonia in trout testis. Biology of Reproduction, 90(4):71-79.
Bhandari, R. K., Nakamura, M., Kobayashi, T., & Nagahama, Y. (2006). Suppression of steroidogenic enzyme expression during androgen-induced sex reversal in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 145(1):20-24.
Blazer, V. S. (2002). Histopathological assessment of gonadal tissue in wild fishes. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 26:85-101.
Blázquez, M., Piferrer, F., Zanuy, S., Carrillo, M., & Donaldson, E. M. (1995). Development of sex control techniques for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) aquaculture: Effects of dietary 17 α-methyltestosterone prior to sex differentiation. Aquaculture, 135(4):329-342.
Cardwell, J. R., & Liley, N. R. (1991). Hormonal control of sex and color change in the stoplight parrotfish, Sparisoma viride. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 81(1):7-20.
Chan, S. T. H., & Yeung, W. S. B. (1983). 4 sex control and sex reversal in fish under natural conditions. Fish Physiology, 9(Part B):171-222.
Chang, C. F., Lau, E. L., & Lin, B. Y. (1995). Estradiol-17β suppresses testicular development and stimulates sex reversal in protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 14(6):481-488.
Chen, F. Y., Chow, M., Chao, T. M., & Lim, R. (1977). Artificial spawning and larval rearing of the grouper, Epinephelus tauvina (Forskal) in Singapore. Singapore Journal of Primary Industries, 5(1):1-21.
Devlin, R. H., & Nagahama, Y. (2002). Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture, 208(3–4):191-364.
Donaldson, E. M., Fagerlund, U. H. M., Higgs, D. A., & McBride, J. R. (1979). Hormonal enhancement of growth. In W. S. Hoar, D. J. Randall, & J. R. Brett (Ed.), Fish Physiology, Vol. VIII: Bioenergetics and Growth. (pp. 455-597). New York: Academic Press.
Forbes, A., & Lehmann, R. (1998). Nanos and Pumilio have critical roles in the development and function of Drosophila germline stem cells. Development, 125(4):679-690.
Frisch, A. (2004). Sex-change and gonadal steroids in sequentially-hermaphroditic teleost fish. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 14(4):481-499.
Han, Y., Peng, C., Wang, L., Guo, J., Lu, M., Chen, J., Liu, Y., Li, S., Zhao, M., Zhang, Y., & Lin, H. (2018). Female-to-male sex reversal in orang-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) caused by overexpressing of Amh in vivo. Biology of Reproduction, 99(6):1205-1215.
Heemstra, P. C., & Randall, J. E. (1993). FAO species catalogue: Vol. 16 groupers of the world (family Serranidae, subfamily Epinephelinae). Rome: FAO.
Huang, S., Wu, Y., Chen, K., Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Luo, Q., Liu, H., Wang, F., Li, K., Fei, S., Zhang, X., & Ou, M. (2023). Gene expression and epigenetic modification of aromatase during sex reversal and gonadal development in blotched snakehead (Channa maculate). Fishes, 8(129):1-16.
Huang, T., Gu, W., Liu, E., Shi, X., Wang, B., Wu, W, Dong, F., & Xu, G. (2021). Comprehensive analysis of miRNA-mRNA/IncRNA during gonadal development of triploid female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Genomics, 113(6):3533-3543.
Humason, G. L. (1979). Animal tissue techniques. San Fransisco: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Iwai, T., Yoshii, A., Yokota, T., Sakai, C., Hori, H., Kanamori, A., & Yamashita, M. (2006). Structural components of the synaptonemal complex, SYCP1 and SYCP3, in the medaka fish Oryzias latipes. Experimental Cell Research, 312(13):2528-2537.
Kajiura"Kobayashi, H., Kobayashi, T., & Nagahama, Y. (2005). Cloning of cDNAs and the differential expression of A"type cyclins and Dmc1 during spermatogenesis in the Japanese eel, a teleost fish. Developmental Dynamics: An Official Publication of the American Association of Anatomists, 232(4):1115-1123.
Kitano, T., Takamune, K., Nagahama, Y., & Abe, S. (2000). Aromatase inhibitor and 17α"methyltestosterone cause sex"reversal from genetical females to phenotypic males and suppression of P450 aromatase gene expression in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Molecular Reproduction and Development: Incorporating Gamete Research, 56(1):1-5.
Koulish, S., & Kramer, C. R. (1989). Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) induces gonad reversal in a protogynous fish, the bluehead wrasse, Thalassoma bifasciatum (Teleostei, Labridae). Journal of Experimental Zoology, 252(2):156-168.
Kramer, C. R., Koulish, S., & Bertacchi, P. L. (1988). The effects of testosterone implants on ovarian morphology in the bluehead wrasse, Thalassoma bifasciatum (Bloch) (Teleostei: Labridae). Journal of Fish Biology, 32(3):397-407.
Kroon, F. J., & Liley, N. R. (2000). The role of steroid hormones in protogynous sex change in the blackeye goby, Coryphopterus nicholsii (Teleostei: Gobiidae). General and Comparative Endocrinology, 118(2):273-283.
Kuo, C. M., Ting, Y. Y., & Yeh, S. L. (1988). Induced sex reversal and spawning of blue-spotted grouper, Epinephelus fario. Aquaculture, 74(1–2):113-126.
Li, Y., Liu, F. (2021). DNA methylation rehapes sex development in zebrafish. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 19: 44-47.
Li, G. L., Liu, X. C., & Lin, H. R. (2006). Effects of aromatizable and nonaromatizable androgens on the sex inversion of red-spotted grouper (Epinephelus akaara). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 32(1):25-33.
Liu, M., & Sadovy, Y. J. (2008). Grouper mariculture in mainland China and Hong Kong. Hongkong: World Aquaculture Society.
Muniasamy, S., Benziger, P. S. S, Kumar, Y. A, Haniffa, M. A, Paray, B. A, Albeshr, M. F., & Al-Umri, S. (2019). Effect of 17-α-methyl testosterone incorporated diets on growth of spotted snakehead, Channa punctatus and white carp, Cirrihinus mrigala. Saudi Journal of Biological Science, 26(3):541-546.
Murata, R., Kobayashi, Y., Karimata, H., Kishimoto, K., Kimura, M., & Nakamura, M. (2014). Transient sex change in the immature Malabar grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus, androgen treatment. Biology of Reproduction, 91(1):21-25.
Nakamura, M., Alam, M. A., Kobayashi, Y., & Bhandari, R. K. (2007). Role of sex hormones in sex change of grouper. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 15:23-27.
Nakamura, M., Bhandari, R. K., & Higa, M. (2003). The role estrogens play in sex differentiation and sex changes of fish. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 28(1):113-117.
Nakamura, S., Kobayashi, K., Nishimura, T., Higashijima, S., & Tanaka, M. (2010). Identification of germline stem cells in the ovary of the teleost medaka. Science, 328(5985):1561-1563.
Navarro-Martin, L., Vinas, J., Ribas, L., Diaz, N., Gutierrez, A., Croce, L. D., Piferrer, F. (2011). DNA methylation of the gonadal aromatase (cyp19a) promotor is involved in temperature-dependent sex ratio shifts in the European sea bass. PloS Genetics, 12:1002447.
Nirmala, A. R. C., & Pandian, T. J. (1983). Effect of steroid injection on food utilization in Channa striatus. Proceedings: Animal Science, 92:221-229.
Oh, S. R., Kang, H. C., Lee, C. H., Hur, S. W., & Lee, Y. D. (2013). Sex reversal and masculinization according to growth in longtooth grouper Epinephelus bruneus. Development & Reproduction, 17(2):79-85.
Overturf, K. (2009). Molecular research in aquaculture. New Jersey: Blackwell Publishing.
Parra, M. T., Viera, A., Gómez, R., Page, J., Benavente, R., Santos, J. L., Rufas, J. S., & Suja, J. A. (2004). Involvement of the cohesin Rad21 and SCP3 in monopolar attachment of sister kinetochores during mouse meiosis I. Journal of Cell Science, 117(7):1221-1234.
Qin, Q., Zhou, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, M., Qin, H., Zhao, C., & Liu, S. (2019). Analysis on the meiosis-related gene (Dmc1, Ph1) expression in autotriploid Carassius auratus. Marine Biotechnology, 21(6):754-761.
Quinitio, G. F., Caberoy, N. B., & Reyes, D. M. (1997). Induction of sex change in female Epinephelus coioides by social control. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture - Bamidgeh, 49(2):77-83.
Ribas, L., Vanezis, K., Imues, M. A., Piferrer, F. (2017). Treatment with a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor feminizes zebrafish and induces long-term expression changes in the gonads. Epigenetic & Chromatin, 10(59):1-16.
Roeder, G. S. (1997). Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango. Genes & Development, 11(20):2600-2621.
Sada, A., Suzuki, A., Suzuki, H., & Saga, Y. (2009). The RNA-binding protein NANOS2 is required to maintain murine spermatogonial stem cells. Science, 325(5946):1394-1398.
Sundaray, J. K., Dixit, S., Rather, A., Rasal, K. D., & Sahoo, L. (2022). Aquaculture omics: An update on the current status of research and data analysis. Marine Genomics, 64:100967.
Tan-Fermin, J. D. (1992). Withdrawal of exogenous 17-alpha methyltestosterone causes reversal of sex-inversed male grouper Epinephelus suillus (Valenciennes). The Philippine Scientist, 29:33-39.
Tan-Fermin, J. D., Garcia, L. M. B., & Castillo, A. R. (1994). Induction of sex inversion in juvenile grouper, Epinephelus suillus (Valenciennes) by injections of 17α-methyltestosterone. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology, 40(4):413-420.
Tao, Y. X., Lin, H. R., Van Der Kraak, G., & Peter, R. E. (1993). Hormonal induction of precocious sex reversal in the ricefield eel, Monopterus albus. Aquaculture, 118(1–2):131-140.
Tsuda, M., Sasaoka, Y., Kiso, M., Abe, K., Haraguchi, S., Kobayashi, S., & Saga, Y. (2003). Conserved role of nanos proteins in germ cell development. Science, 301(5637):1239-1241.
Vatheeswaran, S., & Ali, S. A. (1986). Evaluation certain Substances as growth – promoting agents drawn Penaeus indicus. Indian Journal of Fisheries, 33:95-100.
Wang Q, Liu Y, Peng C, Wang X, Xiao L, Wang D, Chen J, Zhang H, Zhao H, Li S, Zhang Y, & Lin H. (2017). Molecular regulation of sex change induced by methyltestosterone-feeding and methyltestosterone-feeding withdrawal in the protogynous orange-spotted grouper. Biology of Reproduction, 97(2):324-333.
Wu, G. C., Tey, W. G., Li, H. W., & Chang, C. F. (2015). Sexual fate reprogramming in the steroid-induced bi-directional sex change in the protogynous orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. PLoS One, 10(12):e0145438.
Yeh, S. L., Kuo, C. M., Ting, Y. Y., & Chang, C. F. (2003). Androgens stimulate sex change in protogynous grouper, Epinephelus coioides: spawning performance in sex-changed males. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 135(3):375-382.
Yamazaki, I. (1976). Application of hormones in fish culture. Journal of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 33(4):948-958.
You, X., Shan, X., & Shi, Q. (2020). Research advances in the genomics and applications for molecular breeding of aquaculture animals. Aquaculture, 526:735357.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, L., Zhu, T., Tian, J., Li, X., & Lin, H. (2004). Two distinct cytochrome P450 aromatases in the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides): cDNA cloning and differential mRNA expression. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 92(1–2):39-50.
Zhu, Q., Han, C., Liu, S., Ouyang, S., Liu, D., Zhang, Z., Huang, J., Han, L., Li, S., Li, G., Lin, H., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Development and gene expression analysis of gonad during 17α-methyltestosterone-induced sex reversal in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquaculture Reports, 23:101049.