
Date Log
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
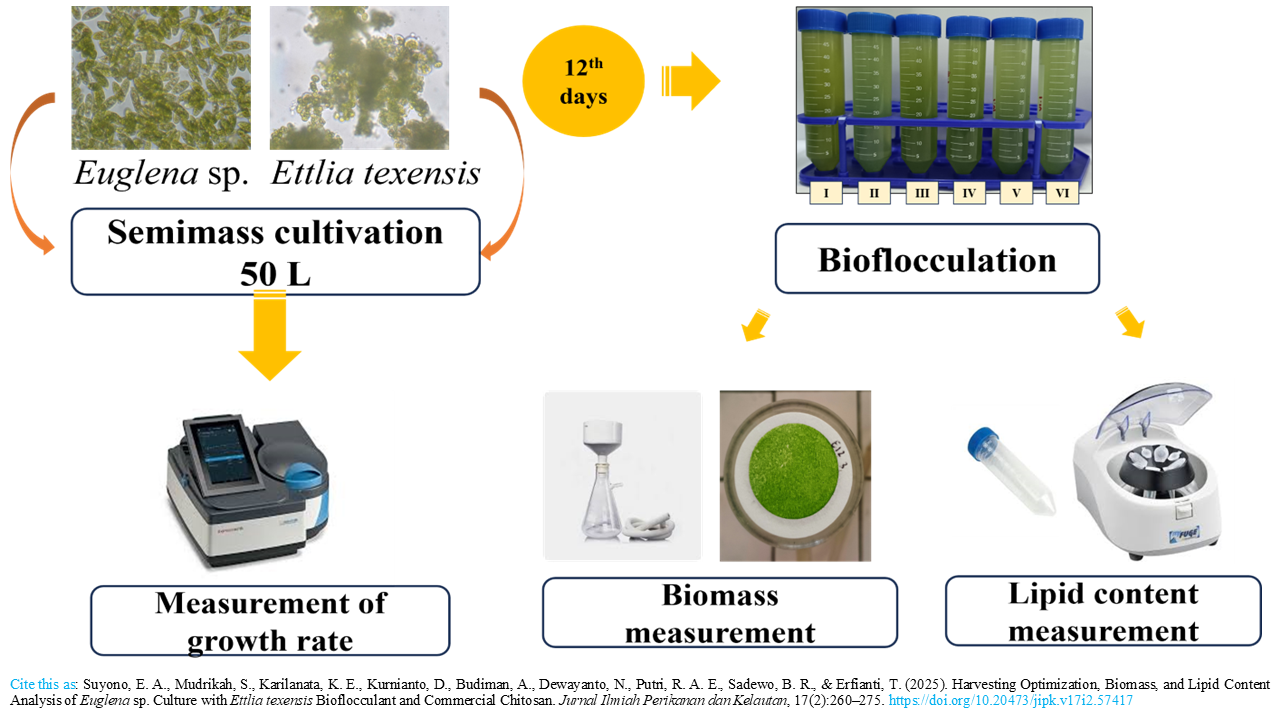
Harvesting Optimization, Biomass, and Lipid Content Analysis of Euglena sp. Culture with Ettlia texensis Bioflocculant and Commercial Chitosan
Corresponding Author(s) : Eko Agus Suyono
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 17 No. 2 (2025): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Highlight Research
- Bioflocculation technique can improve the harvesting effectiveness of semimass culture of Euglena sp.
- The addition of E. texensis can significantly increase the flocculation efficiency of Euglena sp.
- The addition of commercial chitosan was able to increase the flocculation efficiency of Euglena sp.
- The biomass and lipid content produced by Euglena sp. with E. texensis flocculant agent showed higher results than the biomass and lipid content produced by Euglena sp. with commercial chitosan flocculant agent.
Abstract
Euglena sp. has a high potential to be developed as biofuel. However, the high cost and energy required for the harvesting process are hindering the production. Flocculation using natural substances, such as microorganisms and biopolymers, offers a promising solution to minimize energy and production costs, so it is applicable on a mass scale. Ettlia texensis is one of the autoflocculating microalgae that can excrete extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Chitosan is a linear copolymer of D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine produced by the deacetylation of chitin, which is usually exploited by marine crustaceans, shrimp, and crabs. Chitosan has a very high cation load, so it is often used for coagulation or flocculation. This study explores the potential of E. texensis and chitosan as flocculant agents to harvest the mass culture of Euglena sp. by giving different doses E. texensis with 1:0.25 (E3), 1:0.5 (E4), 1:1 (E5), and 1:2 (E6), and chitosan with 1.25 mg (C1), 2.5 mg (C2), 3.75 mg (C3), and 5 mg (C4). This research began with the cultivation of Euglena sp. and E. texensis on a 50 L scale for 12 days. The effectiveness of flocculation was measured by the spectrophotometric method. Based on this research, the best treatment for harvesting Euglena sp. culture by bioflocculation was shown by the addition of chitosan (5 mg) with the recovery of 84.83%, 0.2213 mg/mL biomass, and 0.2117 mg/mL lipid content. Meanwhile, with E. texensis, the best was shown by the ratio of 1:2 with recovery 84.71%, 0.2053 mg/mL biomass, and 0.1753 mg/mL
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Aranaz, I., Alcántara, A. R., Civera, M. C., Arias, C., Elorza, B., Heras Caballero, A. & Acosta, N. (2021). Chitosan: An overview of its properties and applications. Polymers, 13(19):1-22.
- Asiandu, A. P., Nugroho, A. P., Naser, A. S., Sadewo, B. R., Koerniawan, M. D., Budiman, A., Siregar, U. J., Suwanti, L. T., & Suyono, E. A. (2023). The effect of tofu wastewater and ph on the growth kinetics and biomass composition of Euglena sp. Current Applied Science and Technology, 23(2):1-16.
- Babakhani, P., Mahdavi, M. A., Gheshlaghi, R., & Karimian, A. (2022). The shift in carbon source induces pH increase and autoflocculation in microalgal suspensions facilitating multi-approach biomass harvesting. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 12(10):1-12.
- Barros, A. I., Gonçalves, A. L., Simões, M., & Pires, J. C. M. (2015). Harvesting techniques applied to microalgae: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41(1):1489-1500.
- Bligh, E.G. and Dyer, W.J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 37(8):911-917.
- Chang, S. H., Lin, H. T. V., Wu, G. J. & Tsai, G. J. (2015). pH Effects on solubility, zeta potential, and correlation between antibacterial activity and molecular weight of chitosan. Carbohydrate polymers, 134(20):74-81.
- Djunaedi, A. (2016). Microalgae biomass production (Tetraselmis chuii) with different harvesting systems. Jurnal Kelautan Tropis, 18(2):107-111.
- Elcik, H., Karadag, D., Kara, A.I. & Cakmakci, M. (2023). Microalgae biomass harvesting using chitosan flocculant: Optimization of operating parameters by response surface methodology. Separations, 10(9):1-14.
- Erfianti, T., Daryono, B. S., Budiman, A., & Suyono, E. A. (2024). Growth and metabolite enhancement of Acidophile Euglena sp. isolated from Indonesia under different photoperiod cycles. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 16(1):15-30.
- Gris, B., Morosinotto, T., Giacometti, G. M., Bertucco, A., & Sforza, E. (2014). Cultivation of Scenedesmus obliquus in photobioreactors: effects of light intensities and light–dark cycles on growth, productivity, and biochemical composition. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172(5):2377-2389.
- Hadiyanto, H., Widayat, W., Christwardana, M. & Pratiwi, M. E. (2022). The flocculation process of Chlorella sp. using chitosan as a bio-flocculant: Optimization of operating conditions by response surface methodology. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 5(1):1-11.
- Hanief, S., Prasakti, L., Pradana, Y. S., & Cahyono, R. B. (2020). Growth kinetic of. Botryococcus braunii microalgae using logistic and gompertz models. AIP Conference Proceedings, 201(1):1-7.
- Indahsari, H. S., Tassakka, A. C. M. A. R., Dewi, E. N., Yuwono, M., & Suyono, E. A. (2022). Effects of salinity and bioflocculation during Euglena sp. harvest on the production of lipid, chlorophyll, and carotenoid with Skeletonema sp. as a bioflocculant. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 16(4):2901-2911.
- Inwongwan, S., Kruger, N. J., Ratcliffe, R. G., & O’neill, E. C. (2019). Euglena central metabolic pathways and their subcellular locations. Metabolites, 9(6):1-24.
- Khanra, A., Vasistha, S., & Rai, M. P. (2017). Glycerol on lipid enhancement and FAME characterization in algae for raw material of biodiesel. International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, 7(4):1970-1978.
- Kim, M., Lee, B., Kim, H. S., Nam, K., Moon, M., Oh, H. M., & Chang, Y. K. (2019). Increased biomass and lipid production of Ettlia sp. YC001 by optimized C and N sources in heterotrophic culture. Scientific Reports, 9(1):1-12.
- Krzemińska, I., Pawlik-Skowrońska, B., Trzcińska, M., & Tys, J. (2014). Influence of photoperiods on the growth rate and biomass productivity of green microalgae. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 37(4):735-741.
- Lewis, A. & Guéguen, C. (2022). Using chemometric models to predict the biosorption of low levels of dysprosium by Euglena gracilis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(39):58936-58949.
- Li, T., Hu, J., & Zhu, L. (2021). Self‐flocculation as an efficient method to harvest microalgae: A mini‐review. Water (Switzerland), 13(18):1-10.
- Liang, C., Yang, Y., Xia, Y., Yuan, W., Chen, J., Zheng, Z. & Zheng, X. (2022). The optimization of Chlorella vulgaris flocculation harvesting by chitosan and calcium hydroxide. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 62(2):266-272.
- Lim, Y. A., Khong, N. M. H., Priyawardana, S. D., Ooi, K. R., Ilankoon, I. M. S. K., Chong, M. N., & Foo, S. C. (2022). Distinctive correlations between cell concentration and cell size to microalgae biomass under increasing carbon dioxide. Bioresource Technology, 347(6):1-6.
- Low, Y.J. and Lau, S.W. (2017). Effective flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris using chitosan with zeta potential measurement. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 206(1):1-11. IOP Publishing.
- Martins, D. B., Nasário, F. D., Silva-Gonçalves, L. C., de Oliveira Tiera, V. A., Arcisio-Miranda, M., Tiera, M. J. & dos Santos Cabrera, M. P. (2018). Chitosan derivatives targeting lipid bilayers: Synthesis, biological activity and interaction with model membranes. Carbohydrate polymers, 181(3):1213-1223.
- Molitor, H. R., Schaeffer, A. K., & Schnoor, J. L. (2021). Sustainably cultivating and harvesting microalgae through sedimentation and forward osmosis using wastes. ACS Omega, 6(27):17362-17371.
- Moreira, J. B., Kuntzler, S. G., Bezerra, P. Q. M., Cassuriaga, A. P. A., Zaparoli, M., da Silva, J. L. V., Costa, J. A. V., & de Morais, M. G. (2022). Recent Advances of Microalgae Exopolysaccharides for Application as Bioflocculants. Polysaccharides, 3(1):264-276.
- Nicknig, M. A., Azevedo, A. C. D., de Oliveira, H. A. & Schneider, I. A. H. (2024). Cultivation of microalgae (Scenedesmus sp.) using coal mining wastewater and separation via coagulation/flocculation and dissolved air flotation (DAF). Minerals, 14(4):1-14.
- Nie, C.Z., Li, Y., Huang, X.H., Wang, H.P., Wang, X.S., Dong, X.P., Zhu, B.W. and Qin, L., 2024. Multi-scenario application of chitosan emulsions as fat replacers: based on the regulation of chitosan hydrophobicity and emulsion rheological properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 11(13):1-13.
- Nurafifah, I., Hardianto, M. A., Erfianti, T., Amelia, R., Maghfiroh, K. Q., Kurnianto, D., Siswanti, D. U., Sadewo, B. R., Maggandari, R., & Suyono, E. A. (2023). The effect of acidic pH on growth kinetics, biomass productivity, and primary metabolite contents of Euglena sp. Makara Journal of Science, 27(2):97-105.
- Podwin, A., Kubicki, W., & Dziuban, J. A. (2017). Study of the behavior of Euglena viridis, Euglena gracilis and Lepadella patella cultured in all-glass microaquarium. Biomedical Microdevices, 19(3):1-10.
- Purbani, D. C., Ambarwati, W., Kusuma, A. B., & Herliany, N. E. (2019). Identification of marine microalgae from Tambrauw, West Papua. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 11(3):777-790.
- Rashid, N., Rehman, S. U. & Han, J. I. (2013). Rapid harvesting of freshwater microalgae using chitosan. Process Biochemistry, 48(7):1107-1110.
- Salim, S., Kosterink, N. R., Tchetkoua Wacka, N. D., Vermuë, M. H., & Wijffels, R. H. (2014). Mechanism behind autoflocculation of unicellular green microalgae Ettlia texensis. Journal of Biotechnology, 174(1):34-38.
- Salim, S., Vermuë, M. H., & Wijffels, R. H. (2012). Ratio between autoflocculating and target microalgae affects the energy-efficient harvesting by bio-flocculation. Bioresource Technology, 118(16):49-55.
- Salim, Sina, Bosma, R., Vermuë, M. H., & Wijffels, R. H. (2011). Harvesting of microalgae by bio-flocculation. Journal of Applied Phycology, 23(5):849-855. Saliu, F., Magoni, C., Torelli, A., Cozza, R., Lasagni, M. & Labra, M. (2021). Omega-3 rich oils from microalgae: A chitosan mediated in situ transesterification method. Food Chemistry, 337(4):1-8.
- Sapei, L., Agustriyanto, R., Fitriani, E.W., Levy, Z. and Sumampouw, C. (2022). Enhancement of the stability of w/o/w double emulsion by chitosan modified rice husk silica. International Journal of Technology, 13(3):584-595.
- Sogias, I. A., Khutoryanskiy, V. V. & Williams, A. C. (2010). Exploring the factors affecting the solubility of chitosan in water. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 211(4):426-433.
- Teh, K. Y., Loh, S. H., Aziz, A., Takahashi, K., Effendy, A. W. M., & Cha, T. S. (2021). Lipid accumulation patterns and role of different fatty acid types towards mitigating salinity fluctuations in Chlorella vulgaris. Scientific Reports Nature, 11(1):1-12.
- Timotius, V., Suyono, E. A., Suwanti, L. T., Koerniawan, M. D., Budiman, A., & Siregar, U. J. (2022). The content of lipid, chlorophyll, and carotenoid of Euglena sp. under various salinities. Asia-Pacific Journal of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, 30(3):114-122.
- Van Anh, L. T., Ngoc Thu, T. T., & Thi Dong Phuong, N. (2022). Investigation of microalgae culture by autoflocculation methodologies. Vietnam Journal of Biotechnology, 20(3):487-494.
- Wang, Y., Wang, J., Feng, C., Li, J., Wang, N. & Cai, J. (2022). High-quality Chlorella vulgaris biomass harvesting through chitosan and polyacrylamide. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(23):34651-34658.
- Wu, Z., Zhu, Y., Huang, W., Zhang, C., Li, T., & Zhang, Y. (2012). Evaluation of flocculation induced by pH increase for harvesting microalgae and reuse of flocculated medium. Bioresource Technology, 11(8):496-502.
- Xin, K., Guo, R., Wang, X., Yu, Z., Mao, W., Cheng, C., Che, G., Qian, L., Cheng, J., Yang, W., & Gao, Z. (2024). Photoautotrophic growth and cell division of Euglena gracilis with mixed red and blue wavelengths. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 63(11):4746-4755.
- Xu, K., Zou, X., Mouradov, A., Spangenberg, G., Chang, W. & Li, Y. (2021). Efficient bioflocculation of Chlorella vulgaris with a chitosan and walnut protein extract. Biology, 10(5):1-13.
- Yang, Y., & Weathers, P. (2015). Red light and carbon dioxide differentially affect growth, lipid production, and quality in the microalga, Ettlia oleoabundans. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99(1):489-499.
- Yang, R., Li, H., Huang, M., Yang, H. & Li, A. (2016). A review on chitosan-based flocculants and their applications in water treatment. Water research, 95(8):59-89.
- Yin, Z., Chu, R., Zhu, L., Li, S., Mo, F., Hu, D. & Liu, C. (2021). Application of chitosan-based flocculants to harvest microalgal biomass for biofuel production: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 145(11):1-15.
- Zhou, D. Y., Wu, Z. X., Yin, F. W., Song, S., Li, A., Zhu, B. W. & Yu, L. L. (2021). Chitosan and derivatives: Bioactivities and application in foods. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 12(1):407-432.
References
Aranaz, I., Alcántara, A. R., Civera, M. C., Arias, C., Elorza, B., Heras Caballero, A. & Acosta, N. (2021). Chitosan: An overview of its properties and applications. Polymers, 13(19):1-22.
Asiandu, A. P., Nugroho, A. P., Naser, A. S., Sadewo, B. R., Koerniawan, M. D., Budiman, A., Siregar, U. J., Suwanti, L. T., & Suyono, E. A. (2023). The effect of tofu wastewater and ph on the growth kinetics and biomass composition of Euglena sp. Current Applied Science and Technology, 23(2):1-16.
Babakhani, P., Mahdavi, M. A., Gheshlaghi, R., & Karimian, A. (2022). The shift in carbon source induces pH increase and autoflocculation in microalgal suspensions facilitating multi-approach biomass harvesting. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 12(10):1-12.
Barros, A. I., Gonçalves, A. L., Simões, M., & Pires, J. C. M. (2015). Harvesting techniques applied to microalgae: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41(1):1489-1500.
Bligh, E.G. and Dyer, W.J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 37(8):911-917.
Chang, S. H., Lin, H. T. V., Wu, G. J. & Tsai, G. J. (2015). pH Effects on solubility, zeta potential, and correlation between antibacterial activity and molecular weight of chitosan. Carbohydrate polymers, 134(20):74-81.
Djunaedi, A. (2016). Microalgae biomass production (Tetraselmis chuii) with different harvesting systems. Jurnal Kelautan Tropis, 18(2):107-111.
Elcik, H., Karadag, D., Kara, A.I. & Cakmakci, M. (2023). Microalgae biomass harvesting using chitosan flocculant: Optimization of operating parameters by response surface methodology. Separations, 10(9):1-14.
Erfianti, T., Daryono, B. S., Budiman, A., & Suyono, E. A. (2024). Growth and metabolite enhancement of Acidophile Euglena sp. isolated from Indonesia under different photoperiod cycles. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 16(1):15-30.
Gris, B., Morosinotto, T., Giacometti, G. M., Bertucco, A., & Sforza, E. (2014). Cultivation of Scenedesmus obliquus in photobioreactors: effects of light intensities and light–dark cycles on growth, productivity, and biochemical composition. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172(5):2377-2389.
Hadiyanto, H., Widayat, W., Christwardana, M. & Pratiwi, M. E. (2022). The flocculation process of Chlorella sp. using chitosan as a bio-flocculant: Optimization of operating conditions by response surface methodology. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 5(1):1-11.
Hanief, S., Prasakti, L., Pradana, Y. S., & Cahyono, R. B. (2020). Growth kinetic of. Botryococcus braunii microalgae using logistic and gompertz models. AIP Conference Proceedings, 201(1):1-7.
Indahsari, H. S., Tassakka, A. C. M. A. R., Dewi, E. N., Yuwono, M., & Suyono, E. A. (2022). Effects of salinity and bioflocculation during Euglena sp. harvest on the production of lipid, chlorophyll, and carotenoid with Skeletonema sp. as a bioflocculant. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 16(4):2901-2911.
Inwongwan, S., Kruger, N. J., Ratcliffe, R. G., & O’neill, E. C. (2019). Euglena central metabolic pathways and their subcellular locations. Metabolites, 9(6):1-24.
Khanra, A., Vasistha, S., & Rai, M. P. (2017). Glycerol on lipid enhancement and FAME characterization in algae for raw material of biodiesel. International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, 7(4):1970-1978.
Kim, M., Lee, B., Kim, H. S., Nam, K., Moon, M., Oh, H. M., & Chang, Y. K. (2019). Increased biomass and lipid production of Ettlia sp. YC001 by optimized C and N sources in heterotrophic culture. Scientific Reports, 9(1):1-12.
Krzemińska, I., Pawlik-Skowrońska, B., Trzcińska, M., & Tys, J. (2014). Influence of photoperiods on the growth rate and biomass productivity of green microalgae. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 37(4):735-741.
Lewis, A. & Guéguen, C. (2022). Using chemometric models to predict the biosorption of low levels of dysprosium by Euglena gracilis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(39):58936-58949.
Li, T., Hu, J., & Zhu, L. (2021). Self‐flocculation as an efficient method to harvest microalgae: A mini‐review. Water (Switzerland), 13(18):1-10.
Liang, C., Yang, Y., Xia, Y., Yuan, W., Chen, J., Zheng, Z. & Zheng, X. (2022). The optimization of Chlorella vulgaris flocculation harvesting by chitosan and calcium hydroxide. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 62(2):266-272.
Lim, Y. A., Khong, N. M. H., Priyawardana, S. D., Ooi, K. R., Ilankoon, I. M. S. K., Chong, M. N., & Foo, S. C. (2022). Distinctive correlations between cell concentration and cell size to microalgae biomass under increasing carbon dioxide. Bioresource Technology, 347(6):1-6.
Low, Y.J. and Lau, S.W. (2017). Effective flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris using chitosan with zeta potential measurement. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 206(1):1-11. IOP Publishing.
Martins, D. B., Nasário, F. D., Silva-Gonçalves, L. C., de Oliveira Tiera, V. A., Arcisio-Miranda, M., Tiera, M. J. & dos Santos Cabrera, M. P. (2018). Chitosan derivatives targeting lipid bilayers: Synthesis, biological activity and interaction with model membranes. Carbohydrate polymers, 181(3):1213-1223.
Molitor, H. R., Schaeffer, A. K., & Schnoor, J. L. (2021). Sustainably cultivating and harvesting microalgae through sedimentation and forward osmosis using wastes. ACS Omega, 6(27):17362-17371.
Moreira, J. B., Kuntzler, S. G., Bezerra, P. Q. M., Cassuriaga, A. P. A., Zaparoli, M., da Silva, J. L. V., Costa, J. A. V., & de Morais, M. G. (2022). Recent Advances of Microalgae Exopolysaccharides for Application as Bioflocculants. Polysaccharides, 3(1):264-276.
Nicknig, M. A., Azevedo, A. C. D., de Oliveira, H. A. & Schneider, I. A. H. (2024). Cultivation of microalgae (Scenedesmus sp.) using coal mining wastewater and separation via coagulation/flocculation and dissolved air flotation (DAF). Minerals, 14(4):1-14.
Nie, C.Z., Li, Y., Huang, X.H., Wang, H.P., Wang, X.S., Dong, X.P., Zhu, B.W. and Qin, L., 2024. Multi-scenario application of chitosan emulsions as fat replacers: based on the regulation of chitosan hydrophobicity and emulsion rheological properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 11(13):1-13.
Nurafifah, I., Hardianto, M. A., Erfianti, T., Amelia, R., Maghfiroh, K. Q., Kurnianto, D., Siswanti, D. U., Sadewo, B. R., Maggandari, R., & Suyono, E. A. (2023). The effect of acidic pH on growth kinetics, biomass productivity, and primary metabolite contents of Euglena sp. Makara Journal of Science, 27(2):97-105.
Podwin, A., Kubicki, W., & Dziuban, J. A. (2017). Study of the behavior of Euglena viridis, Euglena gracilis and Lepadella patella cultured in all-glass microaquarium. Biomedical Microdevices, 19(3):1-10.
Purbani, D. C., Ambarwati, W., Kusuma, A. B., & Herliany, N. E. (2019). Identification of marine microalgae from Tambrauw, West Papua. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 11(3):777-790.
Rashid, N., Rehman, S. U. & Han, J. I. (2013). Rapid harvesting of freshwater microalgae using chitosan. Process Biochemistry, 48(7):1107-1110.
Salim, S., Kosterink, N. R., Tchetkoua Wacka, N. D., Vermuë, M. H., & Wijffels, R. H. (2014). Mechanism behind autoflocculation of unicellular green microalgae Ettlia texensis. Journal of Biotechnology, 174(1):34-38.
Salim, S., Vermuë, M. H., & Wijffels, R. H. (2012). Ratio between autoflocculating and target microalgae affects the energy-efficient harvesting by bio-flocculation. Bioresource Technology, 118(16):49-55.
Salim, Sina, Bosma, R., Vermuë, M. H., & Wijffels, R. H. (2011). Harvesting of microalgae by bio-flocculation. Journal of Applied Phycology, 23(5):849-855. Saliu, F., Magoni, C., Torelli, A., Cozza, R., Lasagni, M. & Labra, M. (2021). Omega-3 rich oils from microalgae: A chitosan mediated in situ transesterification method. Food Chemistry, 337(4):1-8.
Sapei, L., Agustriyanto, R., Fitriani, E.W., Levy, Z. and Sumampouw, C. (2022). Enhancement of the stability of w/o/w double emulsion by chitosan modified rice husk silica. International Journal of Technology, 13(3):584-595.
Sogias, I. A., Khutoryanskiy, V. V. & Williams, A. C. (2010). Exploring the factors affecting the solubility of chitosan in water. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 211(4):426-433.
Teh, K. Y., Loh, S. H., Aziz, A., Takahashi, K., Effendy, A. W. M., & Cha, T. S. (2021). Lipid accumulation patterns and role of different fatty acid types towards mitigating salinity fluctuations in Chlorella vulgaris. Scientific Reports Nature, 11(1):1-12.
Timotius, V., Suyono, E. A., Suwanti, L. T., Koerniawan, M. D., Budiman, A., & Siregar, U. J. (2022). The content of lipid, chlorophyll, and carotenoid of Euglena sp. under various salinities. Asia-Pacific Journal of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, 30(3):114-122.
Van Anh, L. T., Ngoc Thu, T. T., & Thi Dong Phuong, N. (2022). Investigation of microalgae culture by autoflocculation methodologies. Vietnam Journal of Biotechnology, 20(3):487-494.
Wang, Y., Wang, J., Feng, C., Li, J., Wang, N. & Cai, J. (2022). High-quality Chlorella vulgaris biomass harvesting through chitosan and polyacrylamide. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(23):34651-34658.
Wu, Z., Zhu, Y., Huang, W., Zhang, C., Li, T., & Zhang, Y. (2012). Evaluation of flocculation induced by pH increase for harvesting microalgae and reuse of flocculated medium. Bioresource Technology, 11(8):496-502.
Xin, K., Guo, R., Wang, X., Yu, Z., Mao, W., Cheng, C., Che, G., Qian, L., Cheng, J., Yang, W., & Gao, Z. (2024). Photoautotrophic growth and cell division of Euglena gracilis with mixed red and blue wavelengths. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 63(11):4746-4755.
Xu, K., Zou, X., Mouradov, A., Spangenberg, G., Chang, W. & Li, Y. (2021). Efficient bioflocculation of Chlorella vulgaris with a chitosan and walnut protein extract. Biology, 10(5):1-13.
Yang, Y., & Weathers, P. (2015). Red light and carbon dioxide differentially affect growth, lipid production, and quality in the microalga, Ettlia oleoabundans. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99(1):489-499.
Yang, R., Li, H., Huang, M., Yang, H. & Li, A. (2016). A review on chitosan-based flocculants and their applications in water treatment. Water research, 95(8):59-89.
Yin, Z., Chu, R., Zhu, L., Li, S., Mo, F., Hu, D. & Liu, C. (2021). Application of chitosan-based flocculants to harvest microalgal biomass for biofuel production: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 145(11):1-15.
Zhou, D. Y., Wu, Z. X., Yin, F. W., Song, S., Li, A., Zhu, B. W. & Yu, L. L. (2021). Chitosan and derivatives: Bioactivities and application in foods. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 12(1):407-432.