Date Log
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
Reduction of Raoultella ornithinolytica TN5 Biofilm using Hot Water and Nanochitosan
Corresponding Author(s) : Indun Dewi Puspita
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 17 No. 3 (2025): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
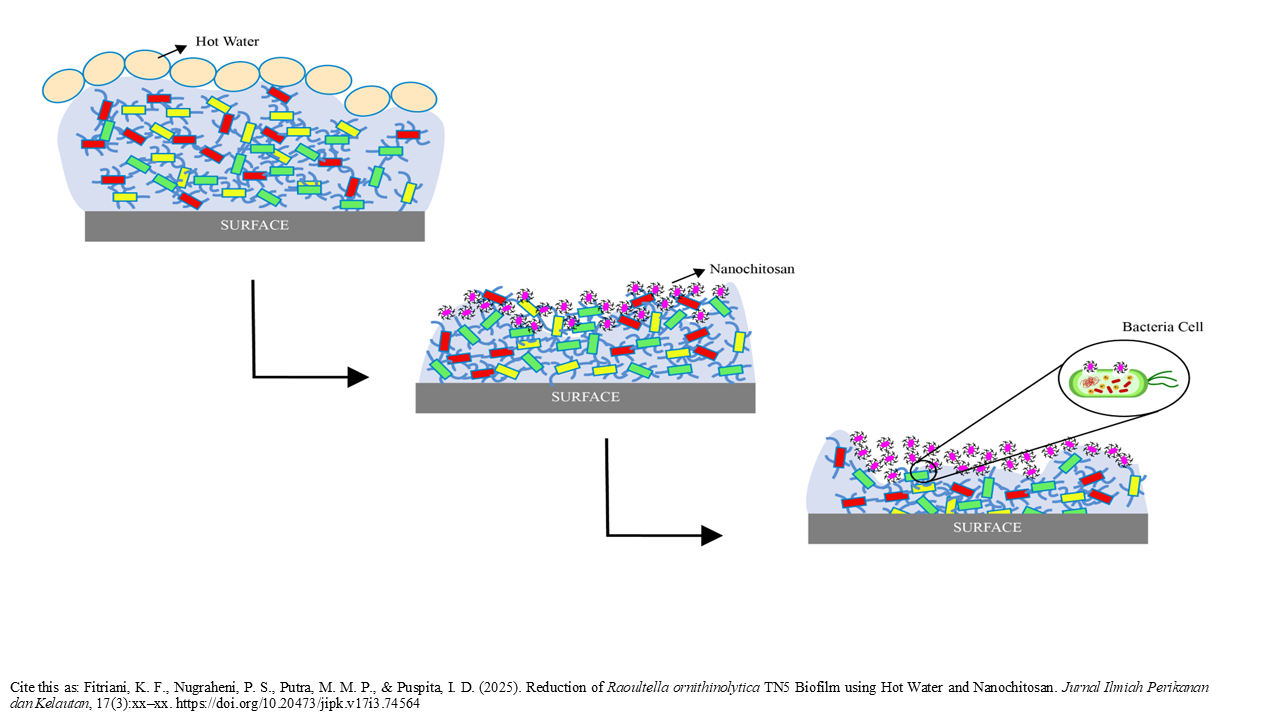
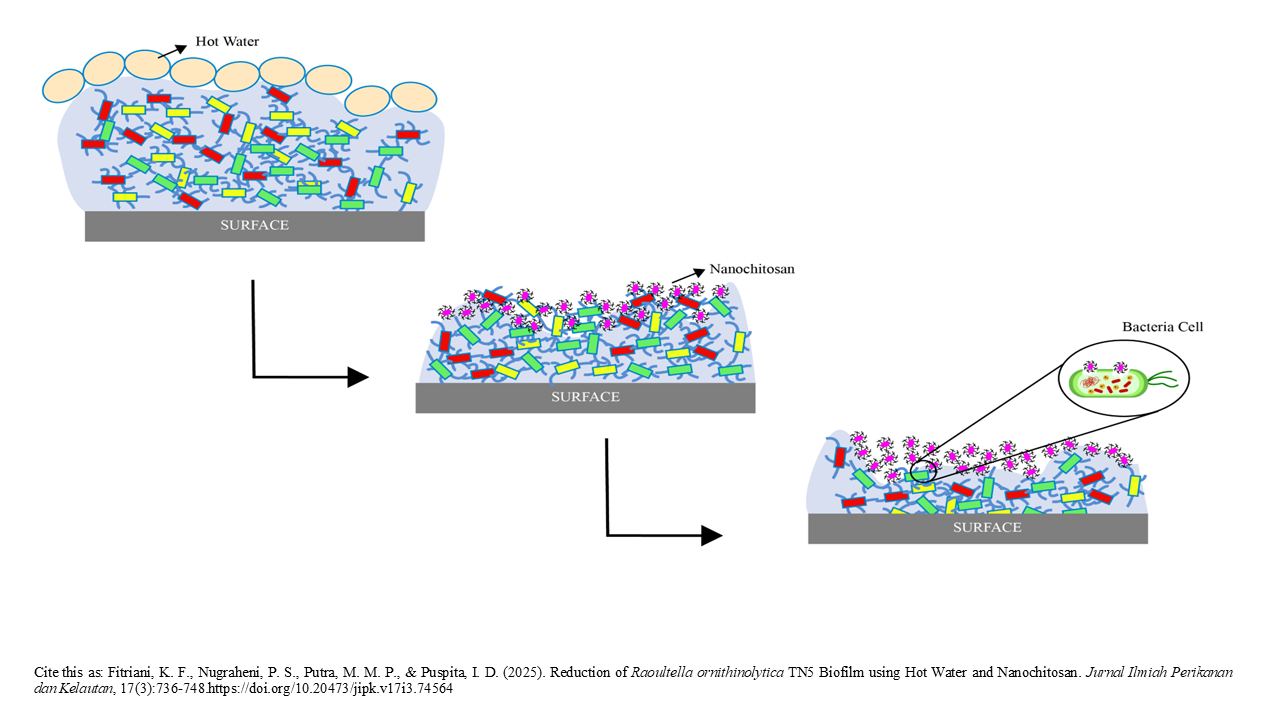
Graphical Abstract
Highlight Research
- The biofilm formation of Raoultella ornithinolytica on a stainless steel surface was analyzed
- Longer duration of hot water immersion leading to a higher reduction of Raoultella ornithinolytica biofilm on stainless steel surface.
- Longer duration of nanochitosan exposure leading to a higher reduction of Raoultella ornithinolytica biofilm on stainless steel surface
- The combination treatment of hot water immersion and nanochitosan shows higher efficacy to reduce Raoultella ornithinolytica biofilm on stainless steel surface compare to sodium hypochlorite treatment.
Abstract
The equipment surfaces in food processing industries have the potential to contaminate products. Bacteria on a surface are able to form a biofilm. This study aimed to determine the effect of a combination treatment using hot water immersion and nanochitosan on the reduction of R. ornithinolytica’s biofilm on stainless steel surfaces. R. ornithinolytica was applied to a stainless steel surface, incubated at 30oC for 48 hours, and tested for its reduction using hot water immersion treatment with different times. The best result from this treatment was when it was used in combination. The viability of cells was determined using a swab and the total plate count method. A scanning electron microscope was used for qualitative observations of biofilm formed on stainless steel before and after sanitation. The result showed that 10 minutes of hot water immersion resulted in significant R. ornithinolytica biofilm reduction compared to 5 minutes of treatment (p<0.05). Furthermore, the combination treatment of 10 minutes of hot water with 15 minutes of nanochitosan (0.1%) immersion showed the highest percent reduction of R. ornithinolytica biofilm (p<0.05). The ability of the combination treatment to eliminate R. ornithinolytica biofilms is equivalent to or even better than sodium hypochlorite treatment.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Abdeltwab, W. M., Abdelaliem, Y. F., Metry, W. A., & Eldeghedy, M. (2019). Antimicrobial effect of chitosan and nano-chitosan against some pathogens and spoilage microorganisms synbiotic dairy products view project antimicrobial effect of chitosan and nano-chitosan against some pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Journal of Advanced Laboratory Research in Biology, 10(1):8-15.
- Achinas, S., Yska, S. K., Charalampogiannis, N., Krooneman, J., & Euverink, G. J. W. (2020). A technological understanding of biofilm detection techniques: A review. Materials, 13(14):1-36.
- Adlu, F. H. (2022). Application of nanochitosan as a natural sanitizer against Morganella morganii TK7 biofilm on various materials of processing equipment. Undergraduate Program. Yogyakarta: Faculty of Agriculture. UGM.
- Aguayo, P. R., Larenas, T. B., Godoy, C. A., Rivas, B. C., González-Casanova, J., Rojas-Gómez, D., & Fuentes, N. C. (2020). Antimicrobial and antibiofilm capacity of chitosan nanoparticles against wild type strain of Pseudomonas sp. isolated from milk of cows diagnosed with bovine mastitis. Antibiotics, 9(9):1-15.
- Alya’ainun, R., Fathoni, E. Y., & Puspita, I. D. (2021). The effect of pH on bacterial growth and histamine formation by Klebsiella pneumoniae CK02 and Raoultella ornithinolytica TN01. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 919(012039):1-9.
- Angarano, V., Smet, C., Akkermans, S., Akritidou, T., Huyck, B., Chieffi, A., & Van Impe, J. F. M. (2020). A reproducible method for growing biofilms on polystyrene surfaces: Biomass and bacterial viability evolution of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 10(13):1-23.
- Anindya, A. L. (2018). Particle size analyser: Some uses of light scattering instruments. Seminar Nasional Instrumentasi, Kontrol dan Otomasi, 1(1):1-4.
- Arifani, I., Pradini, G. W., Arya, I. F. D., & Cahyadi, A. I. (2017). Destructive effect of calcium hypochlorite against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Althea Medical Journal, 4(3):468-473.
- Ballash, G. A., Albers, A. L., Mollenkopf, D. F., Sechrist, E., Adams, R. J., & Wittum, T. E. (2021). Antimicrobial resistant bacteria recovered from retail ground meat products in the US include a Raoultella ornithinolytica co-harboring bla KPC-2 and bla NDM-5. Scientific Reports, 11(1):1-12.
- Behnke, S., Parker, A. E., Woodall, D., & Camper, A. K. (2011). Comparing the chlorine disinfection of detached biofilm clusters with those of sessile biofilms and planktonic cells in single- and dual-species cultures. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(20):7176-7184.
- Beterams, A., Kirse, A., Kreienbrock, L., Stingl, K., Bandick, N., & Reich, F. (2024). Application of hot water and cold air to reduce bacterial contamination on broiler carcasses. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15(1):1-15.
- Bhagwat, V. R. (2019). Safety of water used in food production. Food Safety and Human Health. Academic Press. 219-247.
- Bhumkar, R. D., & Pokharkar, V. B. (2006). Studies on effect of pH on cross-linking of chitosan with sodium tripolyphosphate: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7(2):2-7.
- Busta, F. F. (1976). Practical implications of injured microorganisms in food. Journal of Milk and Food Technology, 39(2):138-145.
- Chandrasekaran, M., Kim, K. D., & Chun, S. C. (2020). Antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles: A review. Processes, 8(9):1-21.
- da Silva Fernandes, M., Kabuki, D. Y., & Kuaye, A. Y. (2015). Biofilms of Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium isolated from the processing of ricotta and the control of these pathogens through cleaning and sanitization procedures. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 200(1):97-103.
- DeQueiroz, G. A., & Day, D. F. (2007). Antimicrobial activity and effectiveness of a combination of sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide in killing and removing Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms from surfaces. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 103(4):794-802.
- El-Naggar, N. E. A., Shiha, A. M., Mahrous, H., & Mohammed, A. B. A. (2024). A sustainable green-approach for biofabrication of chitosan nanoparticles, optimization, characterization, its antifungal activity against phytopathogenic Fusarium culmorum and antitumor activity. Scientific Reports, 14(1):1-23.
- Etani, T., Kondo, S., Yanase, T., Morikawa, T., Aoki, M., Gonda, M., Tomiyama, N., Nagai, T., Iida, K., Iwatsuki, S., Taguchi, K., Naiki, T., Hamamoto, S., Okada, A., Kawai, N., Nakamura, A., & Yasui, T. (2023). Clinical characteristics of Raoultella ornithinolytica bacteremia and antimicrobial susceptibility of Raoultella ornithinolytica. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, 29(5):554-557.
- Flemming, H. C., & Wingender, J. (2010). The biofilm matrix. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8(9):623-633.
- Godoy, C. A., Balic, I., Moreno, A. A., Diaz, O., Arenas Colarte, C., Bruna Larenas, T., Gamboa, A., & Caro Fuentes, N. (2025). Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of chitosan nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine mastitis milk. Pharmaceutics, 17(2):1-17.
- Handayani, K., & Abdullah, S. (2016). Measurement of residual chlorine levels before and after swimming pool water usage at Surya Yudha Water Park, Banjarnegara Regency, 2015. Public Environmental Health Bulletin, 35(1):57-59.
- Hardiningtyas, S. D., Bahri, D. F., & Suptijah, P. (2022). Antimicrobial activity of nanochitosan shrimp shell as a hands sanitizer. Journal of Marine and Coastal Science, 11(1):1-8.
- Hassan, M. I., Taher, F. A., Mohamed, A. F., & Kamel, M. R. (2016). Chitosan nanoparticles prepared from Lucilia cuprina maggots as antibacterial agent. Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology, 46(3):519-526.
- Hoa, B. T. Q., Mahakarnchanakul, W., Sajjaanantakul, T., & Kitpreechavanich, V. (2015). Adhesive microflora on stainless steel coupons in seafood processing plant. Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 3(1-2):28-32.
- Hua, Z., Younce, F., Tang, J., Ryu, D., Rasco, B., Hanrahan, I., & Zhu, M. J. (2021). Efficacy of saturated steam against Listeria innocua biofilm on common food-contact surfaces. Food Control, 125(7):1-8.
- Hwang, C. C., Kung, H. F., Lee, Y. C., Wen, S. Y., Chen, P. Y., Tseng, D. I., & Tsai, Y. H. (2020). Histamine fish poisoning and histamine production by Raoultella ornithinolytica in milkfish surimi. Journal of Food Protection, 83(5):874-880.
- Ihsan, M., Harris, A., Purwati, N., Muliasari, H., Priyambodo, B., Jones, C., & Nankervis, L. (2025). The characteristics of chitosan derived from lobster shells and its effect on fungi activity and water stability of lobster pellets. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 17(2):485-497.
- Indonesian Food and Drug Authority. (2011). Regulation of the food and drug supervisory agency of the republic of Indonesia number HK.03.1023.08.11.07331 of 2011 on cosmetic analysis methods. Jakarta: Indonesian Food and Drug Authority. pp 1-92.
- ISO18593. (2018). Microbiology of the food chain–Horizontal methods for surface sampling. International Organization for Standardization.
- Kanamarlapudi, S. L. R. K., & Muddada, S. (2017). Characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Streptococcus thermophilus CC30. BioMed Research International, 2017:1-11.
- Kang, J. W., Lee, H. Y., & Kang, D. H. (2021). Synergistic bactericidal effect of hot water with citric acid against Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formed on stainless steel. Food Microbiology, 95 (1):1-8.
- Kanki, M., Yoda, T., Tsukamoto, T., & Shibata, T. (2002). Klebsiella pneumoniae produces no histamine: Raoultella planticola and Raoultella omithinolytica strains are histamine producers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(7):3462-3466.
- Karuppuchamy, V., Heldman, D. R., & Snyder, A. B. (2024). A review of food safety in low-moisture foods with current and potential dry-cleaning methods. Journal of Food Science, 89(2):793-810.
- Kharel, K., Yemmireddy, V. K., Graham, C. J., Prinyawiwatkul, W., & Adhikari, A. (2018). Hot water treatment as a kill-step to inactivate Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica, Listeria monocytogenes and Enterococcus faecium on in-shell pecans. Lwt, 97(1):555-560.
- Kurniawidi, D. W., Alaa, S., Nurhaliza, E., Safitri, D. O., Rahayu, S., Ali, M., & Amin, M. (2022). Synthesis and characterization of nano chitosan from vannamei shrimp shell (Litopenaeus vannamei). Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 14(2):380-387.
- Lee, Y. C., Chen, Y. F., Huang, Y. L., Kung, H. F., Chen, T. Y., & Tsai, Y. H. (2016). Hygienic quality, adulteration of pork and histamine production by Raoultella ornithinolytica in milkfish dumpling. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 24(4):762-770.
- Magani, A. K., Tallei, T. E., & Kolondam, B. J. (2020). Antibacterial test of chitosan nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Jurnal Bios Logos, 10(1):7-13.
- Miller, M. A., & Zachary, J. F. (2017). Mechanisms and morphology of cellular injury, adaptation, and death. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease Expert Consult, January.
- Møretrø, T., Moen, B., Heir, E., Hansen, A., & Langsrud, S. (2016). Contamination of salmon fillets and processing plants with spoilage bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 237(1):98-108.
- Murdock, R. C., Braydich-Stolle, L., Schrand, A. M., Schlager, J. J., & Hussain, S. M. (2008). Characterization of nanomaterial dispersion in solution prior to in vitro exposure using dynamic light scattering technique. Toxicological Sciences, 101(2):239-253.
- Nagpal, K., Singh, S. K., & Mishra, D. N. (2010). Chitosan nanoparticles: a promising system in novel drug delivery. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 58(11):1423-1430.
- Nallamuthu, I., Devi, A., & Khanum, F. (2015). Chlorogenic acid loaded chitosan nanoparticles with sustained release property, retained antioxidant activity and enhanced bioavailability. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 10(3):203-211.
- Nocker, A., Lindfeld, E., Wingender, J., Schulte, S., Dumm, M., & Bendinger, B. (2021). Thermal and chemical disinfection of water and biofilms: Only a temporary effect in regard to the autochthonous bacteria. Journal of Water and Health, 19(5):808-822.
- Nugraheni, P. S., Soeriyadi, A. H., Ustadi, Sediawan, W. B., & Budhijanto, W. (2019). Comparison of formulation methods to produce nano-chitosan as inhibitor agent for bacterial growth. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences, 51(3):431-442.
- Ohman, E., Kilgore, S., Waite-Cusic, J., & Kovacevic, J. (2024). Efficacy of cleaning and sanitizing procedures to reduce Listeria monocytogenes on food contact surfaces commonly found in fresh produce operations. Food Microbiology, 118(1):1-8.
- Pan, C., Qian, J., Fan, J., Guo, H., Gou, L., Yang, H., & Liang, C. (2019). Preparation nanoparticle by ionic cross-linked emulsified chitosan and its antibacterial activity. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 568(9):362-370.
- Paomephan, P., Assavanig, A., Chaturongakul, S., Cady, N. C., Bergkvist, M., & Niamsiri, N. (2018). Insight into the antibacterial property of chitosan nanoparticles against Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium and their application as vegetable wash disinfectant. Food Control, 86(1):294-301.
- Pereira, S., Costa-Ribeiro, A., Teixeira, P., Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L., Prado, M., Cerqueira, M. A., & Garrido-Maestu, A. (2023). Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of chitosan nanoparticles against Listeria monocytogenes. Polymers, 15(18):1-11.
- Raffaella, C., Casettari, L., Fagioli, L., Cespi, M., Bonacucina, G., & Baffone, W. (2017). Activity of essential oil-based microemulsions against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms developed on stainless steel surface in different culture media and growth conditions. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 241(1):132-140.
- Rahayu, P., & Khabibi, K. (2016). Adsorption of nickel (II) metal ions by tripolyphosphate-modified chitosan. Journal of Scientific an Applied Chemistry, 19(1):21-26.
- Ricker, E. B., Aljaafari, H. A. S., Bader, T. M., Hundley, B. S., & Nuxoll, E. (2018). Thermal shock susceptibility and regrowth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 34(2):168-176.
- Roiska, R. (2022). Formation of single and multi-species histamine-producing bacteria (HPB) biofilms on polypropylene surfaces and their resistance to sanitizing agents. Thesis. Postgraduate Program. Yogyakarta: Faculty of Agriculture. UGM.
- Safitri, I. (2020). Screening and biofilm formation test of histamine-forming bacteria on stainless steel and polypropylene coupons. Undergraduate Program. Yogyakarta: Faculty of Agriculture. UGM.
- Said, N. I. (2018). Disinfection for the drinking water treatment process. Indonesian Water Journal, 3(1):15-28.
- Saputra, D., Ula, F. R., Fadhila, A. B. N., Sijabat, Y. Y., Romadoni, A. A., & Windarto, S. (2022). Nano-chitosan spray as a preservative and food security of fishery products in the middle of the Covid-19 pandemic. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 14(1):71-82.
- Sarwar, A., Katas, H., & Zin, N. M. (2014). Antibacterial effects of chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles: impact of particle size molecular weight. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 16(7):1-14.
- Schlegelová, J., Babák, V., Holasová, M., Konstantinová, L., Necidová, L., Šišák, F., Vlková, H., Roubal, P., & Jaglic, Z. (2010). Microbial contamination after sanitation of food contact surfaces in dairy and meat processing plants. Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 28(5):450-461.
- Schmidt, R. H. (2012). Basic elements of equipment cleaning and sanitizing in food processing and handling operations 1. IFAS Extension, University of Florida.
- Sektiaji, R. G. B., Rochima, E., Pratama, R. I., & Utama, G. L. (2022). Study of nanochitosan (definition, manufacture, analysis of characteristics and utilization): Review. Asian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Research, 20(4):21-28.
- Susilowati, A., Aspiyanto, A., & Dinoto, A. (2011). Exopolysaccharide (EPS) extraction from gut bacteria cultures in sago biomassa (Mextroxylon sp.) using cross-flow ultrafiltration membrane module (UFCF). Journal of Biological Researchers, 16(2):185-193.
- Tantasuttikul, A., & Mahakarnchanakul, W. (2019). Growth parameters and sanitizer resistance of Raoultella ornithinolytica and Raoultella terrigena isolated from seafood processing plant. Cogent Food and Agriculture, 5(1):1-14.
- Tompkins, N. M., Avens, J. S., Kendall, P. A., & Salman, M. D. (2008). Effect of boiling water carcass immersion on aerobic bacteria counts of poultry skin and processed ground poultry meat. Zoonoses and Public Health, 55(5):235-241.
- Van Bavel, N., Issler, T., Pang, L., Anikoyskiy, M., & Prenner, E. J. (2023). A simple method for synthesis of chitosan nanoparticles with ionic gelation and homogenization. Molecules, 28(11):1-14.
- Warsito, M. F., & Agustiani, F. (2021). A review on factors affecting chitosan nanoparticles formation. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1011(012027):1-10.
- Wesche, A. M., Gurtler, J. B., Marks, B. P., & Ryser, E. T. (2009). Stress, sublethal injury, resuscitation, and virulence of bacterial foodborne pathogens. Journal of Food Protection, 72(5):1121-1138.
References
Abdeltwab, W. M., Abdelaliem, Y. F., Metry, W. A., & Eldeghedy, M. (2019). Antimicrobial effect of chitosan and nano-chitosan against some pathogens and spoilage microorganisms synbiotic dairy products view project antimicrobial effect of chitosan and nano-chitosan against some pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Journal of Advanced Laboratory Research in Biology, 10(1):8-15.
Achinas, S., Yska, S. K., Charalampogiannis, N., Krooneman, J., & Euverink, G. J. W. (2020). A technological understanding of biofilm detection techniques: A review. Materials, 13(14):1-36.
Adlu, F. H. (2022). Application of nanochitosan as a natural sanitizer against Morganella morganii TK7 biofilm on various materials of processing equipment. Undergraduate Program. Yogyakarta: Faculty of Agriculture. UGM.
Aguayo, P. R., Larenas, T. B., Godoy, C. A., Rivas, B. C., González-Casanova, J., Rojas-Gómez, D., & Fuentes, N. C. (2020). Antimicrobial and antibiofilm capacity of chitosan nanoparticles against wild type strain of Pseudomonas sp. isolated from milk of cows diagnosed with bovine mastitis. Antibiotics, 9(9):1-15.
Alya’ainun, R., Fathoni, E. Y., & Puspita, I. D. (2021). The effect of pH on bacterial growth and histamine formation by Klebsiella pneumoniae CK02 and Raoultella ornithinolytica TN01. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 919(012039):1-9.
Angarano, V., Smet, C., Akkermans, S., Akritidou, T., Huyck, B., Chieffi, A., & Van Impe, J. F. M. (2020). A reproducible method for growing biofilms on polystyrene surfaces: Biomass and bacterial viability evolution of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 10(13):1-23.
Anindya, A. L. (2018). Particle size analyser: Some uses of light scattering instruments. Seminar Nasional Instrumentasi, Kontrol dan Otomasi, 1(1):1-4.
Arifani, I., Pradini, G. W., Arya, I. F. D., & Cahyadi, A. I. (2017). Destructive effect of calcium hypochlorite against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Althea Medical Journal, 4(3):468-473.
Ballash, G. A., Albers, A. L., Mollenkopf, D. F., Sechrist, E., Adams, R. J., & Wittum, T. E. (2021). Antimicrobial resistant bacteria recovered from retail ground meat products in the US include a Raoultella ornithinolytica co-harboring bla KPC-2 and bla NDM-5. Scientific Reports, 11(1):1-12.
Behnke, S., Parker, A. E., Woodall, D., & Camper, A. K. (2011). Comparing the chlorine disinfection of detached biofilm clusters with those of sessile biofilms and planktonic cells in single- and dual-species cultures. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(20):7176-7184.
Beterams, A., Kirse, A., Kreienbrock, L., Stingl, K., Bandick, N., & Reich, F. (2024). Application of hot water and cold air to reduce bacterial contamination on broiler carcasses. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15(1):1-15.
Bhagwat, V. R. (2019). Safety of water used in food production. Food Safety and Human Health. Academic Press. 219-247.
Bhumkar, R. D., & Pokharkar, V. B. (2006). Studies on effect of pH on cross-linking of chitosan with sodium tripolyphosphate: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7(2):2-7.
Busta, F. F. (1976). Practical implications of injured microorganisms in food. Journal of Milk and Food Technology, 39(2):138-145.
Chandrasekaran, M., Kim, K. D., & Chun, S. C. (2020). Antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles: A review. Processes, 8(9):1-21.
da Silva Fernandes, M., Kabuki, D. Y., & Kuaye, A. Y. (2015). Biofilms of Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium isolated from the processing of ricotta and the control of these pathogens through cleaning and sanitization procedures. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 200(1):97-103.
DeQueiroz, G. A., & Day, D. F. (2007). Antimicrobial activity and effectiveness of a combination of sodium hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide in killing and removing Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms from surfaces. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 103(4):794-802.
El-Naggar, N. E. A., Shiha, A. M., Mahrous, H., & Mohammed, A. B. A. (2024). A sustainable green-approach for biofabrication of chitosan nanoparticles, optimization, characterization, its antifungal activity against phytopathogenic Fusarium culmorum and antitumor activity. Scientific Reports, 14(1):1-23.
Etani, T., Kondo, S., Yanase, T., Morikawa, T., Aoki, M., Gonda, M., Tomiyama, N., Nagai, T., Iida, K., Iwatsuki, S., Taguchi, K., Naiki, T., Hamamoto, S., Okada, A., Kawai, N., Nakamura, A., & Yasui, T. (2023). Clinical characteristics of Raoultella ornithinolytica bacteremia and antimicrobial susceptibility of Raoultella ornithinolytica. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, 29(5):554-557.
Flemming, H. C., & Wingender, J. (2010). The biofilm matrix. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8(9):623-633.
Godoy, C. A., Balic, I., Moreno, A. A., Diaz, O., Arenas Colarte, C., Bruna Larenas, T., Gamboa, A., & Caro Fuentes, N. (2025). Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of chitosan nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine mastitis milk. Pharmaceutics, 17(2):1-17.
Handayani, K., & Abdullah, S. (2016). Measurement of residual chlorine levels before and after swimming pool water usage at Surya Yudha Water Park, Banjarnegara Regency, 2015. Public Environmental Health Bulletin, 35(1):57-59.
Hardiningtyas, S. D., Bahri, D. F., & Suptijah, P. (2022). Antimicrobial activity of nanochitosan shrimp shell as a hands sanitizer. Journal of Marine and Coastal Science, 11(1):1-8.
Hassan, M. I., Taher, F. A., Mohamed, A. F., & Kamel, M. R. (2016). Chitosan nanoparticles prepared from Lucilia cuprina maggots as antibacterial agent. Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology, 46(3):519-526.
Hoa, B. T. Q., Mahakarnchanakul, W., Sajjaanantakul, T., & Kitpreechavanich, V. (2015). Adhesive microflora on stainless steel coupons in seafood processing plant. Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 3(1-2):28-32.
Hua, Z., Younce, F., Tang, J., Ryu, D., Rasco, B., Hanrahan, I., & Zhu, M. J. (2021). Efficacy of saturated steam against Listeria innocua biofilm on common food-contact surfaces. Food Control, 125(7):1-8.
Hwang, C. C., Kung, H. F., Lee, Y. C., Wen, S. Y., Chen, P. Y., Tseng, D. I., & Tsai, Y. H. (2020). Histamine fish poisoning and histamine production by Raoultella ornithinolytica in milkfish surimi. Journal of Food Protection, 83(5):874-880.
Ihsan, M., Harris, A., Purwati, N., Muliasari, H., Priyambodo, B., Jones, C., & Nankervis, L. (2025). The characteristics of chitosan derived from lobster shells and its effect on fungi activity and water stability of lobster pellets. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 17(2):485-497.
Indonesian Food and Drug Authority. (2011). Regulation of the food and drug supervisory agency of the republic of Indonesia number HK.03.1023.08.11.07331 of 2011 on cosmetic analysis methods. Jakarta: Indonesian Food and Drug Authority. pp 1-92.
ISO18593. (2018). Microbiology of the food chain–Horizontal methods for surface sampling. International Organization for Standardization.
Kanamarlapudi, S. L. R. K., & Muddada, S. (2017). Characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Streptococcus thermophilus CC30. BioMed Research International, 2017:1-11.
Kang, J. W., Lee, H. Y., & Kang, D. H. (2021). Synergistic bactericidal effect of hot water with citric acid against Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formed on stainless steel. Food Microbiology, 95 (1):1-8.
Kanki, M., Yoda, T., Tsukamoto, T., & Shibata, T. (2002). Klebsiella pneumoniae produces no histamine: Raoultella planticola and Raoultella omithinolytica strains are histamine producers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(7):3462-3466.
Karuppuchamy, V., Heldman, D. R., & Snyder, A. B. (2024). A review of food safety in low-moisture foods with current and potential dry-cleaning methods. Journal of Food Science, 89(2):793-810.
Kharel, K., Yemmireddy, V. K., Graham, C. J., Prinyawiwatkul, W., & Adhikari, A. (2018). Hot water treatment as a kill-step to inactivate Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica, Listeria monocytogenes and Enterococcus faecium on in-shell pecans. Lwt, 97(1):555-560.
Kurniawidi, D. W., Alaa, S., Nurhaliza, E., Safitri, D. O., Rahayu, S., Ali, M., & Amin, M. (2022). Synthesis and characterization of nano chitosan from vannamei shrimp shell (Litopenaeus vannamei). Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 14(2):380-387.
Lee, Y. C., Chen, Y. F., Huang, Y. L., Kung, H. F., Chen, T. Y., & Tsai, Y. H. (2016). Hygienic quality, adulteration of pork and histamine production by Raoultella ornithinolytica in milkfish dumpling. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 24(4):762-770.
Magani, A. K., Tallei, T. E., & Kolondam, B. J. (2020). Antibacterial test of chitosan nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Jurnal Bios Logos, 10(1):7-13.
Miller, M. A., & Zachary, J. F. (2017). Mechanisms and morphology of cellular injury, adaptation, and death. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease Expert Consult, January.
Møretrø, T., Moen, B., Heir, E., Hansen, A., & Langsrud, S. (2016). Contamination of salmon fillets and processing plants with spoilage bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 237(1):98-108.
Murdock, R. C., Braydich-Stolle, L., Schrand, A. M., Schlager, J. J., & Hussain, S. M. (2008). Characterization of nanomaterial dispersion in solution prior to in vitro exposure using dynamic light scattering technique. Toxicological Sciences, 101(2):239-253.
Nagpal, K., Singh, S. K., & Mishra, D. N. (2010). Chitosan nanoparticles: a promising system in novel drug delivery. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 58(11):1423-1430.
Nallamuthu, I., Devi, A., & Khanum, F. (2015). Chlorogenic acid loaded chitosan nanoparticles with sustained release property, retained antioxidant activity and enhanced bioavailability. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 10(3):203-211.
Nocker, A., Lindfeld, E., Wingender, J., Schulte, S., Dumm, M., & Bendinger, B. (2021). Thermal and chemical disinfection of water and biofilms: Only a temporary effect in regard to the autochthonous bacteria. Journal of Water and Health, 19(5):808-822.
Nugraheni, P. S., Soeriyadi, A. H., Ustadi, Sediawan, W. B., & Budhijanto, W. (2019). Comparison of formulation methods to produce nano-chitosan as inhibitor agent for bacterial growth. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences, 51(3):431-442.
Ohman, E., Kilgore, S., Waite-Cusic, J., & Kovacevic, J. (2024). Efficacy of cleaning and sanitizing procedures to reduce Listeria monocytogenes on food contact surfaces commonly found in fresh produce operations. Food Microbiology, 118(1):1-8.
Pan, C., Qian, J., Fan, J., Guo, H., Gou, L., Yang, H., & Liang, C. (2019). Preparation nanoparticle by ionic cross-linked emulsified chitosan and its antibacterial activity. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 568(9):362-370.
Paomephan, P., Assavanig, A., Chaturongakul, S., Cady, N. C., Bergkvist, M., & Niamsiri, N. (2018). Insight into the antibacterial property of chitosan nanoparticles against Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium and their application as vegetable wash disinfectant. Food Control, 86(1):294-301.
Pereira, S., Costa-Ribeiro, A., Teixeira, P., Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L., Prado, M., Cerqueira, M. A., & Garrido-Maestu, A. (2023). Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of chitosan nanoparticles against Listeria monocytogenes. Polymers, 15(18):1-11.
Raffaella, C., Casettari, L., Fagioli, L., Cespi, M., Bonacucina, G., & Baffone, W. (2017). Activity of essential oil-based microemulsions against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms developed on stainless steel surface in different culture media and growth conditions. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 241(1):132-140.
Rahayu, P., & Khabibi, K. (2016). Adsorption of nickel (II) metal ions by tripolyphosphate-modified chitosan. Journal of Scientific an Applied Chemistry, 19(1):21-26.
Ricker, E. B., Aljaafari, H. A. S., Bader, T. M., Hundley, B. S., & Nuxoll, E. (2018). Thermal shock susceptibility and regrowth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 34(2):168-176.
Roiska, R. (2022). Formation of single and multi-species histamine-producing bacteria (HPB) biofilms on polypropylene surfaces and their resistance to sanitizing agents. Thesis. Postgraduate Program. Yogyakarta: Faculty of Agriculture. UGM.
Safitri, I. (2020). Screening and biofilm formation test of histamine-forming bacteria on stainless steel and polypropylene coupons. Undergraduate Program. Yogyakarta: Faculty of Agriculture. UGM.
Said, N. I. (2018). Disinfection for the drinking water treatment process. Indonesian Water Journal, 3(1):15-28.
Saputra, D., Ula, F. R., Fadhila, A. B. N., Sijabat, Y. Y., Romadoni, A. A., & Windarto, S. (2022). Nano-chitosan spray as a preservative and food security of fishery products in the middle of the Covid-19 pandemic. Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 14(1):71-82.
Sarwar, A., Katas, H., & Zin, N. M. (2014). Antibacterial effects of chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles: impact of particle size molecular weight. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 16(7):1-14.
Schlegelová, J., Babák, V., Holasová, M., Konstantinová, L., Necidová, L., Šišák, F., Vlková, H., Roubal, P., & Jaglic, Z. (2010). Microbial contamination after sanitation of food contact surfaces in dairy and meat processing plants. Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 28(5):450-461.
Schmidt, R. H. (2012). Basic elements of equipment cleaning and sanitizing in food processing and handling operations 1. IFAS Extension, University of Florida.
Sektiaji, R. G. B., Rochima, E., Pratama, R. I., & Utama, G. L. (2022). Study of nanochitosan (definition, manufacture, analysis of characteristics and utilization): Review. Asian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Research, 20(4):21-28.
Susilowati, A., Aspiyanto, A., & Dinoto, A. (2011). Exopolysaccharide (EPS) extraction from gut bacteria cultures in sago biomassa (Mextroxylon sp.) using cross-flow ultrafiltration membrane module (UFCF). Journal of Biological Researchers, 16(2):185-193.
Tantasuttikul, A., & Mahakarnchanakul, W. (2019). Growth parameters and sanitizer resistance of Raoultella ornithinolytica and Raoultella terrigena isolated from seafood processing plant. Cogent Food and Agriculture, 5(1):1-14.
Tompkins, N. M., Avens, J. S., Kendall, P. A., & Salman, M. D. (2008). Effect of boiling water carcass immersion on aerobic bacteria counts of poultry skin and processed ground poultry meat. Zoonoses and Public Health, 55(5):235-241.
Van Bavel, N., Issler, T., Pang, L., Anikoyskiy, M., & Prenner, E. J. (2023). A simple method for synthesis of chitosan nanoparticles with ionic gelation and homogenization. Molecules, 28(11):1-14.
Warsito, M. F., & Agustiani, F. (2021). A review on factors affecting chitosan nanoparticles formation. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1011(012027):1-10.
Wesche, A. M., Gurtler, J. B., Marks, B. P., & Ryser, E. T. (2009). Stress, sublethal injury, resuscitation, and virulence of bacterial foodborne pathogens. Journal of Food Protection, 72(5):1121-1138.