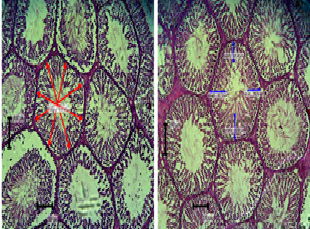
Efek pemberian α-tokoferol terhadap jumlah sel spermatogenik dan sel Leydig pada tikus putih (Rattus norvegicus) yang dipapar 2,3,7,8 Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
Downloads
This research aimed to determine the effect of α-tocopherol on the count of spermatogenic and Leydig cells in rats (Rattus norvegicus) exposed to 2,3,7,8 tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (dioxin). Dioxin is an endocrine-disrupting agent that adversely affects reproductive health, while α-tocopherol maintains fertility. This research used 25 rats aged 10-12 weeks weighing 150-200 grams. Rats were divided into five groups (K, P0, P1, P2 and P3). The K (control group) was administered with corn oil 1 ml/day. P0 was exposed to 700 ng/kg/day dioxin. P1, P2 and P3 was exposed to dioxin at a dose of 700 ng/kg/day and administered with α-tocopherol at a dose of 77, 140 and 259 mg/kg/day respectively. Dioxin exposure, corn oil and α-tocopherol administration were conducted orally for 20 days. On day-21, all rats were sacrificed for histological slides preparation of testicles with hematoxylin-eosin staining. Data were analyzed with analysis of variance and continued with the Duncan test. The results indicated that exposure to dioxin caused a decrease in the number of spermatogenic and Leydig cells. The administration of α-tocopherol at a dose of 140 mg/kg/day eliminated the effect of reducing the number of spermatogenic and Leydig cells caused by exposure to dioxin. The conclusion was the administration of α-tocopherol at 140 mg/kg/day was effective in maintaining the number of spermatogenic and Leydig cells in rats (Rattus norvegicus) exposed to 2,3,7,8 tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.
Birnbaum, L. S. 1995. Developmental effects of dioxins. Environ Health Perspect, Volume 103 (Suppl 7) : 89-94.
Chandra, A.K., A. Chatterjee, R. Ghosh and M. Sarkar. 2010. Vitamin Esupplementation protect chromium (VI)-induced spermatogenic and steroidogenic disorders in testicular tissues of rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology 48 : 972–979
Dirican, E.K., and Y. Kalender. 2012. Dichlorvos-induced testicular toxicity in male rats and the protective role of vitamins C and E. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology 64: 821–830
Dobrzyński, M., I. Całkosiński, I. Przywitowska, J.K. Brzoza,A.C. Waszkiewicz, E. Sołtan and O. Parulska. 2009. Effects of Dioxins in Environmental Pollution on Development of Tooth Disorders. Polish J. of Environ. Stud. 18 (3) : 319-323
El-Gerbed, M. S., El-Saad, A. M. A., Haussein, A. B. 2015. 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachloro-dibenzo-p-dioxin induced testicular toxicity in rats and the protective effect of quercetin: biochemical, histopathological and immunohistochemical studies. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 5 (01) : 099-109.
Hariyatmi. 2004. Kemampuan Vitamin E Sebagai Antioksidan Terhadap Radikal Bebas Pada Usia Lanjut. MIPA. 14 (1) : 54
Holdcraft, R. W and Robert, E. B. 2004. Hormonal Regulation of Spermatogenesis . International Journal of Andrology, 27 : 335-342.
Kimbrough, R.D. 1998. Selected other effects and TEF. Teratogenesis Carcinog. Mutagen. 17: 265- 273.
Milczarek A. 2005. Vitamin E Disease Mechanism IV : Free Radical Damage an Antioxidant Drug.
Oda, S.S. and Z.Kh.El. Maddawy. 2012. Protective effect of vitamin E and selenium combination on deltamethrin induced reproductive toxicity in male rats. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology 64 : 813–819
Wati, W.K., Wurlina, dan Sarmanu. 2014. Potensi vitamin E terhadap Jumlah Sel Spermatogenik pada Mencit yang Terpapar 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Veterinaria Medika. 7(3): 224-231.
Winarti, Christina dan Munarso, S. Joni. 2005. Kajian kontaminasi dioksin pada bahan pangan. Balai Besar Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pascapanen Pertanian.
Yin, H.P., J.P. Xu, X.Q. Zhou, and Y. Wang. 2012. Effects of vitamin E on reproductive hormones and testis structure in chronic dioxin– treated mice. Toxicology and industrial health 28 (2): 152
Copyright (c) 2021 Ainun Machmudia, Hana Eliyani, Widjiati Widjiati, Wurlina Wurlina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Ovozoa by Unair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. The journal allows the author to hold the copyright of the article without restrictions.
2. The journal allows the author(s) to retain publishing rights without restrictions
3. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA).
4. The Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike (CC BY-SA) license allows re-distribution and re-use of a licensed work on the conditions that the creator is appropriately credited and that any derivative work is made available under "the same, similar or a compatible license”. Other than the conditions mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation.