Date Log
Copyright (c) 2024 Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
1. Copyright of the article is transferred to the journal, by the knowledge of the author, whilst the moral right of the publication belongs to the author.
2. The legal formal aspect of journal publication accessibility refers to Creative Commons Atribusi-Non Commercial-Share alike (CC BY-NC-SA), (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)
3. The articles published in the journal are open access and can be used for non-commercial purposes. Other than the aims mentioned above, the editorial board is not responsible for copyright violation
The manuscript authentic and copyright statement submission can be downloaded ON THIS FORM.
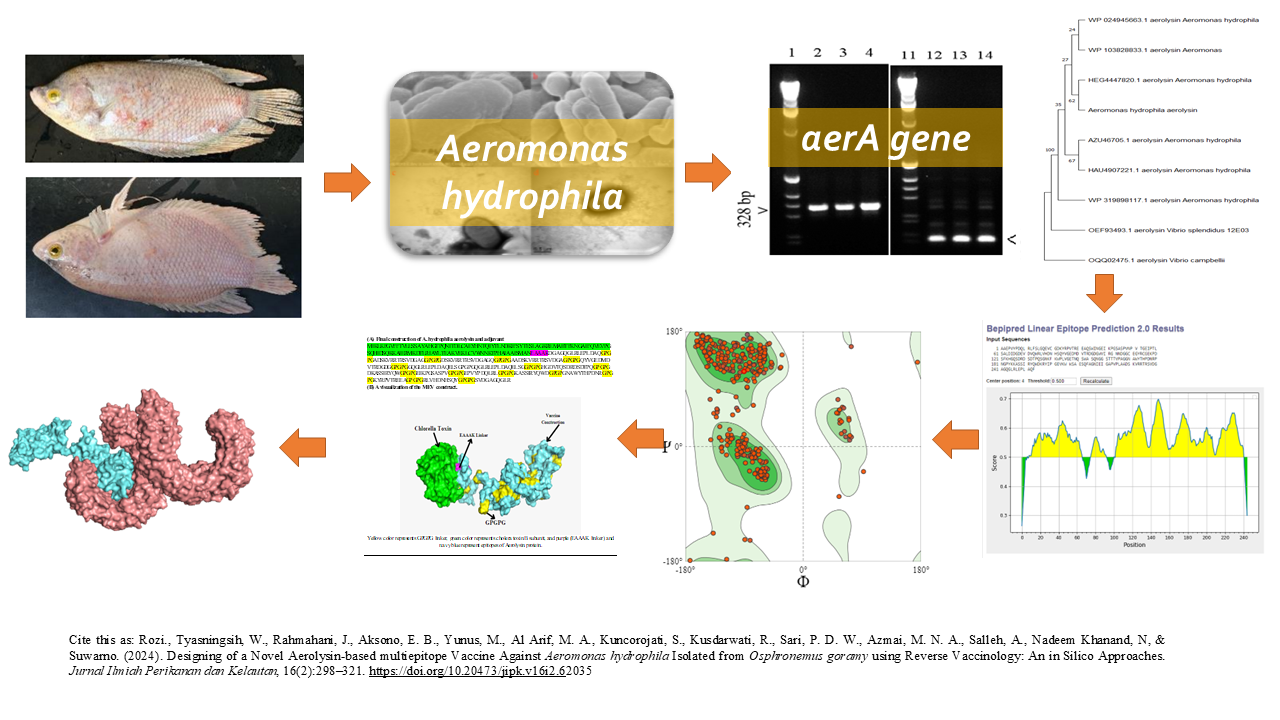
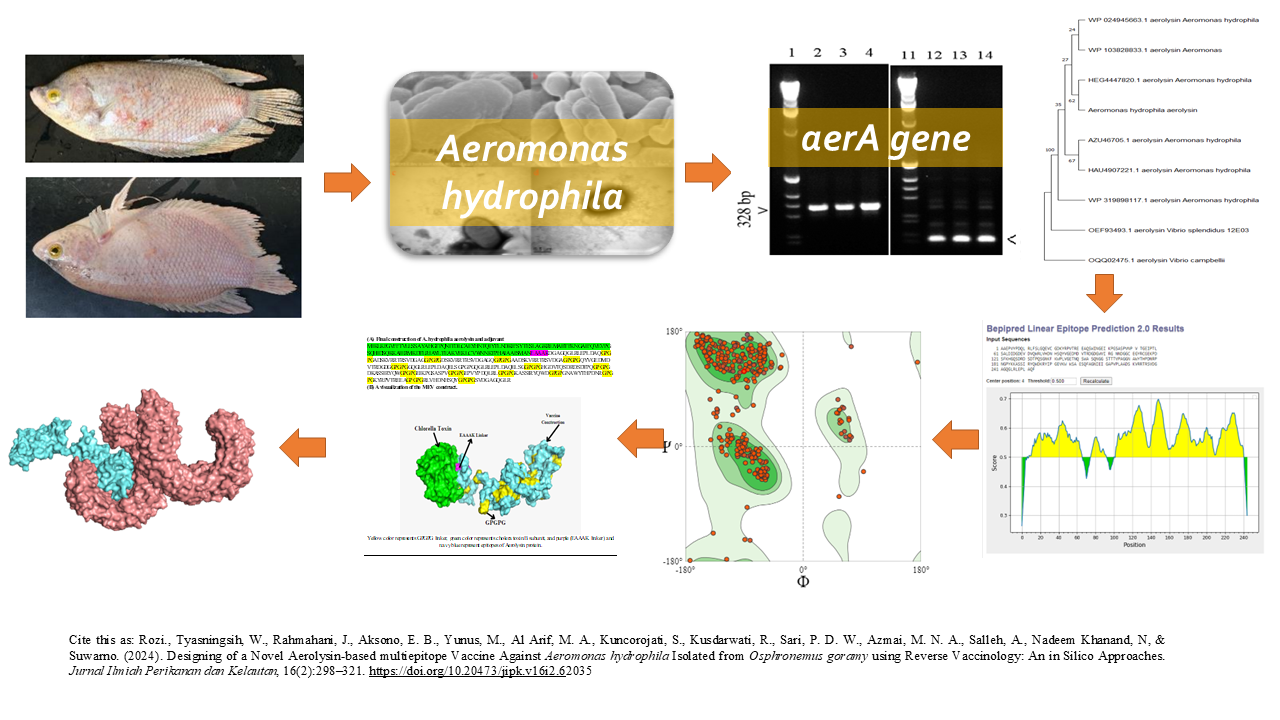
Designing of a Novel Aerolysin-based Multiepitope Vaccine against Aeromonas hydrophila Isolated from Osphronemus goramy Using Reverse Vaccinology: an in Silico Approaches
Corresponding Author(s) : Suwarno
Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, Vol. 16 No. 2 (2024): JURNAL ILMIAH PERIKANAN DAN KELAUTAN
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Highlight Research
- The study aims to develop a multi-epitope vaccine (MEV) against A. hydrophila by targeting the aerolysin toxin, a key virulence factor responsible for infections in fish and humans.
- Computational methods identified and optimized B-cell and T-cell epitopes, focusing on their ability to trigger immune responses without causing toxicity or allergenicity.
- In silico simulations demonstrated that the MEV has a strong binding affinity to immune receptors like TLR-4, MHC-I, and MHC-II, indicating its potential to induce robust cellular and humoral immunity.
- Structural analysis of the MEV showed a stable 3D conformation, with most residues in favorable regions, ensuring stability during immune activation.
- The MEV could enhance disease control in aquaculture and reduce human infection risks, offering a promising solution to address antibiotic resistance and the absence of effective vaccines.
Abstract
Aeromonas hydrophila, gram-negative, is a major pathogen responsible for various diseases in mammals, reptiles, amphibia, and vertebrates, including fish and humans. Targeting the specific toxin aerolysin in A. hydrophila is crucial to address antibiotic resistance and the lack of adequate and protective vaccines against this intracellular pathogen. This study aimed to identify a multi-epitope vaccination (MEV) candidate targeting A. hydrophila aerolysin toxin to combat the disease effectively. Standard biochemical characterization methods and sequencing of the 16S rRNA, rpoB, and aerA genes identified the isolate AHSA1 as A. hydrophila. Subsequently, we identified B and T cell epitopes on the aerolysin protein and separately predicted MHC-I and MHC-II epitopes. The epitopes are then evaluated for toxicity, antigenicity, allergenicity, and solubility. The vaccine design integrated multi-epitope-based constructs, utilizing specialized linkers (GPGPG) and EAAAK linkers to connect epitope peptides with adjuvants in the cholera toxin B component, thereby enhancing immunogenicity. Ramachandran plots showed that 85.25% of the residues were located in the most favorable regions, which was followed by the generously allowed zone (1.30%), the additional allowed regions (10.80%), and the forbidden regions (2.65%), thus confirming the feasibility of the modeled vaccine design. Based on docking simulations, MEV had the highest binding and interaction energies with TLR-4, TLR-9, MHC-I, and MHC-II (-1081.4, -723.2, 866.2, -9043.3 kcal/mol). Based on computational modelling, we expect the Aerolysin MEV candidate design to activate diverse immune mechanisms, stimulate robust responses against A. hydrophila, and maintain safety. The significant solubility, absence of toxicity or allergic response, and minimal side effects in animal testing all contribute to the potential clinical utility of this vaccine candidate.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- Abbott, S. L., Cheung, W. K. W., & Janda, J. M. (2003). The genus Aeromonas: Biochemical characteristics, atypical reactions, and phenotypic identification schemes. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41(6):2348-2357.
- Abdella, B., Abozahra, N. A., Shokrak, N. M., Mohamed, R. A., & El-Helow, E. R. (2023). Whole spectrum of Aeromonas hydrophila virulence determinants and the identification of novel SNPs using comparative pathogenomics. Scientific Reports, 13(1):1-13.
- Alawam, A. S., & Alwethaynani, M. S. (2024). Construction of an aerolysin-based multi-epitope vaccine against Aeromonas hydrophila: An in silico machine learning and artificial intelligence-supported approach. Frontiers in Immunology, 15(1):1-16.
- Albert, M. J., Ansaruzzaman, M., Talukder, K. A., Chopra, A. K., & Kuhn, I.(2000). Prevalence of enterotoxin genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from children with diarrhea, healthy controls, and the environment. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 38(10):3785-3790.
- Al-Kanany, F. N., & Othman, R. M. (2020). Cloning and expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkB gene in E. coli. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 14(1):389-397.
- Ashgar, S. S., Faidah, H., Bantun, F., Jalal, N. A., Qusty, N. F., Darwish, A., Haque, S., & Janahi, E. M. (2023). Integrated immunoinformatics and subtractive proteomics approach for multi-epitope vaccine designing to combat S. pneumoniae TIGR4. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 10(1):1-11.
- Austin, B., & Austin, D. A. (2016). Aeromonadaceae Representatives (Motile Aeromonads). In B. Austin & D. A. Austin (Eds.), Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish (6th ed., pp. 2941-2942). Springer.
- Bibi, S., Ullah, I., Zhu, B., Adnan, M., Liaqat, R., Kong, W.-B., & Niu, S. (2021). In silico analysis of epitope-based vaccine candidate against tuberculosis using reverse vaccinology. Scientific Reports, 11(1):1-16.
- Bidmos, F. A., Siris, S., Gladstone, C. A., & Langford, P. R. (2018). Bacterial vaccine antigen discovery in the reverse vaccinology 2.0 era: Progress and challenges. Frontiers in Immunology, 9(1):1-7.
- Blake, N., Cheney, G. L., Rosenzweig, J. A., Sha, J., & Chopra, A. K. (2024). Antimicrobial resistance in aeromonads and new therapies targeting quorum sensing. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 108(205):1-22.
- Cao, Y., Li, D., Fu, Y., Bai, Q., Chen, Y., Bai, X., Jing, Z., Sun, P., Bao, H., & Li, P. (2017). Rational design and efficacy of a multi-epitope recombinant protein vaccine against foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype A in pigs. Antiviral Research, 140(4):133-141.
- Cao, C., Krapp, L. F., Al Ouahabi, A., König, N. F., Cirauqui, N., Radenovic, A., Lutz, J. F., & Peraro, M. D. (2020). Aerolysin nanopores decode digital information stored in tailored macromolecular analytes. Science Advances, 6(50):1-8.
- Chakraborty, A., Dubey, S., Munang’andu, H. M., & Karunasagar, I. (2023). Oral administration of recombinant outer membrane protein A-based nanovaccine affords protection against Aeromonas hydrophila in zebrafish. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 40(8):1-15.
- Chauhan, V., Rungta, T., Goyal, K., & Singh, M. P. (2019). Designing a multi-epitope based vaccine to combat Kaposi sarcoma utilizing immunoinformatics approach. Scientific Reports, 9(1):1-15.
- Chen, H. X., Chen, F. J., Zhou, Q. J., Shang, S. L., Tang, B., Xu, Z. J., Duan, L. J., Jin, J. L., Xu, G. Z., & Yan, M. C. (2024). Two colistin resistance-producing Aeromonas strains, isolated from coastal waters in Zhejiang, China: characteristics, multi-drug resistance and pathogenicity. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15(1):1-15.
- Chen, J. H., Dong, B. J., & Fan, X. X. (2024). Revolutionizing adjuvant development: harnessing AI for next-generation cancer vaccines. Frontiers in Immunology, 15(1):1-20.
- Chopra, A. K., & Houston, C. W. (1999). Enterotoxins in Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Microbes and Infection, 1(13):1129-1137.
- Cirauqui, N., Abriata, L. A., van der Goot, F. G., & Dal Peraro, M. (2017). Structural, physicochemical and dynamic features conserved within the aerolysin pore-forming toxin family. Scientific Reports, 7, 13958.
- Collatz, M., Mock, F., Barth, E., Hölzer, M., Sachse, K., & Marz, M. (2021). EpiDope: a deep neural network for linear B-cell epitope prediction. Bioinformatics, 37(4):448-455.
- Dashti, F., Raisi, A., Pourali, G., Razavi, Z. S., Ravaei, F., Nahand, J. S., Kourkinejad-Gharaei, F., Mirazimi, S. M. A., Zamani, J., Tarrahimofrad, H., Hashemian, S. M. R., & Mirzaei, H. (2024). A computational approach to design a multiepitope vaccine against H5N1 virus. Virology Journal, 21(67):1-27.
- Dey, J., Mahapatra, S. R., Lata, S., Patro, S., Misra, N., & Suar, M. (2022). Exploring Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule polysaccharide proteins to design multiepitope subunit vaccine to fight against pneumonia. Expert Review of Vaccines, 21(4):569-587.
- Dhanda, S. K., Mahajan, S., Paul, S., Yan, Z., Kim, H., & Jespersen, M. C. (2019). IEDB-AR: Immune epitope database—analysis resource in 2019. Nucleic Acids Research, 47(W1): W502-W506.
- Dimitrov, I., Bangov, I., Flower, D. R., & Doytchinova, I. (2014). AllerTOP v.2—a server for in silico prediction of allergens. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 20(1):1-6.
- Doytchinova, I. A., & Flower, D. R. (2007). Identifying Candidate Subunit Vaccines Using An Alignment-Independent Method Based On Principal Amino Acid Properties. Vaccine, 25(5):856–866.
- Doytchinova, I. A., & Flower, D. R. (2007). VaxiJen: a server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinformatics, 8(1):1-7.
- Dubey, S., Ager-Wick, E., Peng, B., Evensen, Ø., Sørum, H., & Munang’andu, H. M. (2022). Characterization of virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes of Aeromonas media strain SD/21–15 from marine sediments in comparison with other Aeromonas spp. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13(1):1022639.
- Epple, H. J., Mankertz, J., Ignatius, R., Liesenfeld, O., Fromm, M., Zeitz, M., Chakraborty, T., & Schulzke, J. D. (2004). Aeromonas hydrophila beta-hemolysin induces active chloride secretion in colon epithelial cells (HT-29/B6). Infection and Immunity, 72(8):4848-4858.
- Fang, H. M., Ge, R., & Sin, Y. M. (2004). Cloning, characterisation and expression of Aeromonas hydrophila major adhesin. Fish & shellfish immunology, 16(5):645-658.
- Fei, D., Guo, Y., Fan, Q., Li, M., Sun, L., Ma, M., & Li, Y. (2020). Codon optimization, expression in Escherichia coli, and immunogenicity analysis of deformed wing virus (DWV) structural protein. PeerJ, 8(1):1-18.
- Fernández-Bravo, A., & Figueras, M. J. (2020). An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms, 8(1):1-39.
- Figueras, M. J., & Beaz-Hidalgo, R. (2015). Aeromonas infections in humans. In J. Graf (Ed.), Aeromonas (pp. 65-108). Caister Academic Press.
- Foroutan, M., Ghaffarifar, F., Sharifi, Z., & Dalimi, A. (2020). Vaccination with a novel multi-epitope ROP8 DNA vaccine against acute Toxoplasma gondii infection induces strong B and T cell responses in mice. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 69(2):1-13.
- Gasperini, G., Alfini, R., Arato, V., Mancini, F., Aruta, M. G., Kanvatirth, P., Pickard, D., Necchi, F., Saul, A., Rossi, O., Micoli, F., & Mastroeni, P. (2021). Salmonella Paratyphi A outer membrane vesicles displaying Vi polysaccharide as a multivalent vaccine against enteric fever. Infection and Immunity, 89(4):1-20.
- Gasteiger, E., Hoogland, C., Gattiker, A., Duvaud, S., Wilkins, M. R., Appel, R. D., & Bairoch, A. (2005). Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In J. M. Walker (Ed.), The Proteomics Protocols Handbook (pp. 571-607). Humana Press.
- Grote, A., Hiller, K., Scheer, M., Münch, R., Nörtemann, B., Hempel, D. C., & Jahn, D. (2005). JCat: a novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Research, 33(Web Server issue): W526-W531.
- Guo, L., Yin, R., Liu, K., Lv, X., Li, Y., Duan, X., Chu, Y., Xi, T., & Xing, Y. (2014). Immunological features and efficacy of a multi-epitope vaccine CTB-UE against H. pylori in BALB/c mice model. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(8):3495-3507.
- He, R., Yang, X., Liu, C., Chen, X., Wang, L., Xiao, M., Ye, J., Wu, Y., & Ye, L. (2018). Efficient control of chronic LCMV infection by a CD4 T cell epitope-based heterologous prime-boost vaccination in a murine model. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 15(9):815-826.
- Hofer, E., Reis, C. M. F., Theophilo, G. N. D., Cavalcanti, V. O., Lima, N. V., & Henriques, M. F. C. M. (2006). Envolvimento de Aeromonas em surto de doença diarréica aguda em São Bento do Una, Pernambuco. Revista Da Sociedade Brasileira De Medicina Tropical, 39(2):217-220.
- Howard, S. P., & Buckley, J. T. (2012). Aerolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila and related toxins. In Pore-Forming Toxins (pp. 35-52). Springer.
- Iacovache, I., Bischofberger, M., & van der Goot, F. G. (2016). Molecular docking studies confirmed the strong affinity of the MEV construct for immune receptors. Journal of Molecular Biology, 428(12):2345-2356.
- Ikai, A. (1980). Thermostability and aliphatic index of globular proteins. The Journal of Biochemistry, 88(6):1895-1898.
- Ismail, S., Ahmad, S., & Azam, S. S. (2020). Immunoinformatics Characterization Of SARS-Cov-2 Spike Glycoprotein For Prioritization Of Epitope-Based Multivalent Peptide Vaccine. Journal Of Molecular Liquids, 31(4): 113-612.
- Jalal, K., Khan, K., Basharat, Z., Abbas, M. N., Uddin, R., Ali, F., Khan, S. A., & Hassan, S. S. (2022). Reverse vaccinology approach for multi-epitope centered vaccine design against delta variant of the SARS-CoV-2. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(1):1-19.
- Janda, J. M., & Abbott, S. L. (2010). The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clinical microbiology reviews, 23(1):35-73.
- Jespersen, M. C., Peters, B., Nielsen, M., & Marcatili, P. (2017). BepiPred-2.0: Improving sequence-based B-cell epitope prediction using conformational epitopes. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(1):W24-W29.
- Jiang, P., Cai, Y., Chen, J., Ye, X., Mao, S., Zhu, S., Xue, X., Chen, S., & Zhang, L. (2017). Evaluation of tandem Chlamydia trachomatis MOMP multi-epitopes vaccine in BALB/c mice model. Vaccine, 35(23):3096-3103.
- Joshi, A., Krishnan, S., & Kaushik, V. (2022). Codon usage studies and epitope-based peptide vaccine prediction against Tropheryma whipplei. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 20(1):1-12.
- Karkashan, A. (2024). Immunoinformatics assisted profiling of West Nile virus proteome to determine immunodominant epitopes for the development of next-generation multi-peptide vaccine. Frontiers in Immunology, 15(1):1-15.
- King, G. E., Werner, S. B., & Kizer, K. W. (1992). Epidemiology of Aeromonas infections in California. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 15(3): 449-452.
- Kozakov, D., Hall, D. R., Xia, B., Porter, K. A., Padhorny, D., Yueh, C., Beglov, D., & Vajda, S. (2017). The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nature Protocols, 12(2):255-278.
- Kupfer, D. M., da Silva-Tatley, F. M., & Zylstra, G. J. (1997). rpoB gene as a novel molecular marker to infer phylogeny in Planctomycetales. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 72(1):1-10.
- Kyte, J., & Doolittle, R. F. (1982). A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. Journal of Molecular Biology, 157(1):105-132.
- Lamy, B., Kodjo, A., & Laurent, F. (2009). Prospective nationwide study of Aeromonas infections in France. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 47(4):1234-1237.
- Laxminarayan, R., MacLennan, C., & Davies, S. (2024). Vaccines and antimicrobial resistance: from science to policy. Royal Society.
- Lennerz, V., Gross, S., Gallerani, E., Sessa, C., Mach, N., Boehm, S., Hess, D., Von Boehmer, L., Knuth, A., & Ochsenbein, A. F. (2014). Immunologic response to the survivin-derived multi-epitope vaccine EMD640744 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 63(4):381-394.
- Legario, F. S., Choresca, C. H., Jr., Grace, K., Turnbull, J. F., & Crumlish, M. (2023). Identification and characterization of motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in the Philippines. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 134(12): 1-11
- Li, J., Ma, S., Li, Z., Yu, W., Zhou, P., & Ye, X. (2021). Construction and characterization of an Aeromonas hydrophila multi-gene deletion strain and evaluation of its potential as a live-attenuated vaccine in grass carp. Vaccines, 9(5):1-14.
- Linh, N. V., Le, T. D., Ha, T. D., Khongdee, N., Hoseinifar, S. H., Musthafa, M. S., Dawood, M. A. O., & Doan, H. V. (2022). Efficacy of different routes of formalin-killed vaccine administration on immunity and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) challenged with Streptococcus agalactiae. Fishes, 7(6):1-13.
- Liu, B., Zheng, D., Zhou, S., Chen, L., & Yang, J. (2022). VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Research, 50(D1):912-917.
- Lu, C., Meng, S., Jin, Y., Zhang, W., Li, Z., Wang, F., Wang-Johanning, F., Wei, Y., Liu, H., & Tu, H. (2017). A novel multi-epitope vaccine from MMSA-1 and DKK 1 for multiple myeloma immunotherapy. British Journal of Haematology, 178(3):413-426.
- Mahram, A., & Herbordt, M. C. (2015). NCBI BLASTP on high-performance reconfigurable computing systems. ACM Transactions on Reconfigurable Technology and Systems, 7(1):1-20.
- Martin-Carnahan, A., & Joseph, S. W. (2015). Aeromonadaceae. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Martinez-Murcia, A. J., Saavedra, M. J., Mota, V. R., Maier, T., Stackebrandt, E., & Cousin, S. (2008). Aeromonas aquariorum sp. nov., isolated from aquaria of ornamental fish. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology, 58(5):1169-1175.
- Matyar, F., Kaya, A., & Dinçer, S. (2007). Distribution and antibacterial drug resistance of Aeromonas spp. from fresh and brackish waters in Southern Turkey. Annals of Microbiology, 57(1):443-447.
- Moreno, C., Romero, J., & Espejo, R. T. (2002). Polymorphism in repeated 16S rRNA genes is a common property of type strains and environmental isolates of the genus Vibrio. Microbiology, 148(5):1233-1239.
- Mortazavi, A., Doosti, A., & Sharifzadeh, A. (2024). A novel chimeric vaccine containing multiple epitopes for simulating robust immune activation against Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Immunology, 25(1):1-27.
- Nayak, S. K. (2020). Current prospects and challenges in fish vaccine development in India with special reference to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 100(5):283-299.
- Nguyen, T. L., & Kim, H. (2024). Immunoinformatics and computational approaches driven designing a novel vaccine candidate against Powassan virus. Scientific Reports, 14(1):1-15.
- Nielsen, M. E., Høi, L., Schmidt, A. S., Qian, D., Shimada, T., Shen, J. Y., & Larsen, J. L. (2001). Is Aeromonas hydrophila the dominant motile Aeromonas species that causes disease outbreaks in aquaculture production in the Zhejiang Province of China?. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 46(1):23-29.
- Nolla-Salas, J., Codina-Calero, J., Vallés-Angulo, S., Sitges-Serra, A., Zapatero-Ferrándiz, A., Climent, M. C., & Gómez, J. R. (2017). Clinical significance and outcome of Aeromonas spp. infections among 204 adult patients. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 36(3):1393-1403.
- Pablos, M., Huys, G., Cnockaert, M., Rodríguez-Calleja, J. M., Otero, A., & Santos, J. A. (2011). Identification and epidemiological relationships of Aeromonas isolates from patients with diarrhea, drinking water and foods. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 147(2):203-210.
- Pang, M., Jiang, J., Xie, X., Wu, Y., Dong, Y., Kwok, A. H. Y., Zhang, W., & Leung, F. C. (2015). Novel insights into the pathogenicity of epidemic Aeromonas hydrophila ST251 clones from comparative genomics. Scientific Reports, 5, 9833.
- Park, S. W., Lee, B. H., Song, S. H., & Kim, M. K. (2023). Revisiting The Ramachandran Plot Based On Statistical Analysis Of Static And Dynamic Characteristics Of Protein Structures. Journal Of Structural Biology, 21(5):107-939.
- Peatman, E., Mohammed, H., Kirby, A., Shoemaker, C. A., Yildirim-Aksoy, M., & Beck, B. H. (2018). Mechanisms of pathogen virulence and host susceptibility in virulent Aeromonas hydrophila infections of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture, 482(1):1-8.
- Pessoa, R. B. G., de Oliveira, W. F., dos Santos Correia, M. T., da Silva Fontes, A. F., & Breitenbach Barroso Coelho, L. C. (2022). Aeromonas and human health disorders: Clinical approaches. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13:1-15
- Persson, S., Al-Shuweli, S., Yapici, S., Jensen, J. N., & Olsen, K. E. (2015). Identification of clinical Aeromonas species by rpoB and gyrB sequencing and development of a multiplex PCR method for detection of Aeromonas hydrophila, A. caviae, A. veronii, and A. media. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 53(2):653-656.
- Pippy, J. H., & Hare, G. M. (1969). Relationship of river pollution to bacterial infection in salmon (Salmo salar) and suckers (Catostomus commersoni). Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 98(4):685-690.
- Popoff, M., & Véron, M. (1976). A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila group. Journal of General Microbiology, 94(1):11-22.
- Pridgeon, J. W., & Zhang, D. (2014). Complete genome sequence of the highly virulent Aeromonas hydrophila AL09-71 isolated from diseased channel catfish in West Alabama. Genome Announcements, 2(3):1-14.
- Qamar, M. T. U., Shahid, F., Aslam, S., & Ashfaq, U. A. (2020). Reverse vaccinology assisted designing of multiepitope-based subunit vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Infectious Diseases of Poverty, 99(132):1-22.
- Rathore, A. S., Choudhury, S., Arora, A., Tijare, P., & Raghava, G. P. S. (2024). ToxinPred 3.0: An improved method for predicting the toxicity of peptides. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 179(12):1-13.
- Reker, D., Rodrigues, T., Schneider, P., & Schneider, G. (2014). Identifying the macromolecular targets of de novo-designed chemical entities through self-organizing map consensus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(11):4067-4072.
- Rozi., Rahayu, K., Daruti, D. N., & Stella, M. S. P. (2018). Study on characterization, pathogenicity and histopathology of disease caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in gourami (Osphronemus gouramy). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 137 012003
- Rozi., Rahayu, K., & Daruti, D. N. (2018). Detection and analysis of hemolysin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Gouramy (Osphronemus gouramy) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 137 012001
- Saadi, M., Karkashan, A., & Munang’andu, H. M. (2017). Current state of modern biotechnological-based Aeromonas hydrophila vaccines for aquaculture: A systematic review. Biomed Research International, 2019(1):1-11.
- Sagas, D., Hershko, Y., & Levitskyi, K. (2024). Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of antimicrobial resistance and population structure of gastroenteritis-related Aeromonas isolates. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob, 2024(23):1-8.
- Serruto, D., Serino, L., Masignani, V., & Pizza, M. (2012). Genome-based approaches to develop vaccines against bacterial pathogens. Vaccine, 27(25-26):3245-3250.
- Sette, A., & Fikes, J. (2003). Epitope-based vaccines: an update on epitope identification, vaccine design and delivery. Current Opinion in Immunology, 15(4):461-470.
- Sidney, J., Peters, B., Frahm, N., Brander, C., & Sette, A. (2008). HLA class I supertypes: A revised and updated classification. BMC Immunology, 9(1):1-15.
- Slingluff, C. L., Lee, S., Zhao, F., Chianese-Bullock, K. A., Olson, W. C., Butterfield, L. H., Whiteside, T. L., Leming, P. D., & Kirkwood, J. M. (2013). A randomized phase II trial of multiepitope vaccination with melanoma peptides for cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells for patients with metastatic melanoma (E1602). Clinical Cancer Research, 19(15):4228-4238.
- Solanki, V., & Tiwari, V. (2018). Subtractive proteomics to identify novel drug targets and reverse vaccinology for the development of chimeric vaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii. Scientific Reports, 8(1):1-19.
- Solanki, V., Sharma, S., & Tiwari, V. (2021). Subtractive proteomics and reverse vaccinology strategies for designing a multiepitope vaccine targeting membrane proteins of Klebsiella pneumoniae. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics, 27(2):1177-1195.
- Stratmann, T. (2015). Cholera toxin subunit B as adjuvant—An accelerator in protective immunity and a break in autoimmunity. Vaccines, 3(3): 579–596.
- Sughra, F., Hafeez-ur-Rehman, M., Abbas, F., Altaf, I., Hassan, Z., & Bhatti, A. (2022). Molecular characterisation and genetic analysis of aerolysin and haemolysin in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from diseased Labeo rohita by polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Fisheries, 10(3):1-5.
- Toledo, H., Baly, A., Castro, O., Resik, S., Laferté, J., Rolo, F., Navea, L., Lobaina, L., Cruz, O., & Miguez, J. (2001). A phase I clinical trial of a multi-epitope polypeptide TAB9 combined with Montanide ISA 720 adjuvant in non-HIV-1 infected human volunteers. Vaccine, 19(30):4328-4336.
- Ullah, M. A., Sarkar, B., & Islam, S. S. (2020). Exploiting the reverse vaccinology approach to design novel subunit vaccines against Ebola virus. Immunobiology, 225(3):1-15.
- Vita, R., Overton, J. A., Greenbaum, J. A., Ponomarenko, J., Clark, J. D., Cantrell, J. R., Wheeler, D. K., Gabbard, J. L., Hix, D., Sette, A., & Peters, B. (2015). The immune epitope database (IEDB) 3.0. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(D1):D405-D412.
- Vivekanandhan, G., Savithamani, K., Hatha, A. A. M., & Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P. (2002). Antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from marketed fish and prawn of South India. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 76(1-2):165-168.
- Wang, G., Clark, C. G., Liu, C., Pucknell, C., Munro, C. K., Kruk, T. M. A. C., Caldeira, R., Woodward, D. L., & Rodgers, F. G. (2003). Detection and characterization of the hemolysin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria by multiplex PCR. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41(3):1048-1054.
- Wang, P., Sidney, J., Dow, C., Mothé, B., Sette, A., & Peters, B. (2010). A systematic assessment of MHC class II peptide binding predictions and evaluation of a consensus approach. PLoS Computational Biology, 6(4):1-16.
- Waterhouse, A., Bertoni, M., Bienert, S., Studer, G., Tauriello, G., Gumienny, R., Heer, F. T., de Beer, T. A. P., Rempfer, C., Bordoli, L., Lepore, R., & Schwede, T. (2018). SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(W1):W296-W303.
- Wu, C.-J., Chen, P.-L., Tang, H.-J., Chen, H.-M., Tseng, F.-C., Shih, H.-I., Hung, Y.-P., Chung, C.-H., & Ko, W.-C. (2014). Incidence of Aeromonas bacteremia in southern Taiwan: Vibrio and Salmonella bacteremia as comparators. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection, 47(2):145-148.
- Xu, T., Cody, R., Rasmussen-Ivey., Francesco, S., Moen., Fernández-Bravo, A., Lamy, B., et al Mark, R., & Liles. (2023). A Global Survey of Hypervirulent Aeromonas hydrophila (vAh) Identified vAh Strains in the Lower Mekong River Basin and Diverse Opportunistic Pathogens from Farmed Fish and Other Environmental Sources. Microbiology spectrum, 11(2) doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03705-22
- Zhang, X. H., He, X. X., Austin, B., & Zhang, G. (2002). Molecular identification and epidemiological tracing of Aeromonas hydrophila strains isolated from outbreaks of fish disease in China. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 93(2):214-220.
- Zhang, D., Pridgeon, J. W., & Zhang, L. (2012). Complete genome sequence of a moderately virulent Aeromonas hydrophila strain pc104A isolated from the soil of a catfish pond in West Alabama. Genome Announcements, 2(3):1-9.
- Zhang, L. (2018). Multi-epitope vaccines: a promising strategy against tumors and viral infections. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 15(2):182-184.
- Zhang, L., Ma, L., Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Ai, X., & Dong, J. (2022). Sanguinarine protects channel catfish against Aeromonas hydrophila infection by inhibiting aerolysin and biofilm formation. Pathogens, 11(3):1-11.
- Zheng, W., Zhang, C., Bell, E. W., & Zhang, Y. (2019). I-TASSER gateway: A protein structure and function prediction server powered by XSEDE. Future Generation Computer Systems, 99(10):73-85.
- Zhou, W.-Y., Shi, Y., Wu, C., Zhang, W.-J., Mao, X.-H., Guo, G., Li, H.-X., & Zou, Q.-M. (2009). Therapeutic efficacy of a multi-epitope vaccine against Helicobacter pylori infection in BALB/c mice model. Vaccine, 27(36):5013-5019.
- Zhou, A. Q., O’Hern, C. S., & Regan, L. (2011). Revisiting the Ramachandran plot from a new angle. Protein Science, 20(7):1166-1171.
References
Abbott, S. L., Cheung, W. K. W., & Janda, J. M. (2003). The genus Aeromonas: Biochemical characteristics, atypical reactions, and phenotypic identification schemes. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41(6):2348-2357.
Abdella, B., Abozahra, N. A., Shokrak, N. M., Mohamed, R. A., & El-Helow, E. R. (2023). Whole spectrum of Aeromonas hydrophila virulence determinants and the identification of novel SNPs using comparative pathogenomics. Scientific Reports, 13(1):1-13.
Alawam, A. S., & Alwethaynani, M. S. (2024). Construction of an aerolysin-based multi-epitope vaccine against Aeromonas hydrophila: An in silico machine learning and artificial intelligence-supported approach. Frontiers in Immunology, 15(1):1-16.
Albert, M. J., Ansaruzzaman, M., Talukder, K. A., Chopra, A. K., & Kuhn, I.(2000). Prevalence of enterotoxin genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from children with diarrhea, healthy controls, and the environment. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 38(10):3785-3790.
Al-Kanany, F. N., & Othman, R. M. (2020). Cloning and expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkB gene in E. coli. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 14(1):389-397.
Ashgar, S. S., Faidah, H., Bantun, F., Jalal, N. A., Qusty, N. F., Darwish, A., Haque, S., & Janahi, E. M. (2023). Integrated immunoinformatics and subtractive proteomics approach for multi-epitope vaccine designing to combat S. pneumoniae TIGR4. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 10(1):1-11.
Austin, B., & Austin, D. A. (2016). Aeromonadaceae Representatives (Motile Aeromonads). In B. Austin & D. A. Austin (Eds.), Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish (6th ed., pp. 2941-2942). Springer.
Bibi, S., Ullah, I., Zhu, B., Adnan, M., Liaqat, R., Kong, W.-B., & Niu, S. (2021). In silico analysis of epitope-based vaccine candidate against tuberculosis using reverse vaccinology. Scientific Reports, 11(1):1-16.
Bidmos, F. A., Siris, S., Gladstone, C. A., & Langford, P. R. (2018). Bacterial vaccine antigen discovery in the reverse vaccinology 2.0 era: Progress and challenges. Frontiers in Immunology, 9(1):1-7.
Blake, N., Cheney, G. L., Rosenzweig, J. A., Sha, J., & Chopra, A. K. (2024). Antimicrobial resistance in aeromonads and new therapies targeting quorum sensing. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 108(205):1-22.
Cao, Y., Li, D., Fu, Y., Bai, Q., Chen, Y., Bai, X., Jing, Z., Sun, P., Bao, H., & Li, P. (2017). Rational design and efficacy of a multi-epitope recombinant protein vaccine against foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype A in pigs. Antiviral Research, 140(4):133-141.
Cao, C., Krapp, L. F., Al Ouahabi, A., König, N. F., Cirauqui, N., Radenovic, A., Lutz, J. F., & Peraro, M. D. (2020). Aerolysin nanopores decode digital information stored in tailored macromolecular analytes. Science Advances, 6(50):1-8.
Chakraborty, A., Dubey, S., Munang’andu, H. M., & Karunasagar, I. (2023). Oral administration of recombinant outer membrane protein A-based nanovaccine affords protection against Aeromonas hydrophila in zebrafish. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 40(8):1-15.
Chauhan, V., Rungta, T., Goyal, K., & Singh, M. P. (2019). Designing a multi-epitope based vaccine to combat Kaposi sarcoma utilizing immunoinformatics approach. Scientific Reports, 9(1):1-15.
Chen, H. X., Chen, F. J., Zhou, Q. J., Shang, S. L., Tang, B., Xu, Z. J., Duan, L. J., Jin, J. L., Xu, G. Z., & Yan, M. C. (2024). Two colistin resistance-producing Aeromonas strains, isolated from coastal waters in Zhejiang, China: characteristics, multi-drug resistance and pathogenicity. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15(1):1-15.
Chen, J. H., Dong, B. J., & Fan, X. X. (2024). Revolutionizing adjuvant development: harnessing AI for next-generation cancer vaccines. Frontiers in Immunology, 15(1):1-20.
Chopra, A. K., & Houston, C. W. (1999). Enterotoxins in Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Microbes and Infection, 1(13):1129-1137.
Cirauqui, N., Abriata, L. A., van der Goot, F. G., & Dal Peraro, M. (2017). Structural, physicochemical and dynamic features conserved within the aerolysin pore-forming toxin family. Scientific Reports, 7, 13958.
Collatz, M., Mock, F., Barth, E., Hölzer, M., Sachse, K., & Marz, M. (2021). EpiDope: a deep neural network for linear B-cell epitope prediction. Bioinformatics, 37(4):448-455.
Dashti, F., Raisi, A., Pourali, G., Razavi, Z. S., Ravaei, F., Nahand, J. S., Kourkinejad-Gharaei, F., Mirazimi, S. M. A., Zamani, J., Tarrahimofrad, H., Hashemian, S. M. R., & Mirzaei, H. (2024). A computational approach to design a multiepitope vaccine against H5N1 virus. Virology Journal, 21(67):1-27.
Dey, J., Mahapatra, S. R., Lata, S., Patro, S., Misra, N., & Suar, M. (2022). Exploring Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule polysaccharide proteins to design multiepitope subunit vaccine to fight against pneumonia. Expert Review of Vaccines, 21(4):569-587.
Dhanda, S. K., Mahajan, S., Paul, S., Yan, Z., Kim, H., & Jespersen, M. C. (2019). IEDB-AR: Immune epitope database—analysis resource in 2019. Nucleic Acids Research, 47(W1): W502-W506.
Dimitrov, I., Bangov, I., Flower, D. R., & Doytchinova, I. (2014). AllerTOP v.2—a server for in silico prediction of allergens. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 20(1):1-6.
Doytchinova, I. A., & Flower, D. R. (2007). Identifying Candidate Subunit Vaccines Using An Alignment-Independent Method Based On Principal Amino Acid Properties. Vaccine, 25(5):856–866.
Doytchinova, I. A., & Flower, D. R. (2007). VaxiJen: a server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinformatics, 8(1):1-7.
Dubey, S., Ager-Wick, E., Peng, B., Evensen, Ø., Sørum, H., & Munang’andu, H. M. (2022). Characterization of virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes of Aeromonas media strain SD/21–15 from marine sediments in comparison with other Aeromonas spp. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13(1):1022639.
Epple, H. J., Mankertz, J., Ignatius, R., Liesenfeld, O., Fromm, M., Zeitz, M., Chakraborty, T., & Schulzke, J. D. (2004). Aeromonas hydrophila beta-hemolysin induces active chloride secretion in colon epithelial cells (HT-29/B6). Infection and Immunity, 72(8):4848-4858.
Fang, H. M., Ge, R., & Sin, Y. M. (2004). Cloning, characterisation and expression of Aeromonas hydrophila major adhesin. Fish & shellfish immunology, 16(5):645-658.
Fei, D., Guo, Y., Fan, Q., Li, M., Sun, L., Ma, M., & Li, Y. (2020). Codon optimization, expression in Escherichia coli, and immunogenicity analysis of deformed wing virus (DWV) structural protein. PeerJ, 8(1):1-18.
Fernández-Bravo, A., & Figueras, M. J. (2020). An update on the genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, epidemiology, and pathogenicity. Microorganisms, 8(1):1-39.
Figueras, M. J., & Beaz-Hidalgo, R. (2015). Aeromonas infections in humans. In J. Graf (Ed.), Aeromonas (pp. 65-108). Caister Academic Press.
Foroutan, M., Ghaffarifar, F., Sharifi, Z., & Dalimi, A. (2020). Vaccination with a novel multi-epitope ROP8 DNA vaccine against acute Toxoplasma gondii infection induces strong B and T cell responses in mice. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 69(2):1-13.
Gasperini, G., Alfini, R., Arato, V., Mancini, F., Aruta, M. G., Kanvatirth, P., Pickard, D., Necchi, F., Saul, A., Rossi, O., Micoli, F., & Mastroeni, P. (2021). Salmonella Paratyphi A outer membrane vesicles displaying Vi polysaccharide as a multivalent vaccine against enteric fever. Infection and Immunity, 89(4):1-20.
Gasteiger, E., Hoogland, C., Gattiker, A., Duvaud, S., Wilkins, M. R., Appel, R. D., & Bairoch, A. (2005). Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In J. M. Walker (Ed.), The Proteomics Protocols Handbook (pp. 571-607). Humana Press.
Grote, A., Hiller, K., Scheer, M., Münch, R., Nörtemann, B., Hempel, D. C., & Jahn, D. (2005). JCat: a novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Research, 33(Web Server issue): W526-W531.
Guo, L., Yin, R., Liu, K., Lv, X., Li, Y., Duan, X., Chu, Y., Xi, T., & Xing, Y. (2014). Immunological features and efficacy of a multi-epitope vaccine CTB-UE against H. pylori in BALB/c mice model. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(8):3495-3507.
He, R., Yang, X., Liu, C., Chen, X., Wang, L., Xiao, M., Ye, J., Wu, Y., & Ye, L. (2018). Efficient control of chronic LCMV infection by a CD4 T cell epitope-based heterologous prime-boost vaccination in a murine model. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 15(9):815-826.
Hofer, E., Reis, C. M. F., Theophilo, G. N. D., Cavalcanti, V. O., Lima, N. V., & Henriques, M. F. C. M. (2006). Envolvimento de Aeromonas em surto de doença diarréica aguda em São Bento do Una, Pernambuco. Revista Da Sociedade Brasileira De Medicina Tropical, 39(2):217-220.
Howard, S. P., & Buckley, J. T. (2012). Aerolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila and related toxins. In Pore-Forming Toxins (pp. 35-52). Springer.
Iacovache, I., Bischofberger, M., & van der Goot, F. G. (2016). Molecular docking studies confirmed the strong affinity of the MEV construct for immune receptors. Journal of Molecular Biology, 428(12):2345-2356.
Ikai, A. (1980). Thermostability and aliphatic index of globular proteins. The Journal of Biochemistry, 88(6):1895-1898.
Ismail, S., Ahmad, S., & Azam, S. S. (2020). Immunoinformatics Characterization Of SARS-Cov-2 Spike Glycoprotein For Prioritization Of Epitope-Based Multivalent Peptide Vaccine. Journal Of Molecular Liquids, 31(4): 113-612.
Jalal, K., Khan, K., Basharat, Z., Abbas, M. N., Uddin, R., Ali, F., Khan, S. A., & Hassan, S. S. (2022). Reverse vaccinology approach for multi-epitope centered vaccine design against delta variant of the SARS-CoV-2. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(1):1-19.
Janda, J. M., & Abbott, S. L. (2010). The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clinical microbiology reviews, 23(1):35-73.
Jespersen, M. C., Peters, B., Nielsen, M., & Marcatili, P. (2017). BepiPred-2.0: Improving sequence-based B-cell epitope prediction using conformational epitopes. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(1):W24-W29.
Jiang, P., Cai, Y., Chen, J., Ye, X., Mao, S., Zhu, S., Xue, X., Chen, S., & Zhang, L. (2017). Evaluation of tandem Chlamydia trachomatis MOMP multi-epitopes vaccine in BALB/c mice model. Vaccine, 35(23):3096-3103.
Joshi, A., Krishnan, S., & Kaushik, V. (2022). Codon usage studies and epitope-based peptide vaccine prediction against Tropheryma whipplei. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 20(1):1-12.
Karkashan, A. (2024). Immunoinformatics assisted profiling of West Nile virus proteome to determine immunodominant epitopes for the development of next-generation multi-peptide vaccine. Frontiers in Immunology, 15(1):1-15.
King, G. E., Werner, S. B., & Kizer, K. W. (1992). Epidemiology of Aeromonas infections in California. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 15(3): 449-452.
Kozakov, D., Hall, D. R., Xia, B., Porter, K. A., Padhorny, D., Yueh, C., Beglov, D., & Vajda, S. (2017). The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nature Protocols, 12(2):255-278.
Kupfer, D. M., da Silva-Tatley, F. M., & Zylstra, G. J. (1997). rpoB gene as a novel molecular marker to infer phylogeny in Planctomycetales. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 72(1):1-10.
Kyte, J., & Doolittle, R. F. (1982). A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. Journal of Molecular Biology, 157(1):105-132.
Lamy, B., Kodjo, A., & Laurent, F. (2009). Prospective nationwide study of Aeromonas infections in France. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 47(4):1234-1237.
Laxminarayan, R., MacLennan, C., & Davies, S. (2024). Vaccines and antimicrobial resistance: from science to policy. Royal Society.
Lennerz, V., Gross, S., Gallerani, E., Sessa, C., Mach, N., Boehm, S., Hess, D., Von Boehmer, L., Knuth, A., & Ochsenbein, A. F. (2014). Immunologic response to the survivin-derived multi-epitope vaccine EMD640744 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 63(4):381-394.
Legario, F. S., Choresca, C. H., Jr., Grace, K., Turnbull, J. F., & Crumlish, M. (2023). Identification and characterization of motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in the Philippines. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 134(12): 1-11
Li, J., Ma, S., Li, Z., Yu, W., Zhou, P., & Ye, X. (2021). Construction and characterization of an Aeromonas hydrophila multi-gene deletion strain and evaluation of its potential as a live-attenuated vaccine in grass carp. Vaccines, 9(5):1-14.
Linh, N. V., Le, T. D., Ha, T. D., Khongdee, N., Hoseinifar, S. H., Musthafa, M. S., Dawood, M. A. O., & Doan, H. V. (2022). Efficacy of different routes of formalin-killed vaccine administration on immunity and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) challenged with Streptococcus agalactiae. Fishes, 7(6):1-13.
Liu, B., Zheng, D., Zhou, S., Chen, L., & Yang, J. (2022). VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Research, 50(D1):912-917.
Lu, C., Meng, S., Jin, Y., Zhang, W., Li, Z., Wang, F., Wang-Johanning, F., Wei, Y., Liu, H., & Tu, H. (2017). A novel multi-epitope vaccine from MMSA-1 and DKK 1 for multiple myeloma immunotherapy. British Journal of Haematology, 178(3):413-426.
Mahram, A., & Herbordt, M. C. (2015). NCBI BLASTP on high-performance reconfigurable computing systems. ACM Transactions on Reconfigurable Technology and Systems, 7(1):1-20.
Martin-Carnahan, A., & Joseph, S. W. (2015). Aeromonadaceae. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Martinez-Murcia, A. J., Saavedra, M. J., Mota, V. R., Maier, T., Stackebrandt, E., & Cousin, S. (2008). Aeromonas aquariorum sp. nov., isolated from aquaria of ornamental fish. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology, 58(5):1169-1175.
Matyar, F., Kaya, A., & Dinçer, S. (2007). Distribution and antibacterial drug resistance of Aeromonas spp. from fresh and brackish waters in Southern Turkey. Annals of Microbiology, 57(1):443-447.
Moreno, C., Romero, J., & Espejo, R. T. (2002). Polymorphism in repeated 16S rRNA genes is a common property of type strains and environmental isolates of the genus Vibrio. Microbiology, 148(5):1233-1239.
Mortazavi, A., Doosti, A., & Sharifzadeh, A. (2024). A novel chimeric vaccine containing multiple epitopes for simulating robust immune activation against Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Immunology, 25(1):1-27.
Nayak, S. K. (2020). Current prospects and challenges in fish vaccine development in India with special reference to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 100(5):283-299.
Nguyen, T. L., & Kim, H. (2024). Immunoinformatics and computational approaches driven designing a novel vaccine candidate against Powassan virus. Scientific Reports, 14(1):1-15.
Nielsen, M. E., Høi, L., Schmidt, A. S., Qian, D., Shimada, T., Shen, J. Y., & Larsen, J. L. (2001). Is Aeromonas hydrophila the dominant motile Aeromonas species that causes disease outbreaks in aquaculture production in the Zhejiang Province of China?. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 46(1):23-29.
Nolla-Salas, J., Codina-Calero, J., Vallés-Angulo, S., Sitges-Serra, A., Zapatero-Ferrándiz, A., Climent, M. C., & Gómez, J. R. (2017). Clinical significance and outcome of Aeromonas spp. infections among 204 adult patients. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 36(3):1393-1403.
Pablos, M., Huys, G., Cnockaert, M., Rodríguez-Calleja, J. M., Otero, A., & Santos, J. A. (2011). Identification and epidemiological relationships of Aeromonas isolates from patients with diarrhea, drinking water and foods. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 147(2):203-210.
Pang, M., Jiang, J., Xie, X., Wu, Y., Dong, Y., Kwok, A. H. Y., Zhang, W., & Leung, F. C. (2015). Novel insights into the pathogenicity of epidemic Aeromonas hydrophila ST251 clones from comparative genomics. Scientific Reports, 5, 9833.
Park, S. W., Lee, B. H., Song, S. H., & Kim, M. K. (2023). Revisiting The Ramachandran Plot Based On Statistical Analysis Of Static And Dynamic Characteristics Of Protein Structures. Journal Of Structural Biology, 21(5):107-939.
Peatman, E., Mohammed, H., Kirby, A., Shoemaker, C. A., Yildirim-Aksoy, M., & Beck, B. H. (2018). Mechanisms of pathogen virulence and host susceptibility in virulent Aeromonas hydrophila infections of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture, 482(1):1-8.
Pessoa, R. B. G., de Oliveira, W. F., dos Santos Correia, M. T., da Silva Fontes, A. F., & Breitenbach Barroso Coelho, L. C. (2022). Aeromonas and human health disorders: Clinical approaches. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13:1-15
Persson, S., Al-Shuweli, S., Yapici, S., Jensen, J. N., & Olsen, K. E. (2015). Identification of clinical Aeromonas species by rpoB and gyrB sequencing and development of a multiplex PCR method for detection of Aeromonas hydrophila, A. caviae, A. veronii, and A. media. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 53(2):653-656.
Pippy, J. H., & Hare, G. M. (1969). Relationship of river pollution to bacterial infection in salmon (Salmo salar) and suckers (Catostomus commersoni). Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 98(4):685-690.
Popoff, M., & Véron, M. (1976). A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila group. Journal of General Microbiology, 94(1):11-22.
Pridgeon, J. W., & Zhang, D. (2014). Complete genome sequence of the highly virulent Aeromonas hydrophila AL09-71 isolated from diseased channel catfish in West Alabama. Genome Announcements, 2(3):1-14.
Qamar, M. T. U., Shahid, F., Aslam, S., & Ashfaq, U. A. (2020). Reverse vaccinology assisted designing of multiepitope-based subunit vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Infectious Diseases of Poverty, 99(132):1-22.
Rathore, A. S., Choudhury, S., Arora, A., Tijare, P., & Raghava, G. P. S. (2024). ToxinPred 3.0: An improved method for predicting the toxicity of peptides. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 179(12):1-13.
Reker, D., Rodrigues, T., Schneider, P., & Schneider, G. (2014). Identifying the macromolecular targets of de novo-designed chemical entities through self-organizing map consensus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(11):4067-4072.
Rozi., Rahayu, K., Daruti, D. N., & Stella, M. S. P. (2018). Study on characterization, pathogenicity and histopathology of disease caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in gourami (Osphronemus gouramy). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 137 012003
Rozi., Rahayu, K., & Daruti, D. N. (2018). Detection and analysis of hemolysin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Gouramy (Osphronemus gouramy) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 137 012001
Saadi, M., Karkashan, A., & Munang’andu, H. M. (2017). Current state of modern biotechnological-based Aeromonas hydrophila vaccines for aquaculture: A systematic review. Biomed Research International, 2019(1):1-11.
Sagas, D., Hershko, Y., & Levitskyi, K. (2024). Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of antimicrobial resistance and population structure of gastroenteritis-related Aeromonas isolates. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob, 2024(23):1-8.
Serruto, D., Serino, L., Masignani, V., & Pizza, M. (2012). Genome-based approaches to develop vaccines against bacterial pathogens. Vaccine, 27(25-26):3245-3250.
Sette, A., & Fikes, J. (2003). Epitope-based vaccines: an update on epitope identification, vaccine design and delivery. Current Opinion in Immunology, 15(4):461-470.
Sidney, J., Peters, B., Frahm, N., Brander, C., & Sette, A. (2008). HLA class I supertypes: A revised and updated classification. BMC Immunology, 9(1):1-15.
Slingluff, C. L., Lee, S., Zhao, F., Chianese-Bullock, K. A., Olson, W. C., Butterfield, L. H., Whiteside, T. L., Leming, P. D., & Kirkwood, J. M. (2013). A randomized phase II trial of multiepitope vaccination with melanoma peptides for cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells for patients with metastatic melanoma (E1602). Clinical Cancer Research, 19(15):4228-4238.
Solanki, V., & Tiwari, V. (2018). Subtractive proteomics to identify novel drug targets and reverse vaccinology for the development of chimeric vaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii. Scientific Reports, 8(1):1-19.
Solanki, V., Sharma, S., & Tiwari, V. (2021). Subtractive proteomics and reverse vaccinology strategies for designing a multiepitope vaccine targeting membrane proteins of Klebsiella pneumoniae. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics, 27(2):1177-1195.
Stratmann, T. (2015). Cholera toxin subunit B as adjuvant—An accelerator in protective immunity and a break in autoimmunity. Vaccines, 3(3): 579–596.
Sughra, F., Hafeez-ur-Rehman, M., Abbas, F., Altaf, I., Hassan, Z., & Bhatti, A. (2022). Molecular characterisation and genetic analysis of aerolysin and haemolysin in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from diseased Labeo rohita by polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Fisheries, 10(3):1-5.
Toledo, H., Baly, A., Castro, O., Resik, S., Laferté, J., Rolo, F., Navea, L., Lobaina, L., Cruz, O., & Miguez, J. (2001). A phase I clinical trial of a multi-epitope polypeptide TAB9 combined with Montanide ISA 720 adjuvant in non-HIV-1 infected human volunteers. Vaccine, 19(30):4328-4336.
Ullah, M. A., Sarkar, B., & Islam, S. S. (2020). Exploiting the reverse vaccinology approach to design novel subunit vaccines against Ebola virus. Immunobiology, 225(3):1-15.
Vita, R., Overton, J. A., Greenbaum, J. A., Ponomarenko, J., Clark, J. D., Cantrell, J. R., Wheeler, D. K., Gabbard, J. L., Hix, D., Sette, A., & Peters, B. (2015). The immune epitope database (IEDB) 3.0. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(D1):D405-D412.
Vivekanandhan, G., Savithamani, K., Hatha, A. A. M., & Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P. (2002). Antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from marketed fish and prawn of South India. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 76(1-2):165-168.
Wang, G., Clark, C. G., Liu, C., Pucknell, C., Munro, C. K., Kruk, T. M. A. C., Caldeira, R., Woodward, D. L., & Rodgers, F. G. (2003). Detection and characterization of the hemolysin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria by multiplex PCR. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41(3):1048-1054.
Wang, P., Sidney, J., Dow, C., Mothé, B., Sette, A., & Peters, B. (2010). A systematic assessment of MHC class II peptide binding predictions and evaluation of a consensus approach. PLoS Computational Biology, 6(4):1-16.
Waterhouse, A., Bertoni, M., Bienert, S., Studer, G., Tauriello, G., Gumienny, R., Heer, F. T., de Beer, T. A. P., Rempfer, C., Bordoli, L., Lepore, R., & Schwede, T. (2018). SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(W1):W296-W303.
Wu, C.-J., Chen, P.-L., Tang, H.-J., Chen, H.-M., Tseng, F.-C., Shih, H.-I., Hung, Y.-P., Chung, C.-H., & Ko, W.-C. (2014). Incidence of Aeromonas bacteremia in southern Taiwan: Vibrio and Salmonella bacteremia as comparators. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection, 47(2):145-148.
Xu, T., Cody, R., Rasmussen-Ivey., Francesco, S., Moen., Fernández-Bravo, A., Lamy, B., et al Mark, R., & Liles. (2023). A Global Survey of Hypervirulent Aeromonas hydrophila (vAh) Identified vAh Strains in the Lower Mekong River Basin and Diverse Opportunistic Pathogens from Farmed Fish and Other Environmental Sources. Microbiology spectrum, 11(2) doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03705-22
Zhang, X. H., He, X. X., Austin, B., & Zhang, G. (2002). Molecular identification and epidemiological tracing of Aeromonas hydrophila strains isolated from outbreaks of fish disease in China. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 93(2):214-220.
Zhang, D., Pridgeon, J. W., & Zhang, L. (2012). Complete genome sequence of a moderately virulent Aeromonas hydrophila strain pc104A isolated from the soil of a catfish pond in West Alabama. Genome Announcements, 2(3):1-9.
Zhang, L. (2018). Multi-epitope vaccines: a promising strategy against tumors and viral infections. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 15(2):182-184.
Zhang, L., Ma, L., Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Ai, X., & Dong, J. (2022). Sanguinarine protects channel catfish against Aeromonas hydrophila infection by inhibiting aerolysin and biofilm formation. Pathogens, 11(3):1-11.
Zheng, W., Zhang, C., Bell, E. W., & Zhang, Y. (2019). I-TASSER gateway: A protein structure and function prediction server powered by XSEDE. Future Generation Computer Systems, 99(10):73-85.
Zhou, W.-Y., Shi, Y., Wu, C., Zhang, W.-J., Mao, X.-H., Guo, G., Li, H.-X., & Zou, Q.-M. (2009). Therapeutic efficacy of a multi-epitope vaccine against Helicobacter pylori infection in BALB/c mice model. Vaccine, 27(36):5013-5019.
Zhou, A. Q., O’Hern, C. S., & Regan, L. (2011). Revisiting the Ramachandran plot from a new angle. Protein Science, 20(7):1166-1171.