EATING OUTSIDE HOME DURING PANDEMIC: PERSPECTIVE BASED ON HEALTH BELIEF MODEL AND FUTURE IMPLICATIONS
Downloads
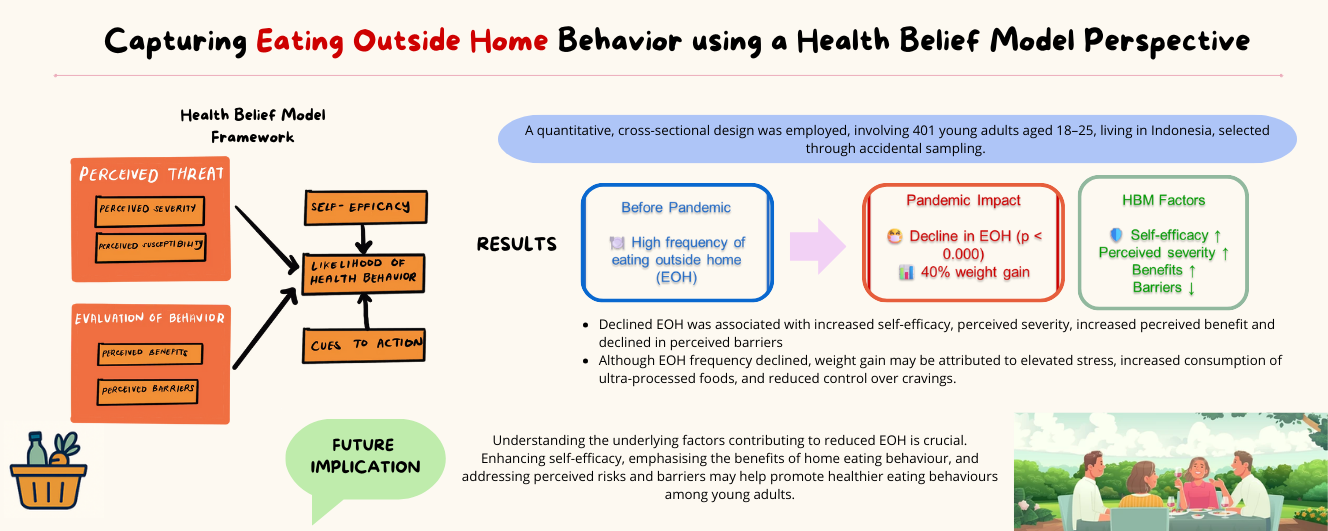
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant decline in eating outside the home (EOH). This study aimed to compare eating habits before and after the pandemic using the Health Belief Model (HBM) to explore the implications of EOH and its potential long-term effects. A quantitative cross-sectional design was employed, involving 401 young adults aged 18–25 years living in Indonesia, selected through accidental sampling. Data on the participants’ general characteristics, EOH frequency, and health beliefs were collected online using SurveyMonkey. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize each variable, and binary logistic regression was conducted to identify the predictors of EOH behavior and frequency. The majority of the respondents were female, unmarried, and held a diploma or undergraduate degree. Nearly 40% reported weight gain during the pandemic, although the frequency of EOH significantly declined (p < 0.000). The frequency of EOH was significantly associated with self-efficacy in eating at home, perceived severity, perceived benefits, and perceived barriers (p < 0.05). In conclusion, understanding the underlying factors contributing to reduced EOH is crucial. Enhancing self-efficacy, emphasizing the benefits of home eating, and addressing perceived risks and barriers may help promote healthier eating behaviors among young adults.
Adriani, M. dan Wirjatmadi, B. 2012. Peranan Gizi dalam Siklus Kehidupan. Edisi 1. Jakarta: Kencana.
Ammar, A., Brach, M., Trabelsi, K., Chtourou, H., Boukhris, O., Masmoudi, L., ... & ECLB-COVID19 Consortium. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 home confinement on eating behaviour and physical activity: results of the ECLB-COVID19 international online survey. Nutrients, 12(6), 1583.
Attamimy, H.B., Qomaruddin, M.B. (2017). Aplikasi Health Belief Model pada Perilaku Pencegahan Demam Berdarah Dengue. Jurnal Promker, 5(2), 245-255.
Bezerra, I. N., & Sichieri, R. (2009). Eating out of home and obesity: a Brazilian nationwide survey. Public health nutrition, 12(11), 2037-2043.
Bhutani, S., & Cooper, J. A. (2020). COVID‐19–related home confinement in adults: Weight gain risks and opportunities. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 28(9), 1576.
Bhutani, S., Vandellen, M. R., & Cooper, J. A. (2021). Longitudinal weight gain and related risk behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic in adults in the US. Nutrients, 13(2), 671.
Boushey, C. J., Coulston, A. M., Rock, C. L., & Monsen, E. (Eds.). (2001). Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Elsevier.
Brown, J. E., Isaacs, J. S., Krinke, U. B., Lechtenberg, E., Murtaugh, M. A., Sharbaugh, C., ... & Wooldridge, N. H. (2017). Nutrition through the life cycle (p. 624). Boston (MA): Cengage Learning.
Contento, I. R. (2011). Nutrition education: linking research, theory, and practice. Jones and Barlett Publishers.
Green, E. C., Murphy, E. M., & Gryboski, K. (2020). The health belief model. The Wiley encyclopedia of health psychology, 211-214.
Gesteiro, E., García-Carro, A., Aparicio-Ugarriza, R., & González-Gross, M. (2022). Eating out of home: influence on nutrition, health, and policies: a scoping review. Nutrients, 14(6), 1265.
Llanaj, E., Ádány, R., Lachat, C., & D’Haese, M. (2018). Examining food intake and eating out of home patterns among university students. PLoS One, 13(10), e0197874.
Mahmudiono, T., Rachmah, Q., Indriani, D., Permatasari, E. A., Hera, N. A., & Chen, H. L. (2022). Food and beverage consumption habits through the perception of health belief model (grab food or go food) in surabaya and pasuruan. Nutrients, 14(21), 4482.
Polsky, J. Y., & Garriguet, D. (2021). Eating away from home in Canada: impact on dietary intake. Health Reports, 32(8), 26-34.
Popkin, B. M., Duffey, K., & Gordon-Larsen, P. (2005). Environmental influences on food choice, physical activity and energy balance. Physiology & behavior, 86(5), 603-613.
Rosenstock, I.M. (1974). The Health Belief and Preventive Health Behavior. Health Education Monograph, 2(4): 354.
Seguin, R. A., Aggarwal, A., Vermeylen, F., & Drewnowski, A. (2016). Consumption frequency of foods away from home linked with higher body mass index and lower fruit and vegetable intake among adults: a cross‐sectional study. Journal of environmental and public health, 2016(1), 3074241.
Taher, A. K., Evans, N., & Evans, C. E. (2019). The cross-sectional relationships between consumption of takeaway food, eating meals outside the home and diet quality in British adolescents. Public health nutrition, 22(1), 63-73.
Walker-Clarke, A., Walasek, L., & Meyer, C. (2022). Psychosocial factors influencing the eating behaviours of older adults: A systematic review. Ageing Research Reviews, 77, 101597.
Yono, N. H., Widiyanah, I., & Ramadhon, S. (2021). Jurnal Administrasi Pendidikan, 28(special issue), 112-120.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- MEDIA GIZI INDONESIA Journal is the copyright owner of all materials published on this website.
- The formal legal provisions for access to digital articles of this electronic journal are subject to the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0), which means that MEDIA GIZI INDONESIA Journal and readers reserve the right to save, transmit media / format, manage in database, maintain, and publish articles as long as it continues to include the name of the Author.
- Printed and published print and electronic manuscripts are open access for educational, research and library purposes. In addition to these objectives, the editorial board shall not be liable for violations of copyright law.


2.png)





















